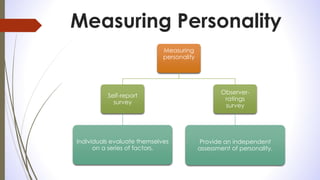
Personality can be defined as an individual's unique patterns of thinking, feeling and behaving. It is measured through self-report surveys and observer ratings. Personality is determined by both heredity and environmental factors such as relationships and work environments. Common personality traits include extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness. Two popular models for assessing personality are the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and the Big Five model. Other relevant traits include locus of control, self-monitoring, risk-taking, and type A vs type B behaviors. Personality influences behaviors and outcomes at work.