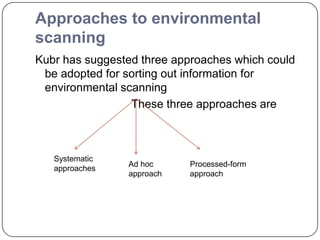
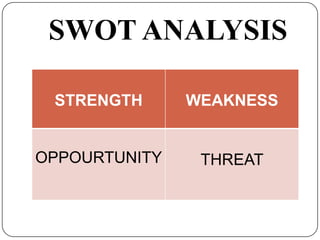
This document discusses environmental appraisal and business environment. It defines environment and describes the characteristics and types of business environment, including internal and external factors. The external environment is further divided into micro and macro factors. The roles of government in the business environment are regulatory, participative, and protective. Key sectors of the business environment are also outlined such as economic, international, market, political, regulatory, socio-cultural, supplier, and technological. The document also discusses environmental scanning, approaches to scanning, and SWOT analysis.