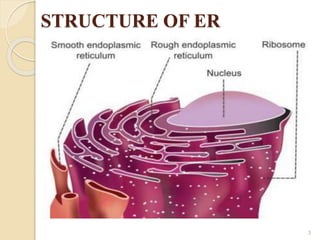
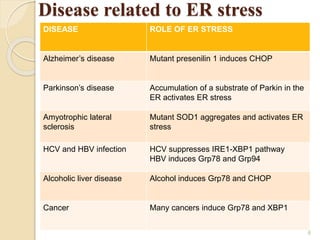
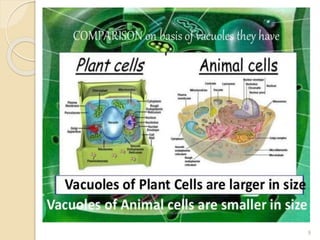
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that consists of a network of membrane sacs and tubules. The ER has two main types: rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes and is the site of protein synthesis, while smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid and steroid synthesis. In skeletal muscle cells, smooth ER forms the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which stores and releases calcium ions to regulate muscle contraction. Without the ER, cells would not be able to synthesize proteins or lipids, carry out important metabolic processes, and in muscle cells, regulate contraction, likely resulting in cell death.