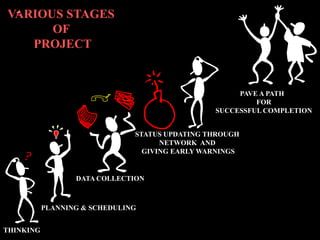
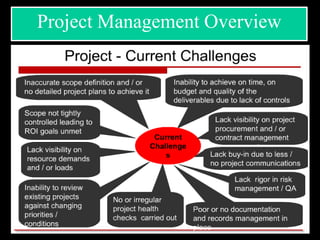
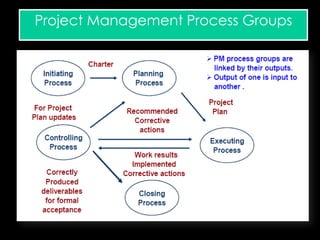
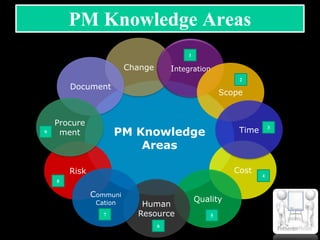
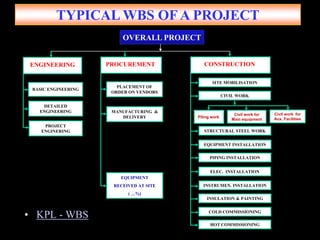
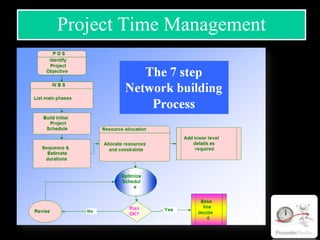
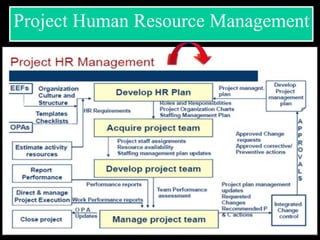
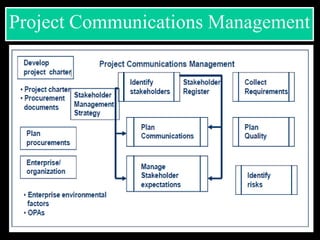
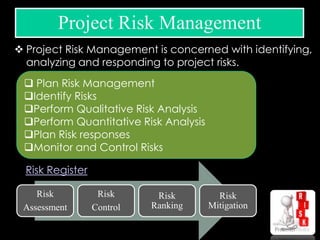
The document discusses various aspects of project management. It begins by outlining the different stages of a project including planning and scheduling, data collection, status updates, and ensuring successful completion. It then defines what a project is, its key characteristics, and how project management applies knowledge and techniques to meet stakeholder needs and expectations. The document also discusses why companies and individuals use project management and what goes into a project management plan. It provides overviews of the project management process, process groups, knowledge areas, and integration management.




























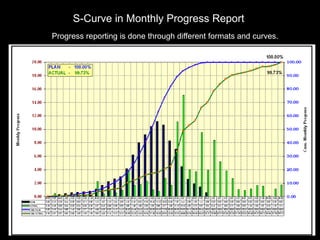
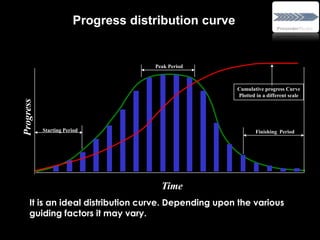
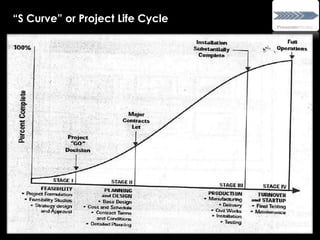
![S- Curve is the graphic display of cumulative progress
plotted against time.
Ideal S - Curve is a sinusoidal curve based on the
following formulae:
Y = [1 - sin(x/xn*180 + 90 ) *50]
Y – Percent progress
x – Period at which s-curve value required
xn – Total period
The name is derived from the 'S' like nature of the curve.
S-Curve
What is “S Curve”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanagement-130721095616-phpapp01/85/Project-management-39-320.jpg)