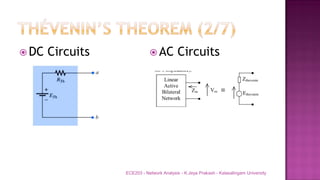
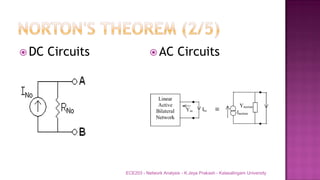
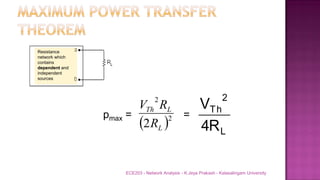
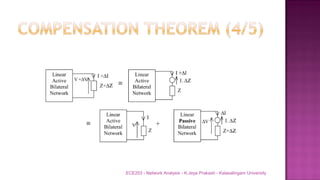
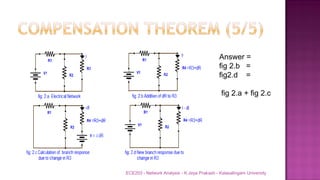
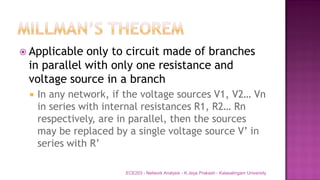
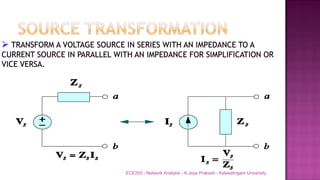
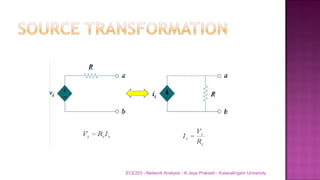
The document discusses various circuit analysis theorems including Thévenin's theorem, Norton's theorem, and superposition theorem. Thévenin's theorem states that any linear bilateral network can be reduced to an equivalent circuit with a voltage source and series resistance. Norton's theorem is the dual of Thévenin's theorem, representing an equivalent circuit with a current source and parallel conductance. Superposition theorem allows analyzing circuit responses by separately applying each independent source and summing the responses.