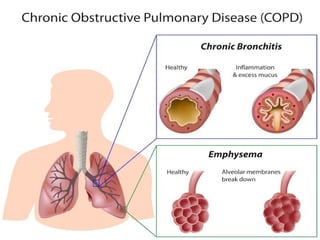
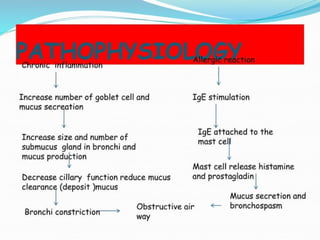
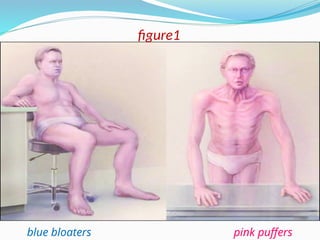
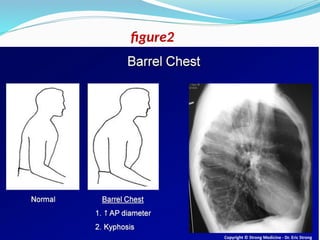
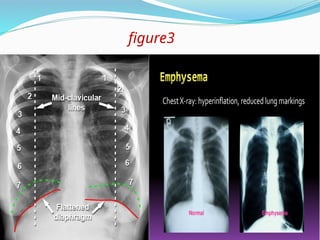
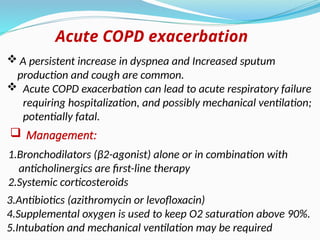
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive and irreversible condition characterized by chronic dyspnea and airflow limitation, often caused by factors such as tobacco smoke and environmental pollutants. It comprises two main types: chronic bronchitis and emphysema, which may coexist and lead to various symptoms and complications requiring proper diagnosis and management. Effective management includes smoking cessation, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation, alongside patient education and monitoring.