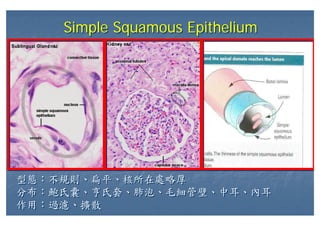
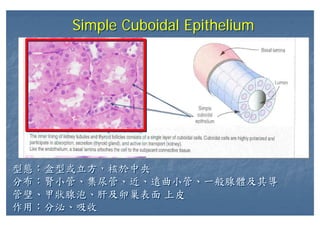
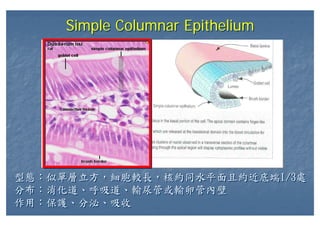
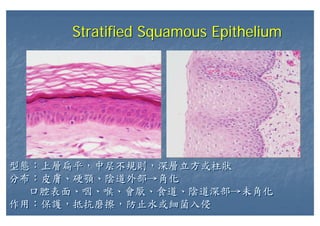
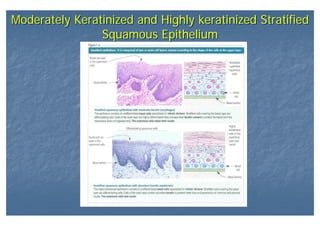
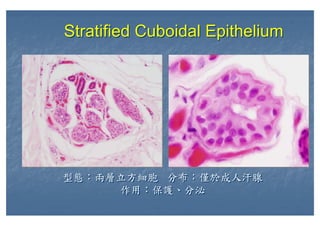
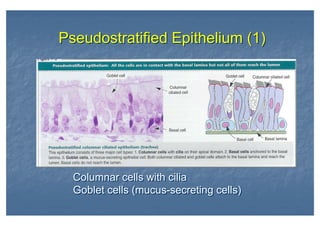
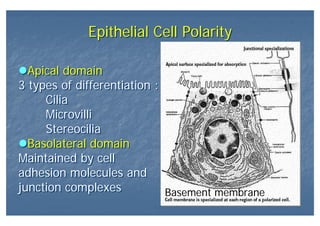
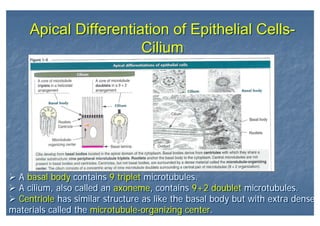
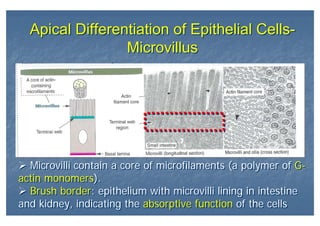
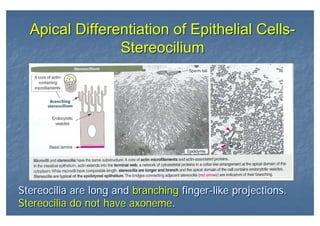
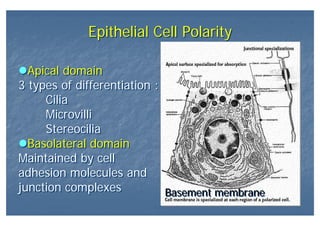
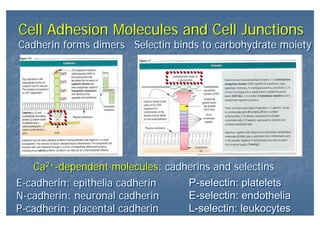
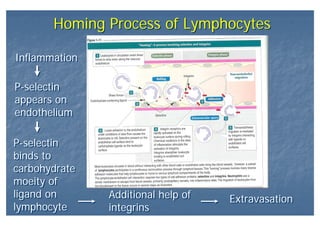
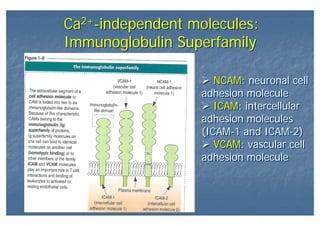
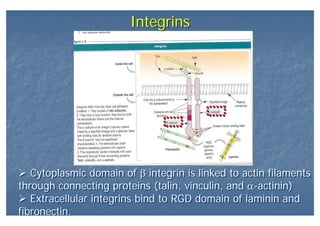
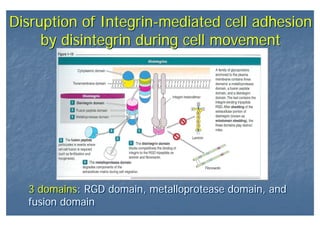
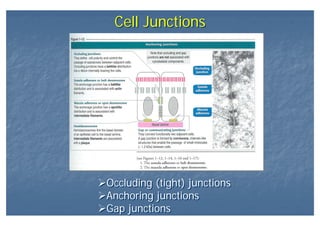
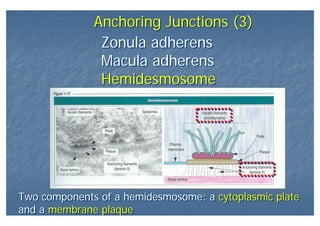
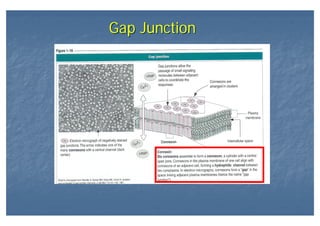
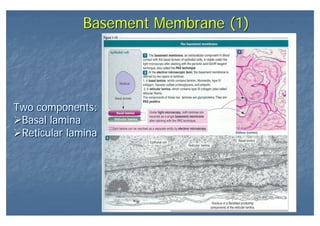
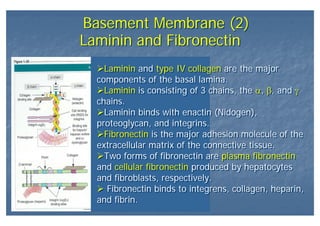
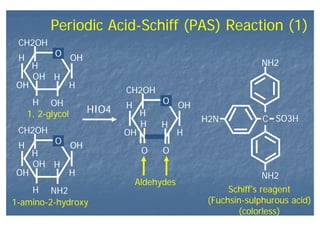
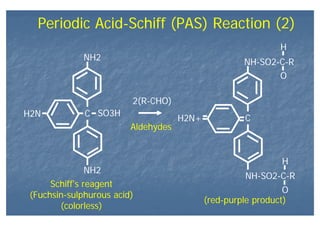
