1) Atoms are the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still retain its properties. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles called subatomic particles - protons, neutrons, and electrons.
2) Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus. Neutrons have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. Electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus.
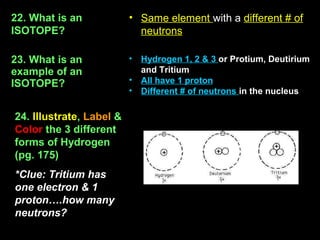
3) The number of protons determines which element an atom is. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The number of neutrons can vary forming different isotopes of an element.