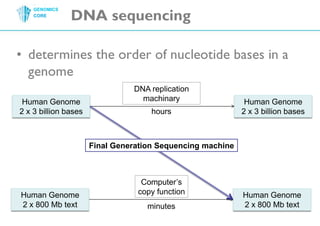
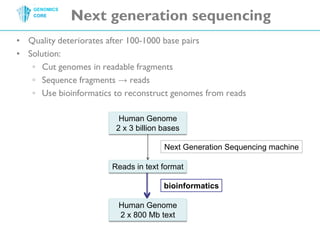
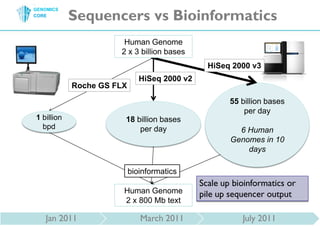
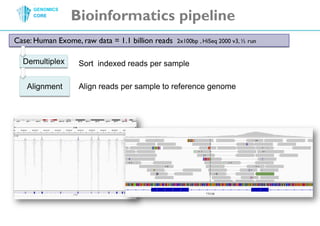
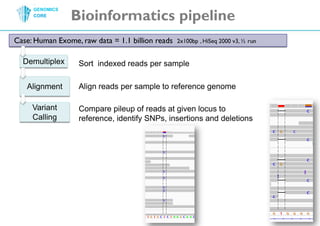
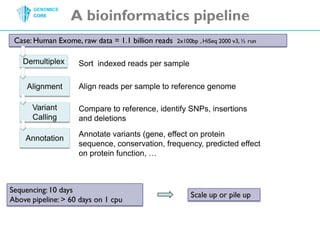
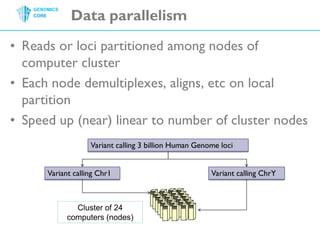
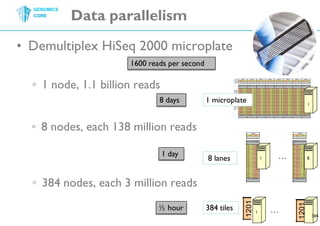
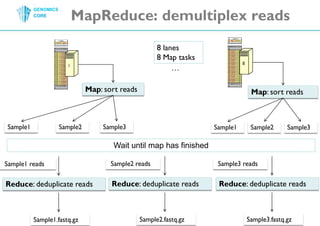
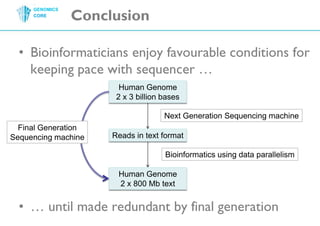
The document discusses the processing of raw DNA sequence data at the Genomics Core, highlighting the techniques of next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics used to reconstruct human genomes. It emphasizes the importance of data parallelism for scaling up bioinformatics analyses and presents various computational strategies like MapReduce to handle large datasets efficiently. The conclusion underlines the necessity of adding more computer nodes to keep pace with evolving sequencing technologies.