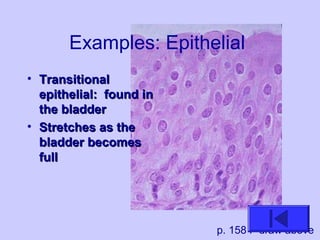
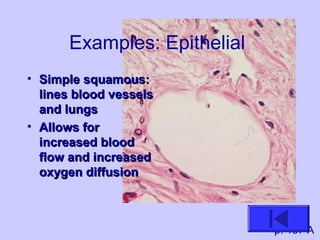
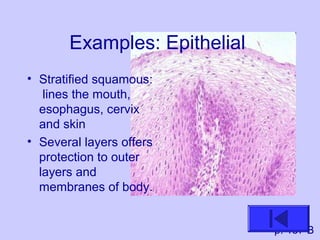
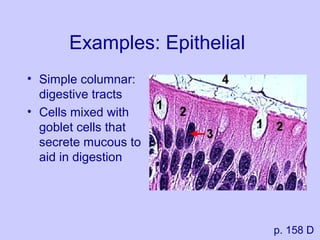
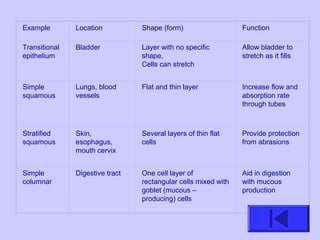
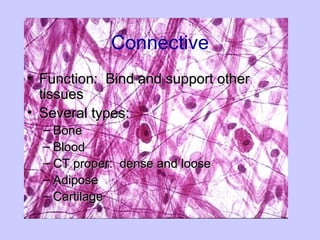
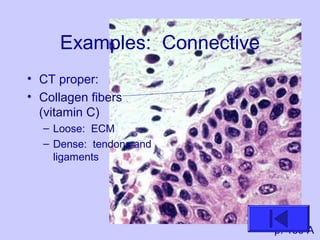
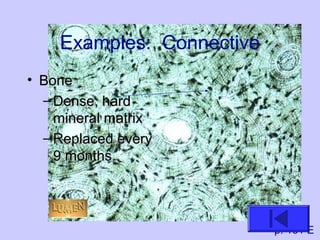
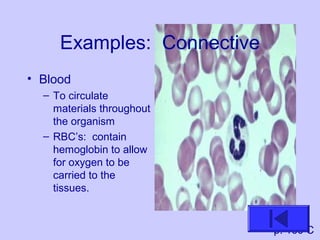
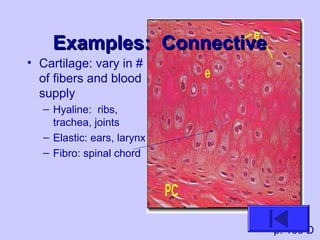
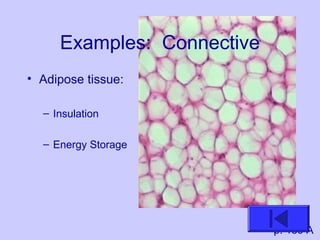
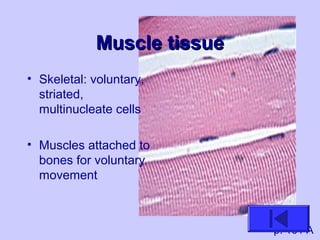
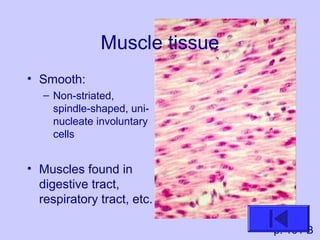
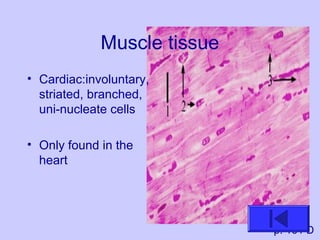
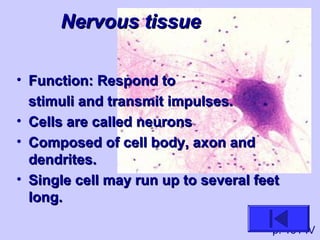
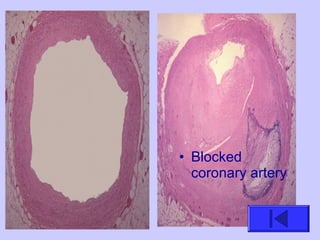
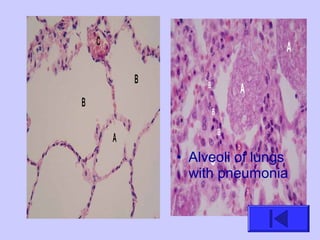
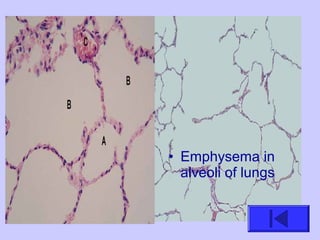
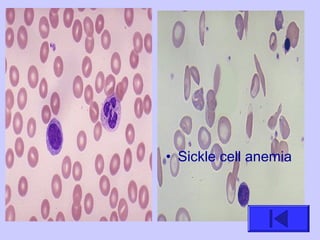
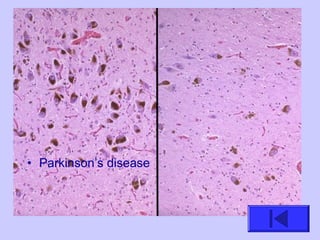
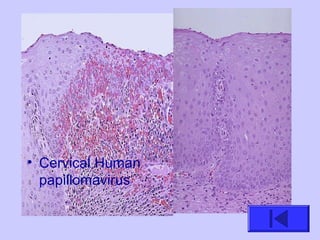
