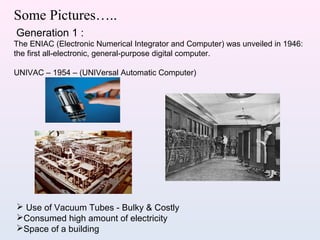
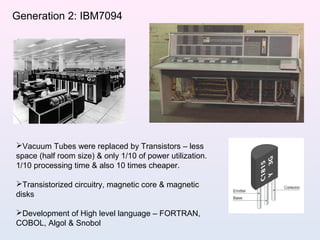
The document provides an overview of computers, highlighting their evolution from mechanical calculators to modern microprocessors. It discusses the history of computing, major technological advancements, and practical applications of computers in everyday life. Additionally, it offers tips for beginners and emphasizes the importance of computers in various fields such as communication, education, and entertainment.