The document discusses the concept of strategy, its origins and evolution. It provides definitions of strategy from various sources and outlines some key points:
- Strategy originates from the Greek word "Strategia" meaning generalship and refers to leading an army. The earliest known work on strategy is Sun Tzu's The Art of War from 500 BC.
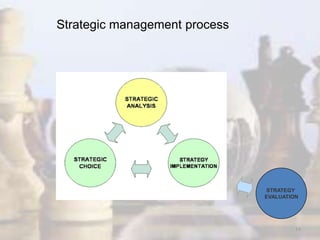
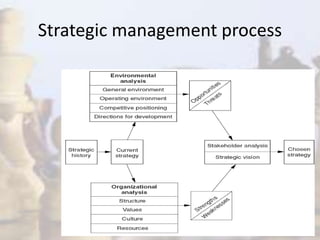
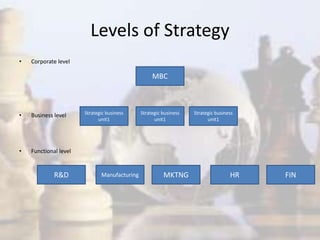
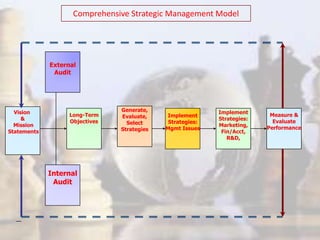
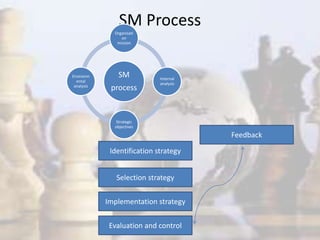
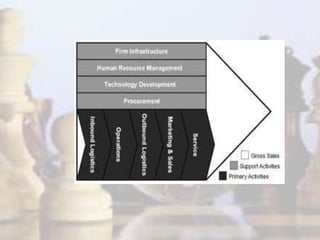
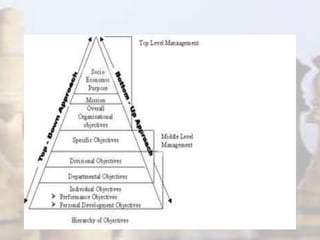
- Strategy involves determining long-term goals and objectives, and developing courses of action to achieve these goals. It provides coherence and direction to organizational actions.
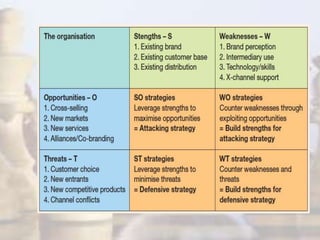
- Strategic management has evolved with changes in the industrial environment and now demands that firms be future-oriented, able to respond to opportunities and threats, and build competitive advantages.
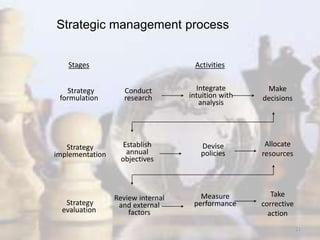
- The strategic management