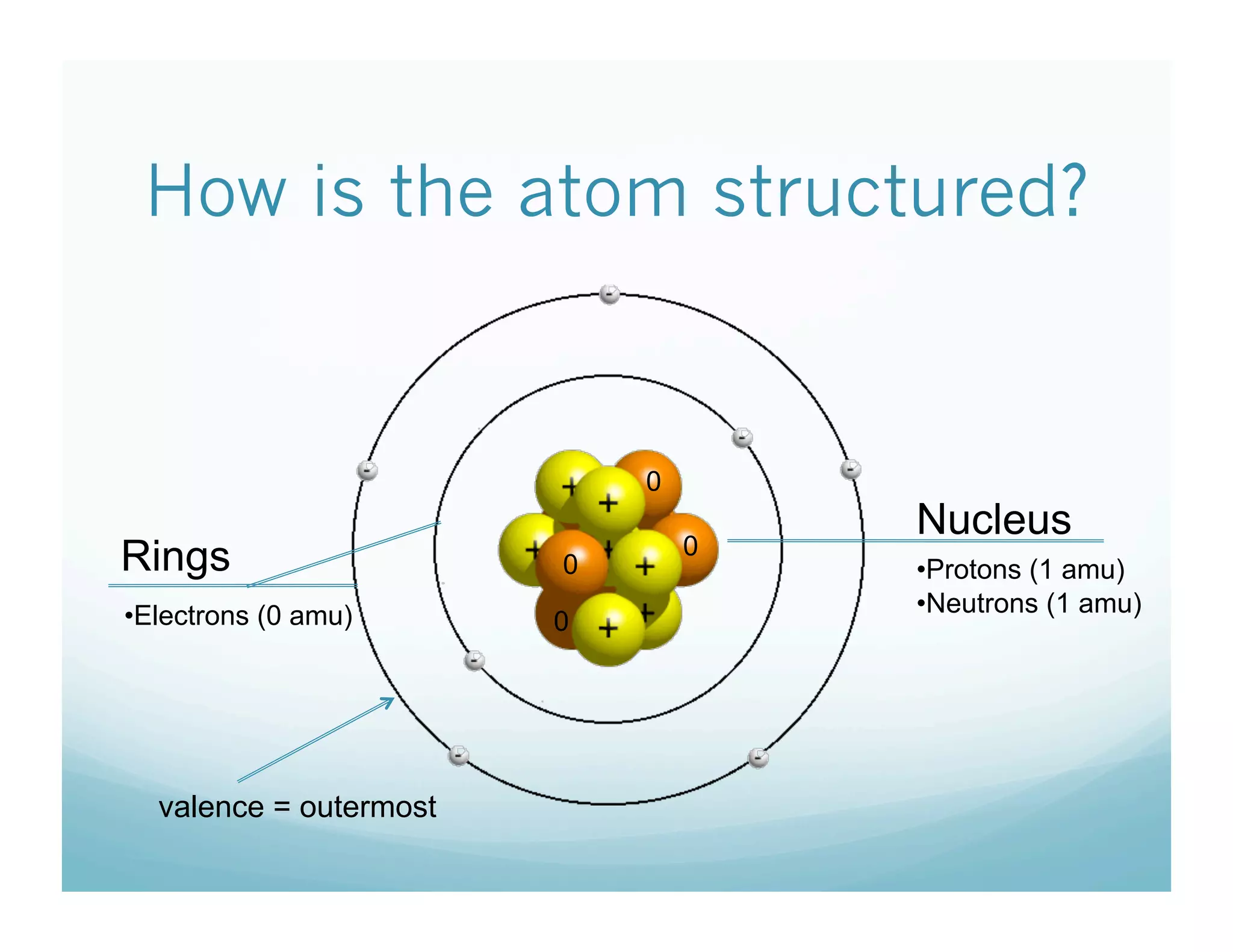
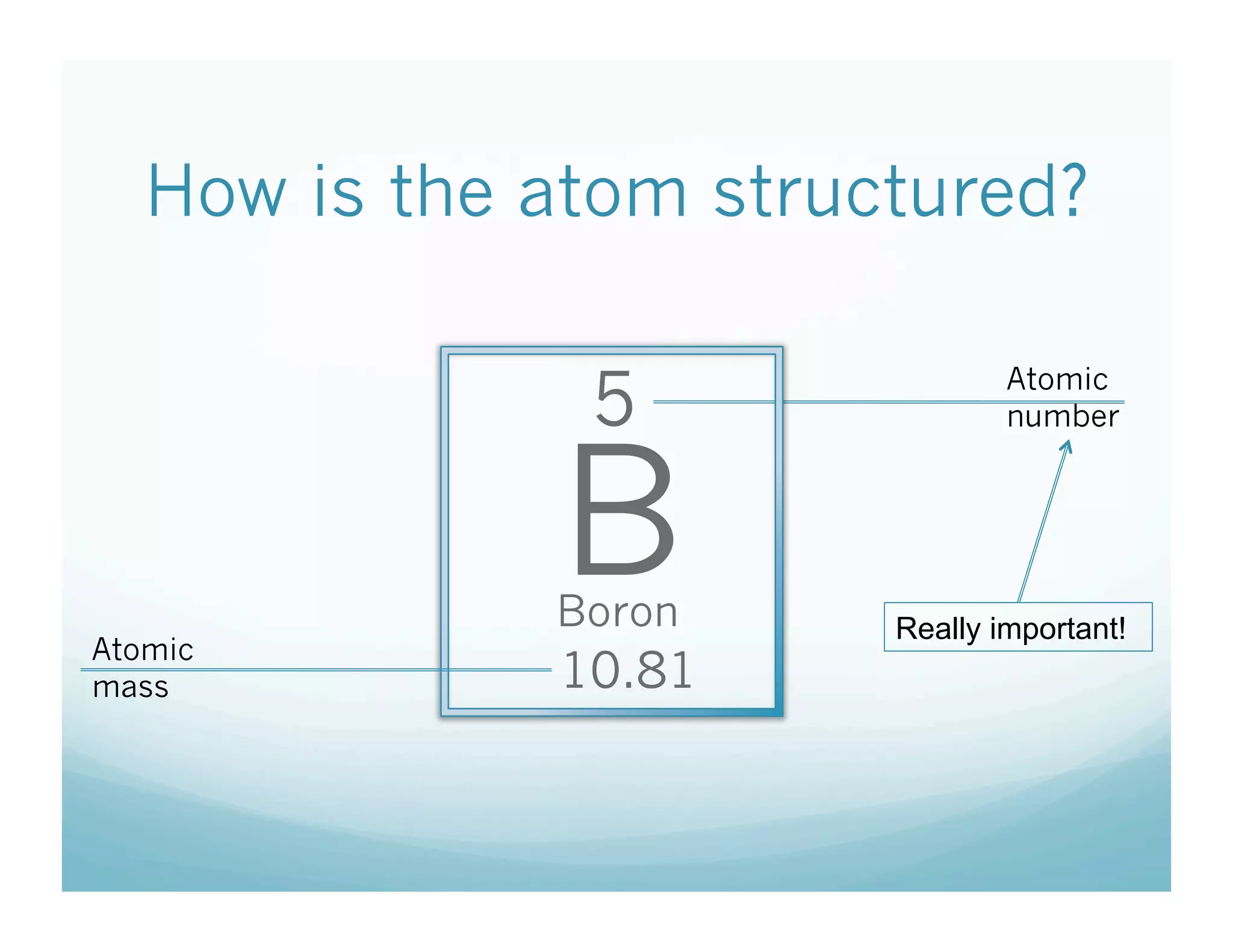
This document provides an overview of an upcoming chemistry class covering atomic structure. The weekly schedule outlines topics to be covered each day, including atomic radius, electronegativity, atomic structure, and a midterm exam on Friday. Students are instructed to sketch the periodic table and label families for homework. The document then reviews atomic structure, including the dense nucleus at the center containing protons and neutrons, and less dense electron shells. Examples are given to calculate protons, neutrons, and electrons in different atoms. Homework assigned is to make a study notecard and complete a review worksheet in preparation for the midterm.