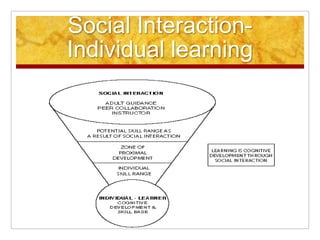
Vygotsky's social development theory stresses that social interaction plays a fundamental role in cognitive development. Children can achieve more when supported by social interaction such as collaboration with peers or guidance from adults. Vygotsky defined the "zone of proximal development" as the difference between what a child can do independently and what they can do with help. Within this zone, scaffolding from social interaction allows children to develop skills and internalize higher-level thinking.