Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times




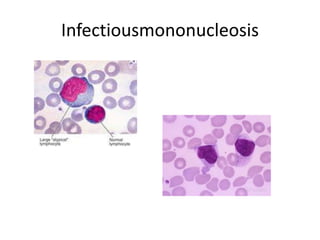



This document discusses non-malignant lymphocyte disorders, including both acquired and congenital types. Acquired disorders are quantitative in nature and include infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and toxoplasmosis. Infectious mononucleosis commonly affects young adults and is characterized by lymphocytosis, reactive lymphocytes, and elevated liver enzymes. Toxoplasmosis is transmitted through undercooked meat or contact with cat feces and poses risks to unborn children.







