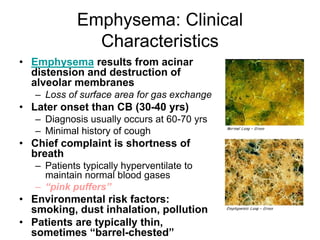
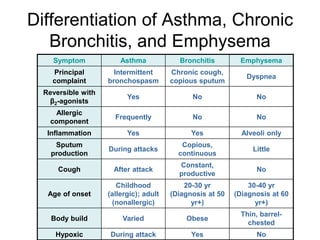
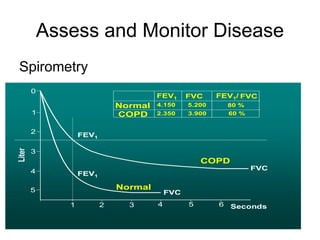
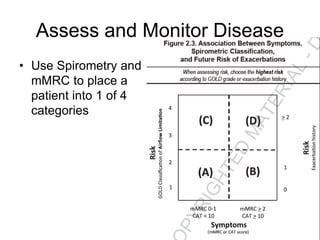
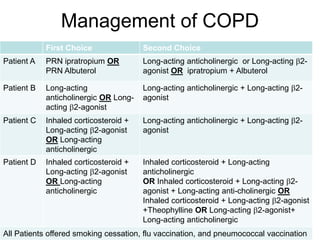
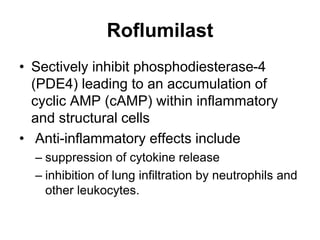
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is characterized by poorly reversible airflow limitation caused by chronic inflammation in the lungs. The two main conditions that make up COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis involves excessive mucus production and cough, while emphysema results in the destruction of lung tissue and loss of elasticity. Management of COPD focuses on reducing risk factors like smoking, managing stable disease with bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, and treating exacerbations which present as worsening symptoms.