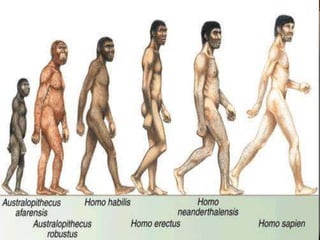
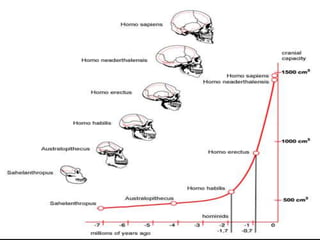
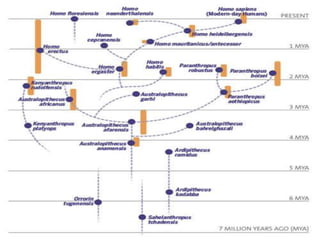
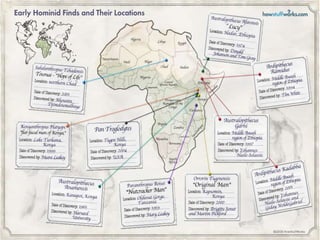
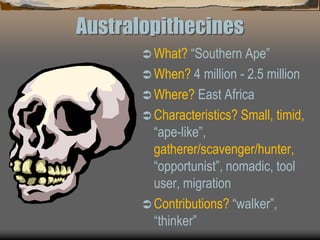
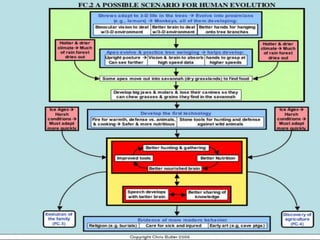
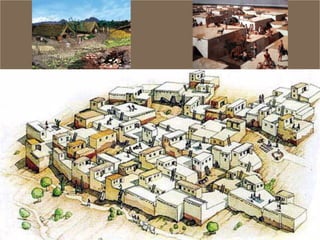
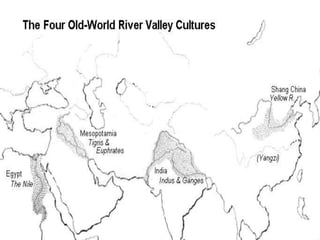
The document summarizes prehistory from 6 billion BCE to 10,000 BCE. During this period before written records, archaeologists excavate sites and artifacts to understand past human life. Anthropologists study the finds to describe humans and infer how they lived. Historians then synthesize this evidence to tell the story of prehistory. The document outlines major human species like Australopithecines and Homo Erectus, and eras like the Paleolithic and Neolithic as agriculture emerged. It provides an overview of how prehistoric life changed from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled farmers, and the beginnings of civilization.