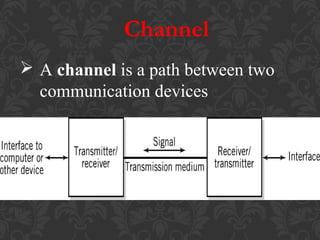
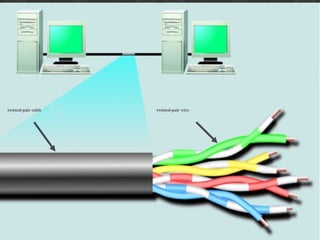
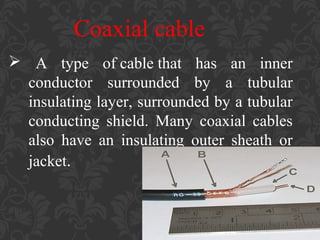
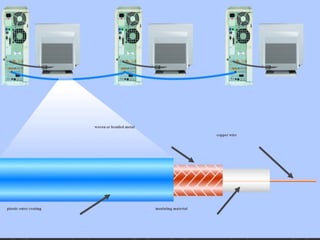
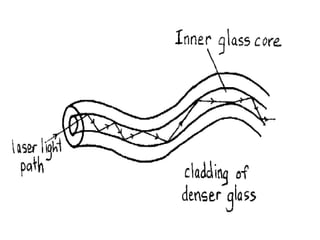
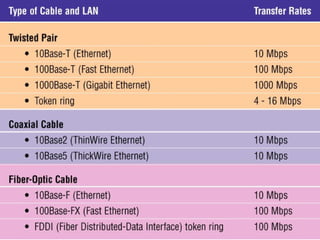
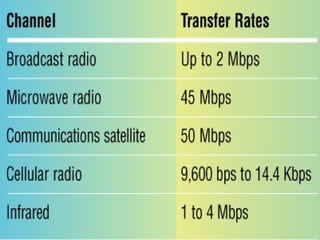
The document discusses different types of communication channels and transmission media. A channel is a path between communication devices that can be characterized by its signaling transmission method, medium used, bandwidth, directions of signal flow, and noise characteristics. Signaling can be analog or digital. Transmission direction can be point-to-point, simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex. Media include physical wired media like twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optics, as well as wireless media like broadcast radio, cellular radio, microwaves, and infrared. Fiber-optics transmit light between fiber ends and are used for long distance, high bandwidth communications.