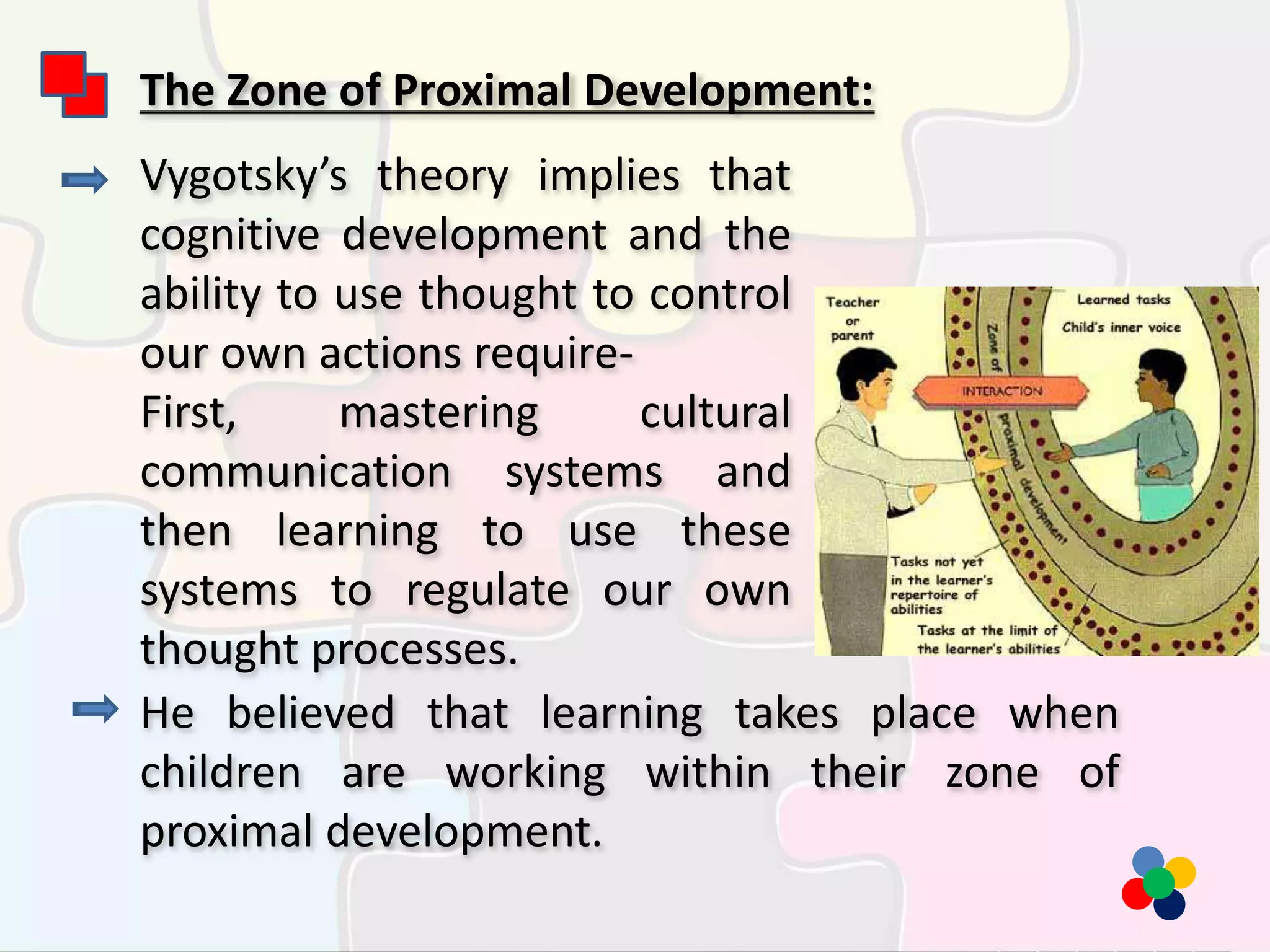
Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist who developed the theory of social constructivism, focusing on the important role of culture and social interaction in cognitive development. His theory proposes that intellectual development depends on cultural tools like language and counting systems. In contrast to Piaget, Vygotsky believed that cognitive development is strongly linked to input from others and occurs through social learning within a child's zone of proximal development with scaffolding from more knowledgeable individuals. His theory emphasizes using private speech and cooperative learning to internalize cultural knowledge and self-regulate independent thinking.