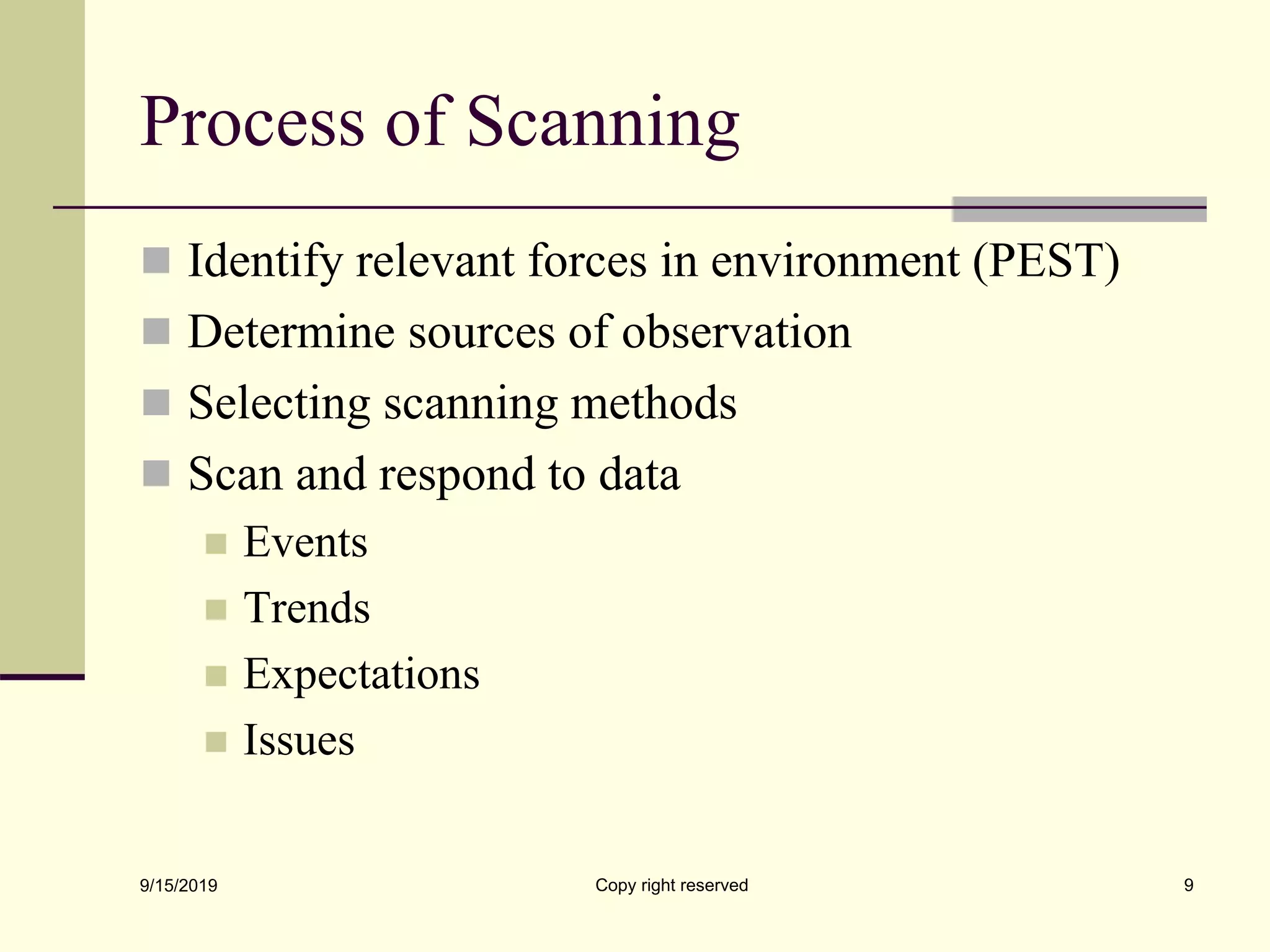
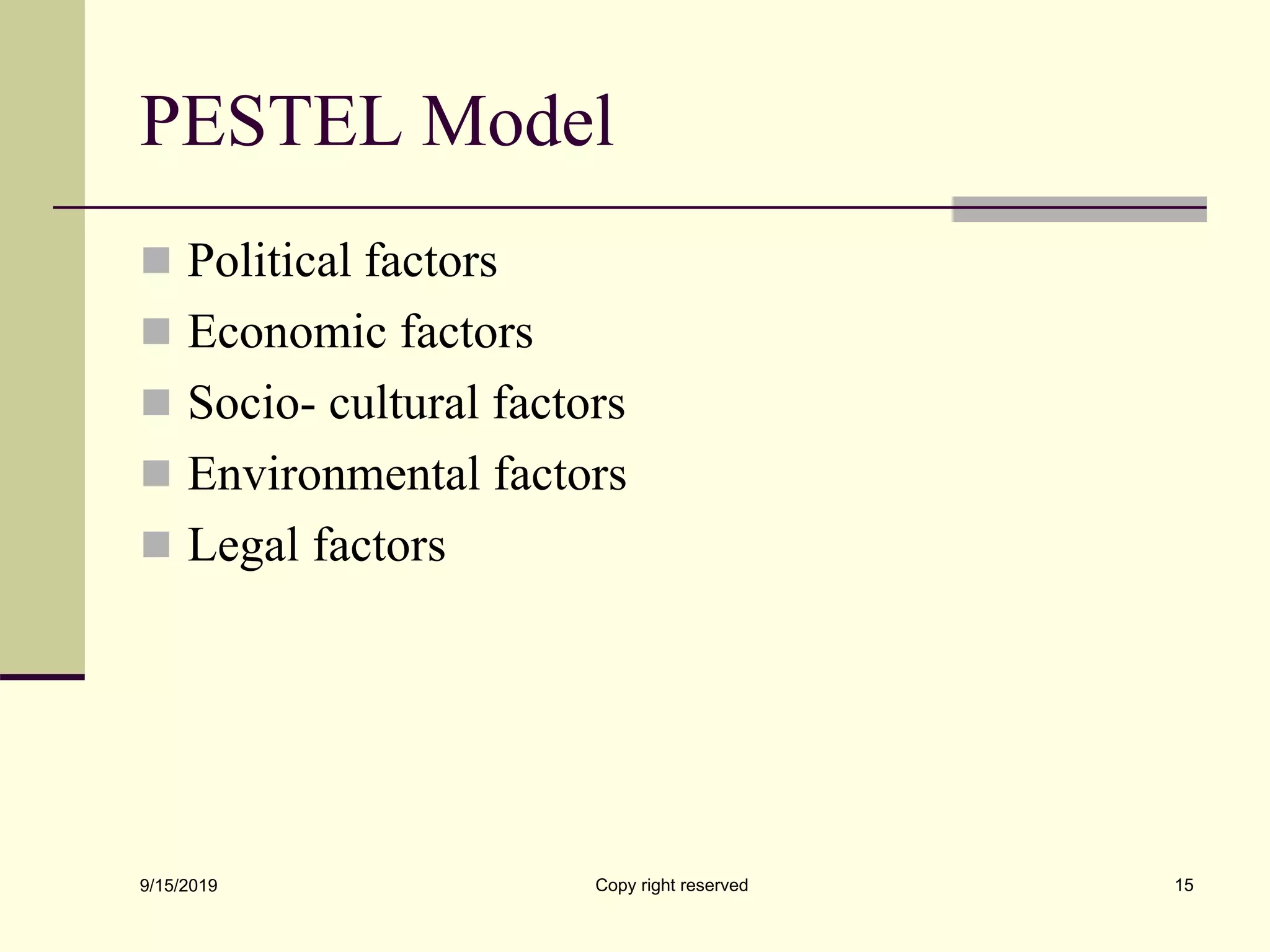
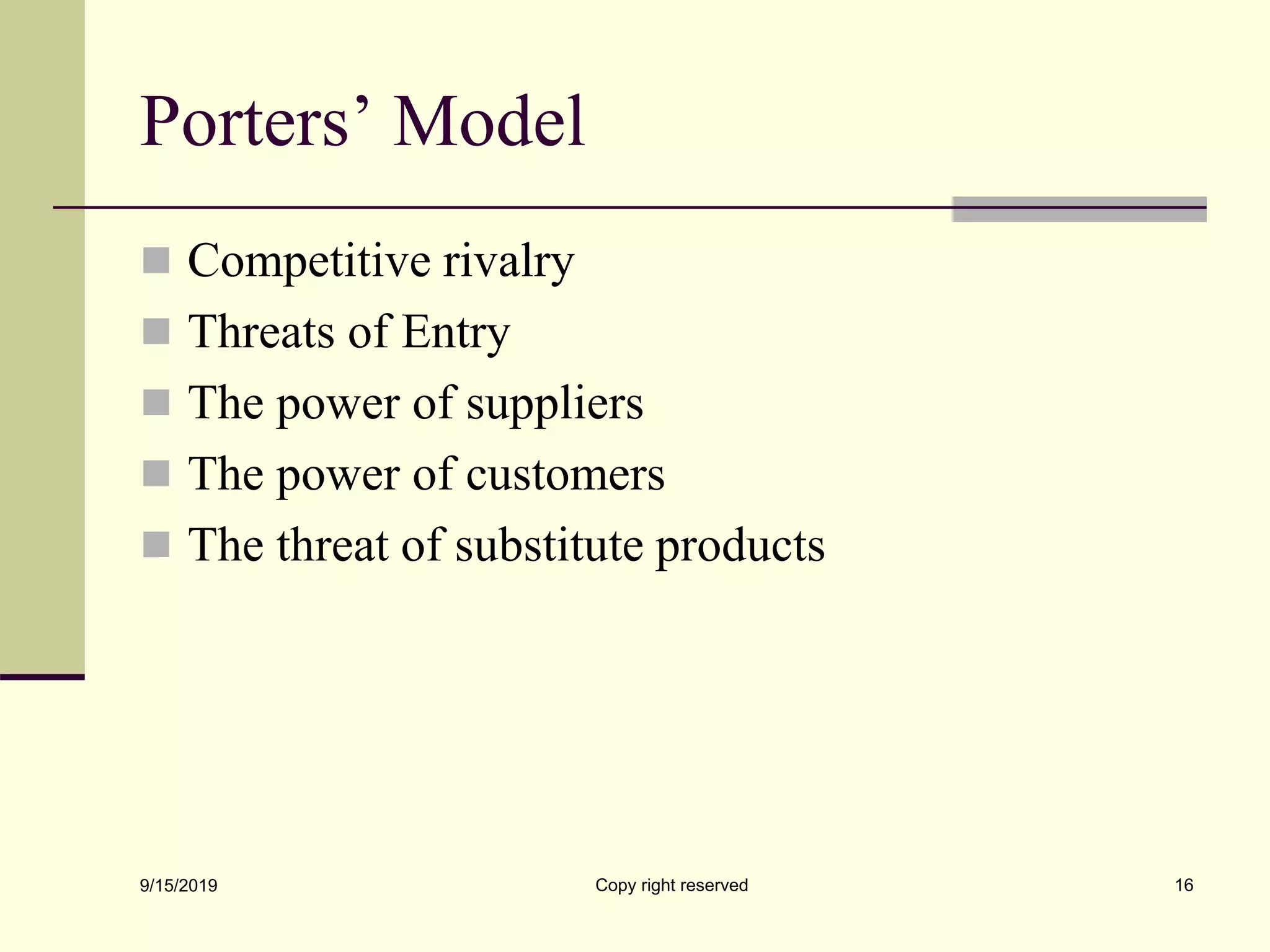
The document discusses environmental analysis, which involves assessing emerging trends and identifying opportunities and threats from a firm's economic, political, legal, technological, and social environments. It describes the main processes of environmental analysis as scanning, monitoring, forecasting, and assessment. Scanning involves monitoring environmental changes that could impact a business. Monitoring tracks trends and events, while forecasting estimates future situations. Assessment identifies key opportunities and threats. The document also outlines several models for environmental analysis, including PEST, PESTEL, and Porter's models, which analyze political/legal, economic, socio-cultural, and technological forces.