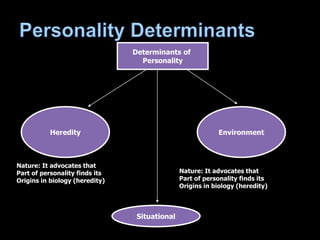
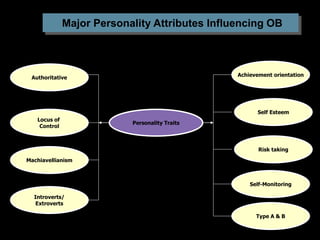
This document discusses personality in organizational behavior. It defines personality as relatively stable patterns of behavior and internal states that explain individual tendencies. Personality has both internal elements like thoughts and genetics, and external observable behaviors. It is shaped by both heredity and environment. Understanding personality can help predict behaviors and manage diversity in organizations. Several major personality attributes are discussed like locus of control, Machiavellianism, risk-taking, and types A and B. Determinants of personality include heredity, environment, and situational factors. Personality theories can contribute to understanding individuals in the workplace.