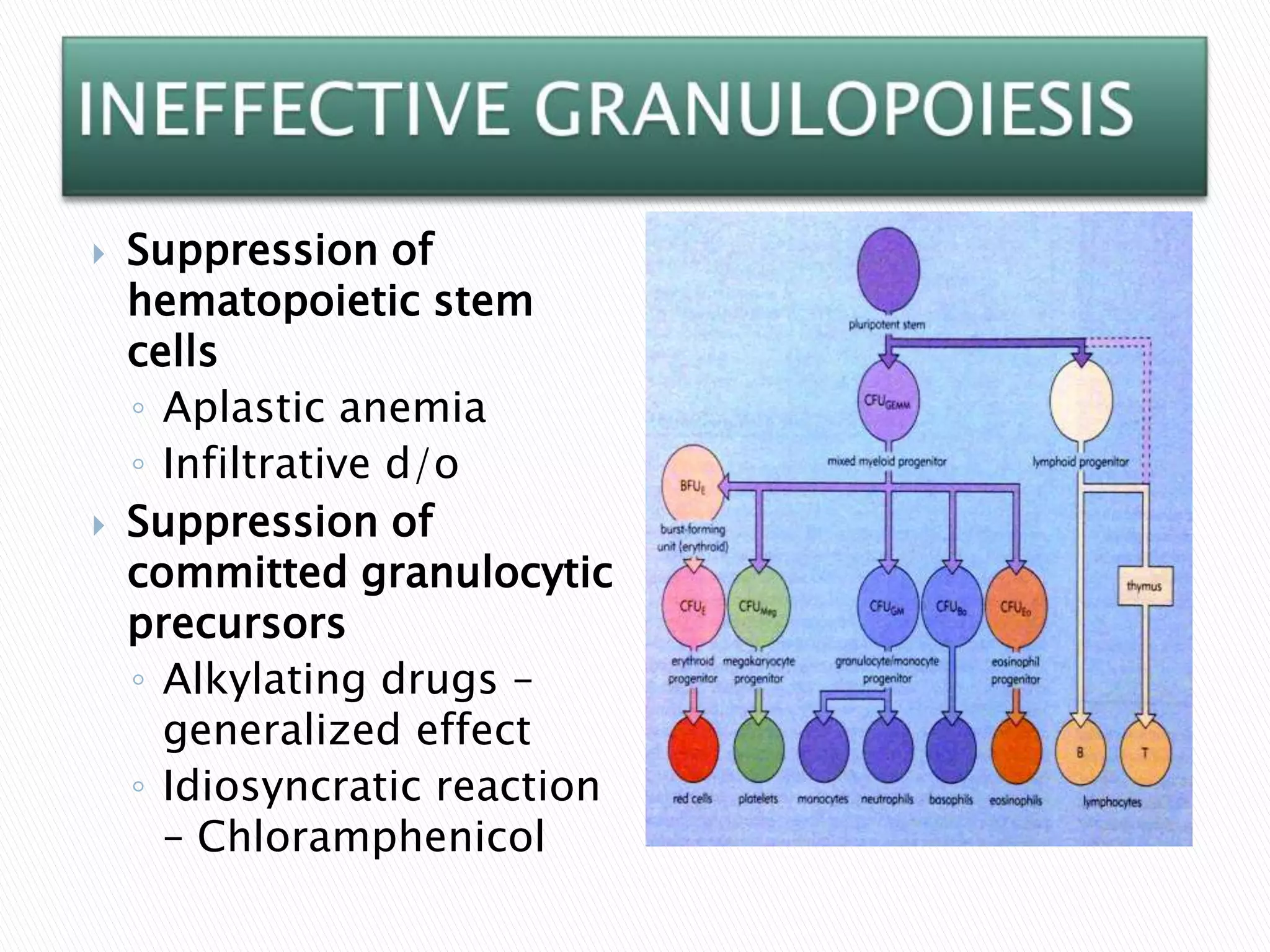
This document discusses leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis. It defines them as abnormally low white blood cell counts, specifically a reduction in granulocytes or neutrophils. Neutropenia is classified as mild, moderate, or severe based on neutrophil counts. Agranulocytosis is a marked reduction or absence of neutrophils in the blood and bone marrow. The causes include ineffective granulopoiesis, accelerated removal/destruction of neutrophils, and most commonly drug toxicity from chemotherapy agents, antipsychotics, antibiotics, and others. Signs and symptoms relate to increased risk of infection. Treatment involves antibiotics, growth factors, and withdrawing the causal drug.