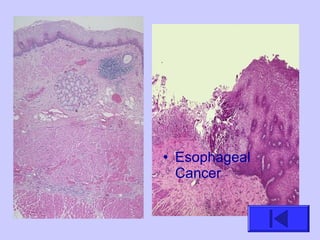
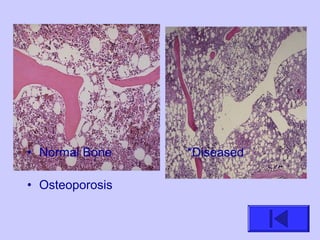
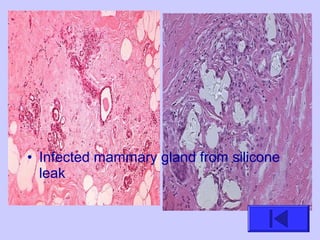
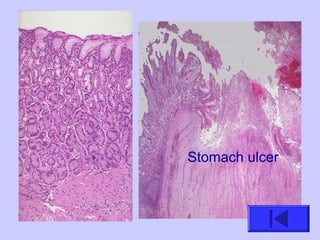
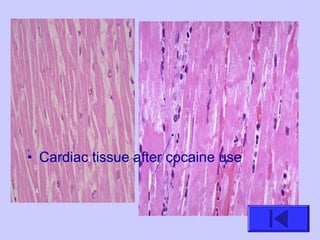
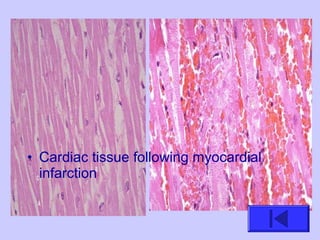
The document introduces the four basic tissue types - epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It states that all animals are composed of only these four tissue types, which are organized to form organs and functional systems of the body. Examples of each tissue type are then described, including their locations, shapes, and main functions. Epithelial tissues cover surfaces, connective tissues provide structure and binding, muscle tissues enable movement, and nervous tissues transmit signals. Life processes like respiration, circulation, and digestion rely on the coordinated function of these four tissue types.