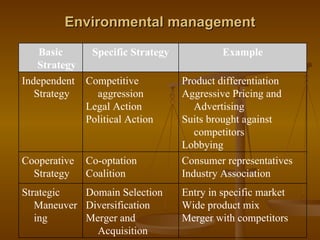
The document discusses the business environment and its elements that influence businesses. It identifies key elements like suppliers, financial institutions, customers, competitors, owners, labor unions, community, and government. It also discusses environmental management strategies like independent, cooperative, and strategic maneuvering strategies. The document outlines social responsibilities of businesses to consumers, employees, investors, and the environment. It concludes by outlining challenges businesses may face from the economic, competitive, social/cultural, political-legal, and technological environments.