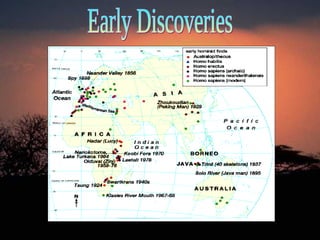
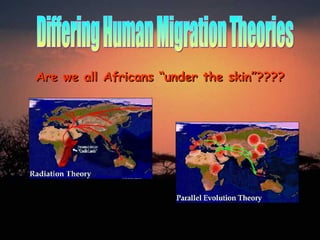
1. The document discusses the evolution of early humans from 4 million years ago to the development of civilizations. It outlines 4 stages of early human development and the key species at each stage.
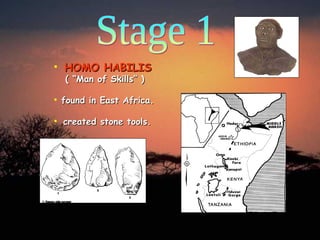
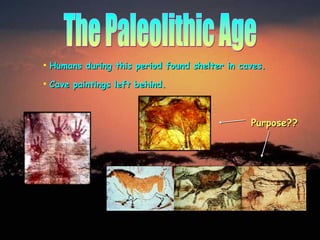
2. During the Paleolithic Age between 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago, early humans like Homo habilis and Homo erectus lived nomadic lifestyles, hunting and gathering food. They began using tools and fire.
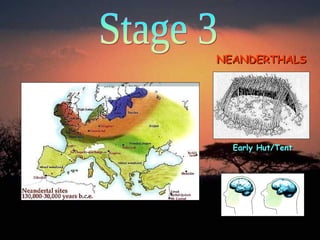
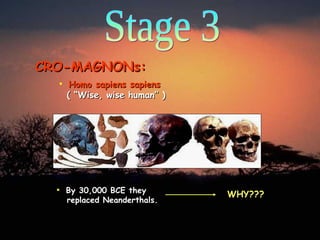
3. From 200,000 to 10,000 years ago in Stage 3, Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons inhabited Europe and Asia. Cro-Magnons eventually replaced Neanderthals. The last Ice Age occurred from 70,000 to