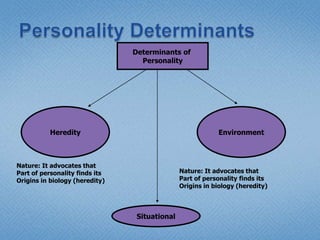
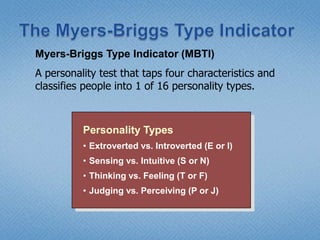
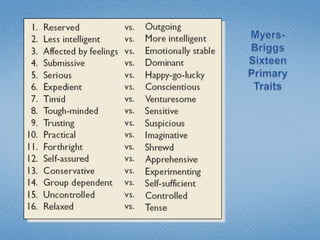
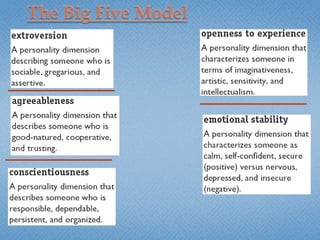
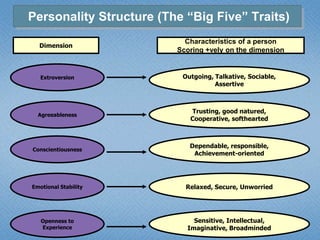
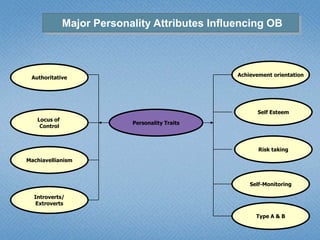
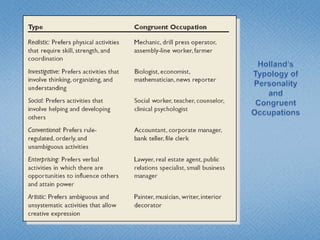
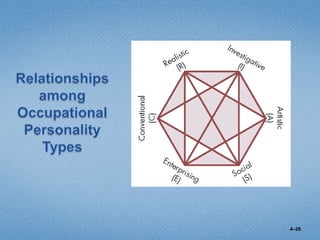
Personality refers to the set of traits and behaviors that characterize an individual. It has both internal elements like thoughts and genetics as well as external and observable behaviors. Personality is relatively stable but can be shaped by both heredity and environment. There are several theories for describing personality types including the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and the Big Five model. Understanding personality is important in organizational behavior for predicting behaviors, managing diversity, and achieving person-job fit.