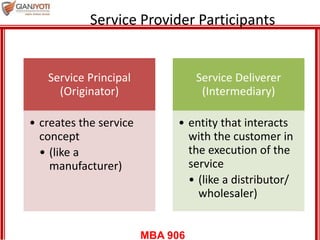
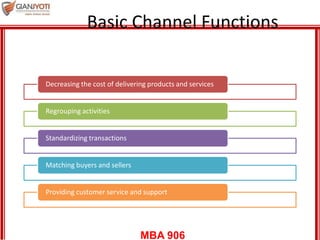
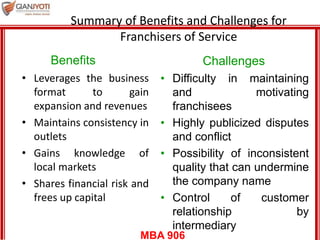
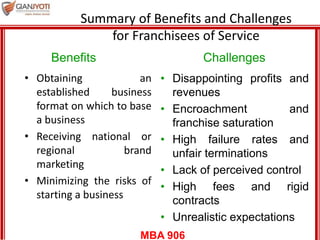
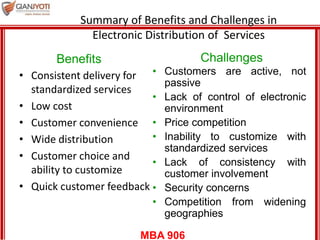
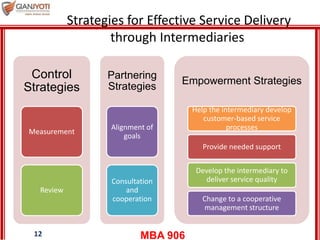
This document discusses delivering services through intermediaries and electronic channels. It covers key issues when involving intermediaries like conflicts over objectives and control. The document outlines different types of distribution channels and criteria for evaluating channel alternatives. It provides examples of key intermediaries for service delivery like franchisees, agents/brokers, and electronic channels. Benefits and challenges are summarized for each. Finally, strategies for effective service delivery through intermediaries are presented focusing on control, measurement, partnering, and empowerment.