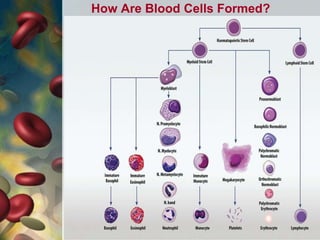
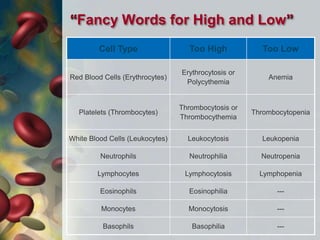
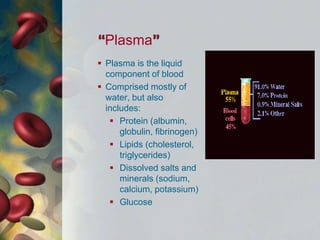
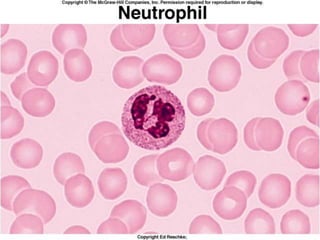
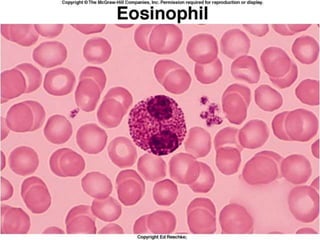
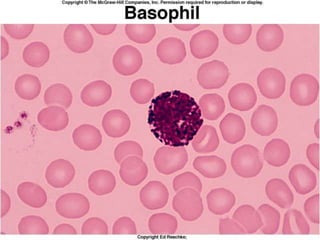
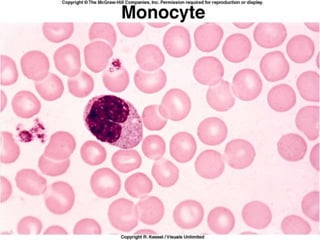
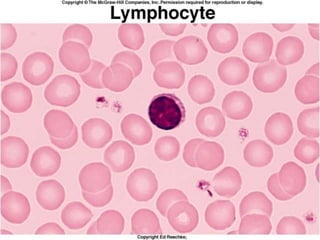
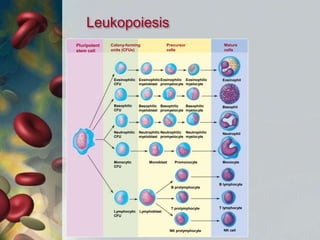
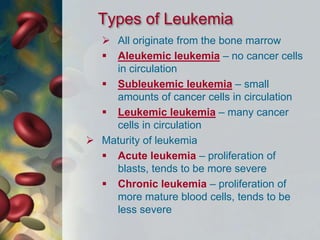
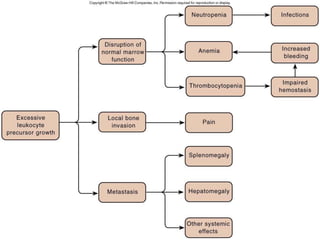
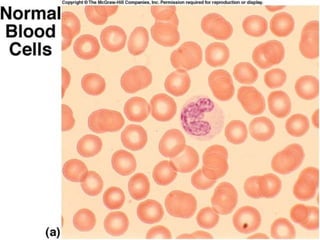
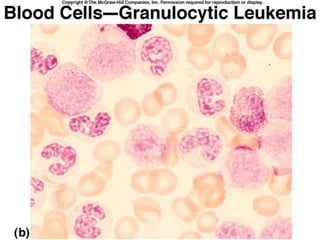
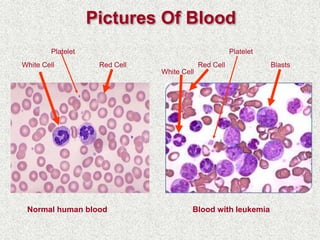
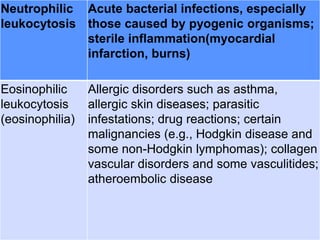
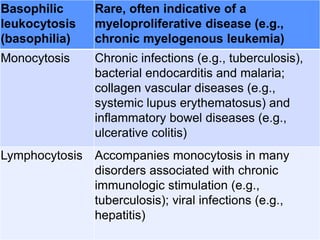
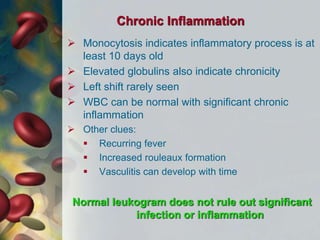
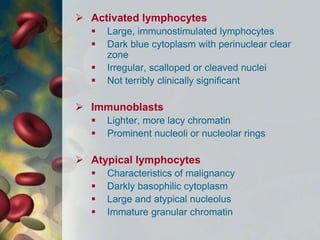
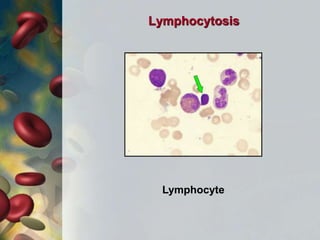
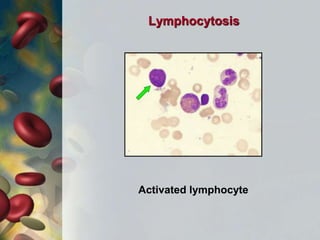
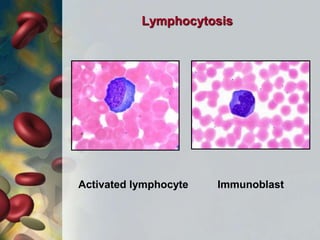
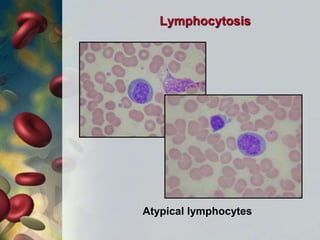
This document discusses leukocytosis, an increased number of white blood cells in the blood. It describes the different types of white blood cells and their normal functions. Leukocytosis can be caused by infections, inflammatory disorders, cancers, and medications. The main types of leukocytosis are neutrophilia, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, eosinophilia, and basophilia. Reactive leukocytosis is usually a response to infection or inflammation, while very high or persistent leukocytosis may indicate leukemia or other diseases.