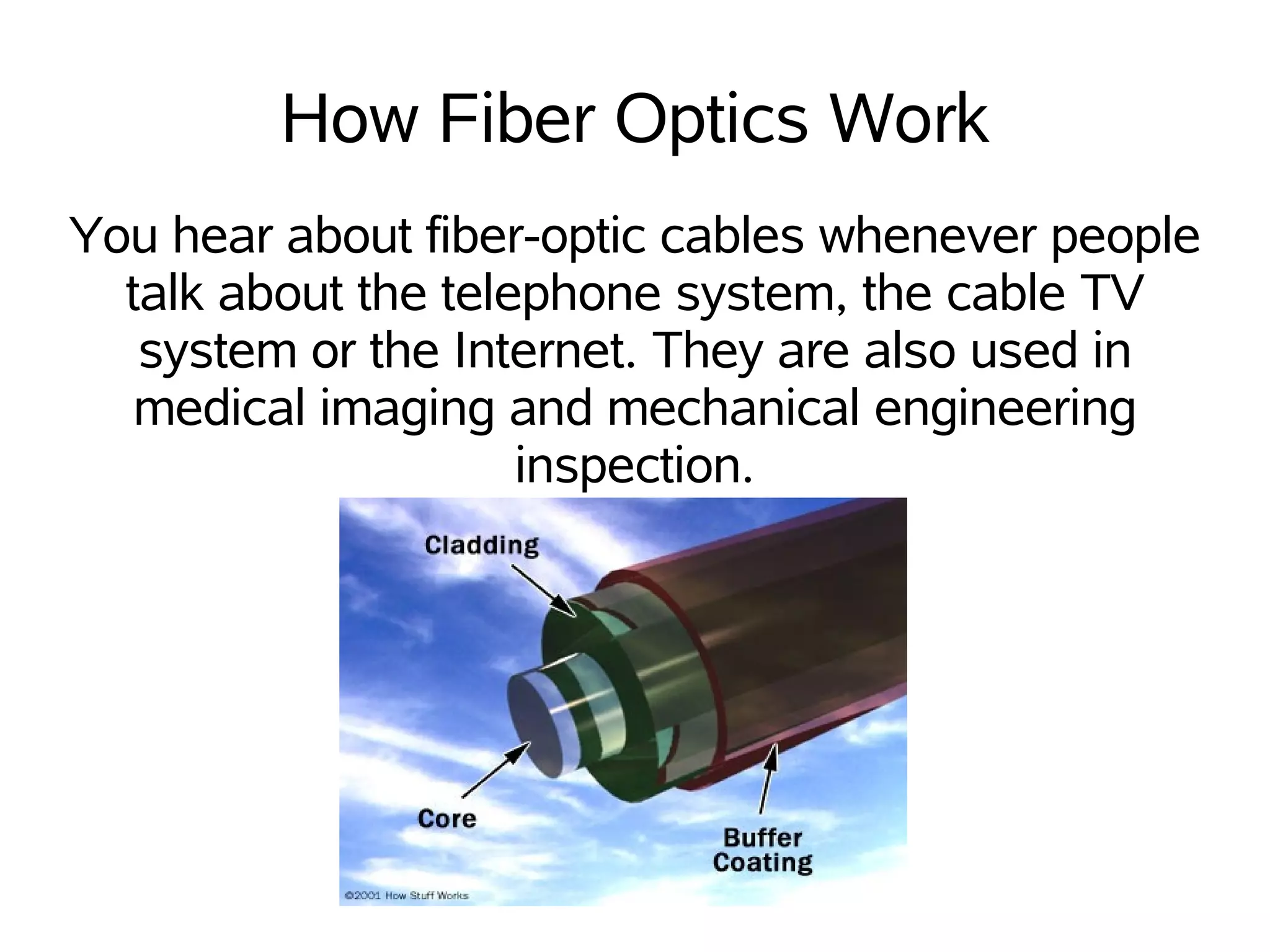
Fiber optics use thin strands of glass called optical fibers to transmit light signals over long distances. Light travels through the core of the fiber, which is surrounded by cladding that reflects the light down the length of the fiber. Fiber optic systems include a transmitter that produces light signals, the optical fiber that carries the signals, and a receiver that interprets the signals. Fiber optics have advantages over metal wires like lower costs, higher data capacity, and less signal degradation over long distances.