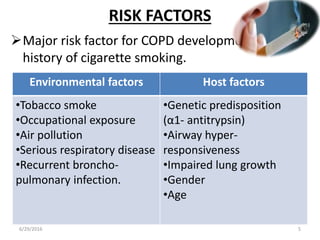
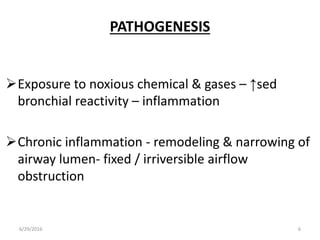
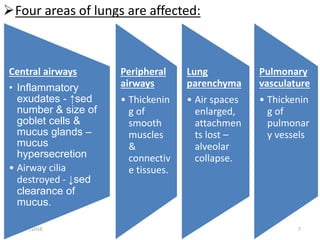
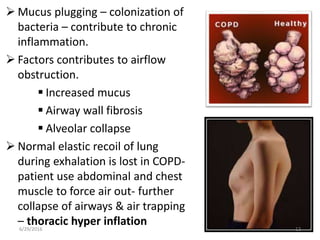
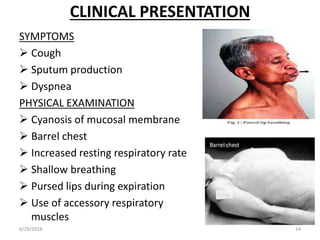
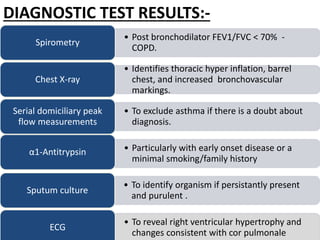
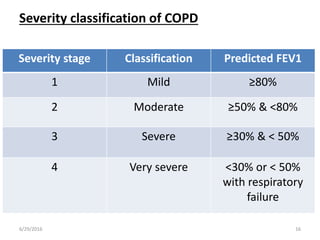
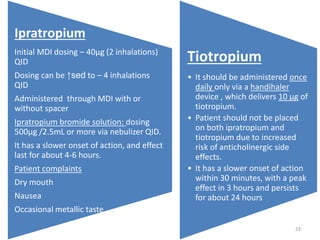
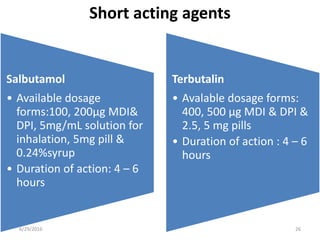
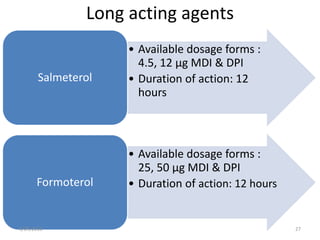
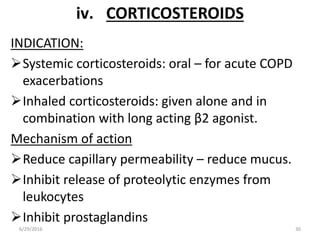
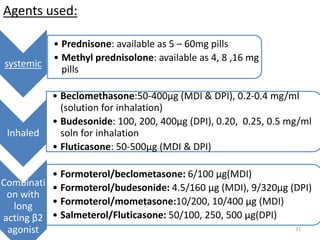
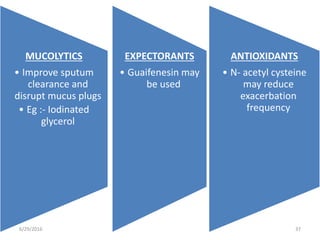
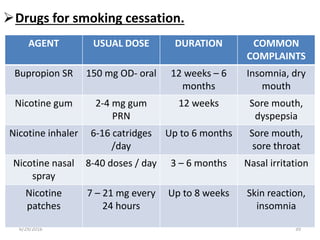
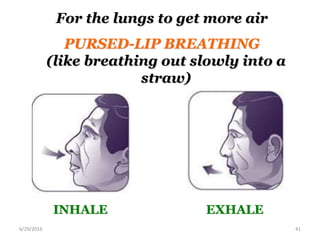
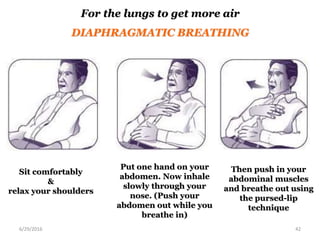
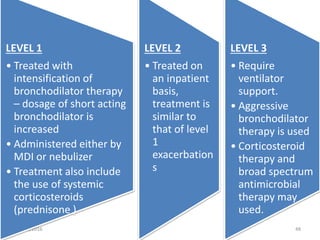
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by airflow limitation that is usually progressive and not fully reversible. It includes conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The major risk factor is a history of cigarette smoking. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and dyspnea. Diagnosis is made based on spirometry results showing an FEV1/FVC ratio of less than 70% post-bronchodilator. Treatment focuses on bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, and managing exacerbations.