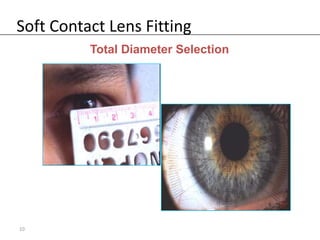
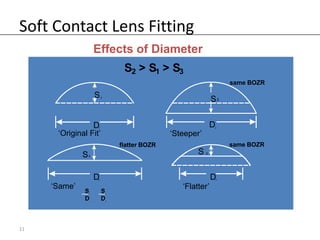
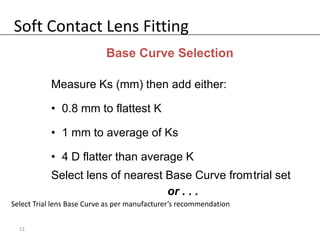
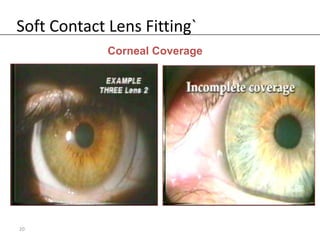
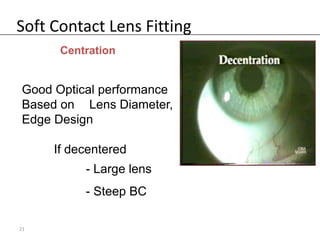
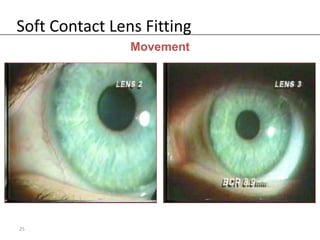
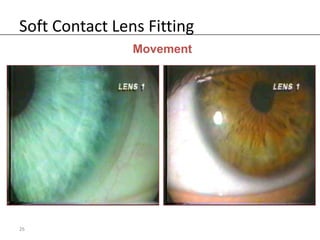
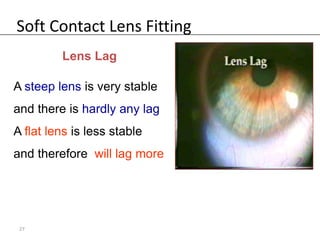
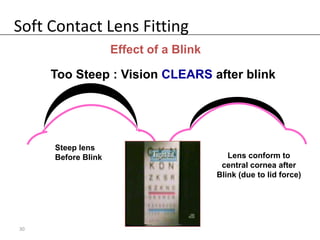
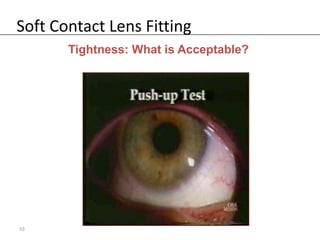
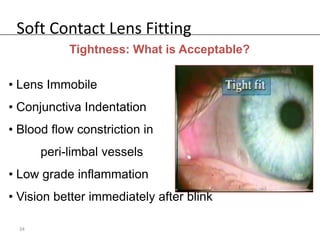
Fitting soft contact lenses requires considering many patient-specific factors to achieve excellent vision and ocular health. A proper fit involves selecting the correct total diameter, base curve, thickness, and material based on the patient's prescription, corneal shape, lifestyle, and health. Trial lenses are used to evaluate fit parameters like coverage, centration, movement, comfort, and vision to optimize on-eye performance while avoiding issues like tightness or looseness that could impact ocular health or vision. The goal is to find a lens that provides optimum vision and good comfort without causing any ocular insult.