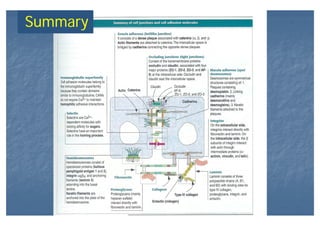
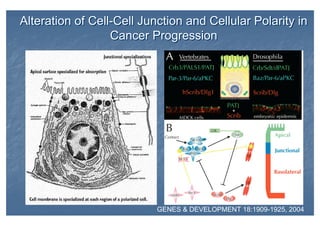
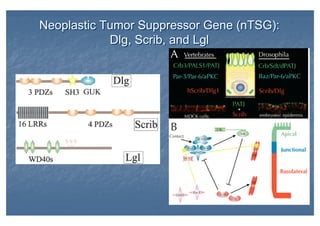
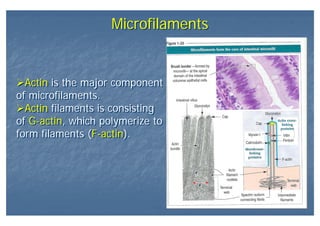
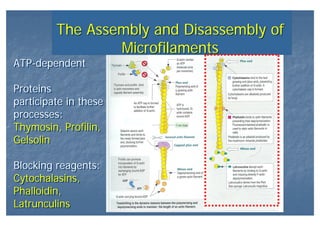
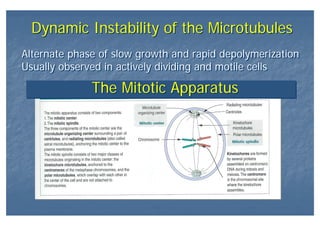
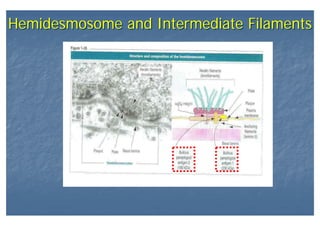
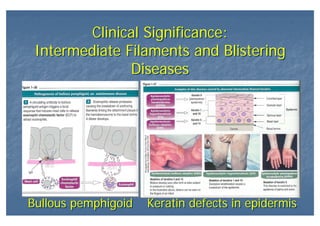
This document outlines the structure and classification of epithelial tissues and their cellular components. It discusses the five main types of simple epithelia - simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal - as well as pseudostratified epithelia. It describes the cellular polarity of epithelia, including their apical and basolateral domains, and covers the roles of cell junctions like tight junctions, desmosomes, and hemidesmosomes in maintaining epithelial structure and function. Key cellular structures that help epithelia perform specialized roles like microvilli, cilia, and stereocilia are also summarized.