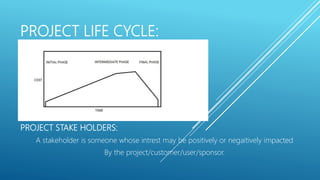
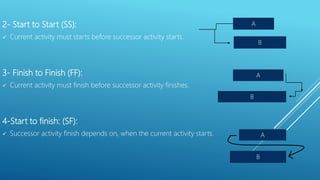
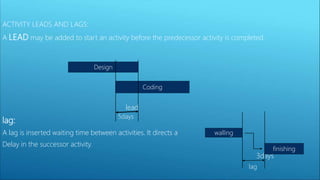
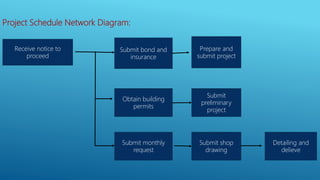
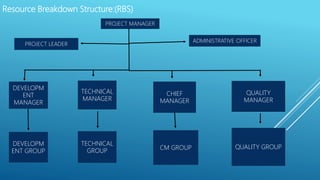
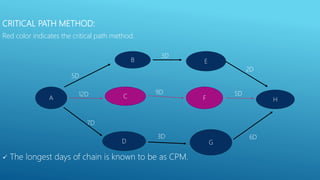
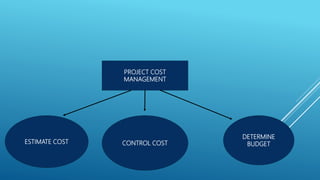
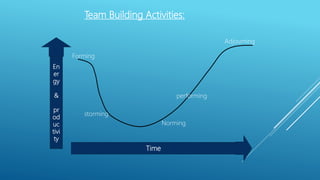
This document outlines the key aspects of project management based on the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). It discusses the 11 major processes involved in project management: integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communication management, procurement management, and risk management. For each process, it describes the main activities and tools used to plan, monitor, and control the project according to the project life cycle.