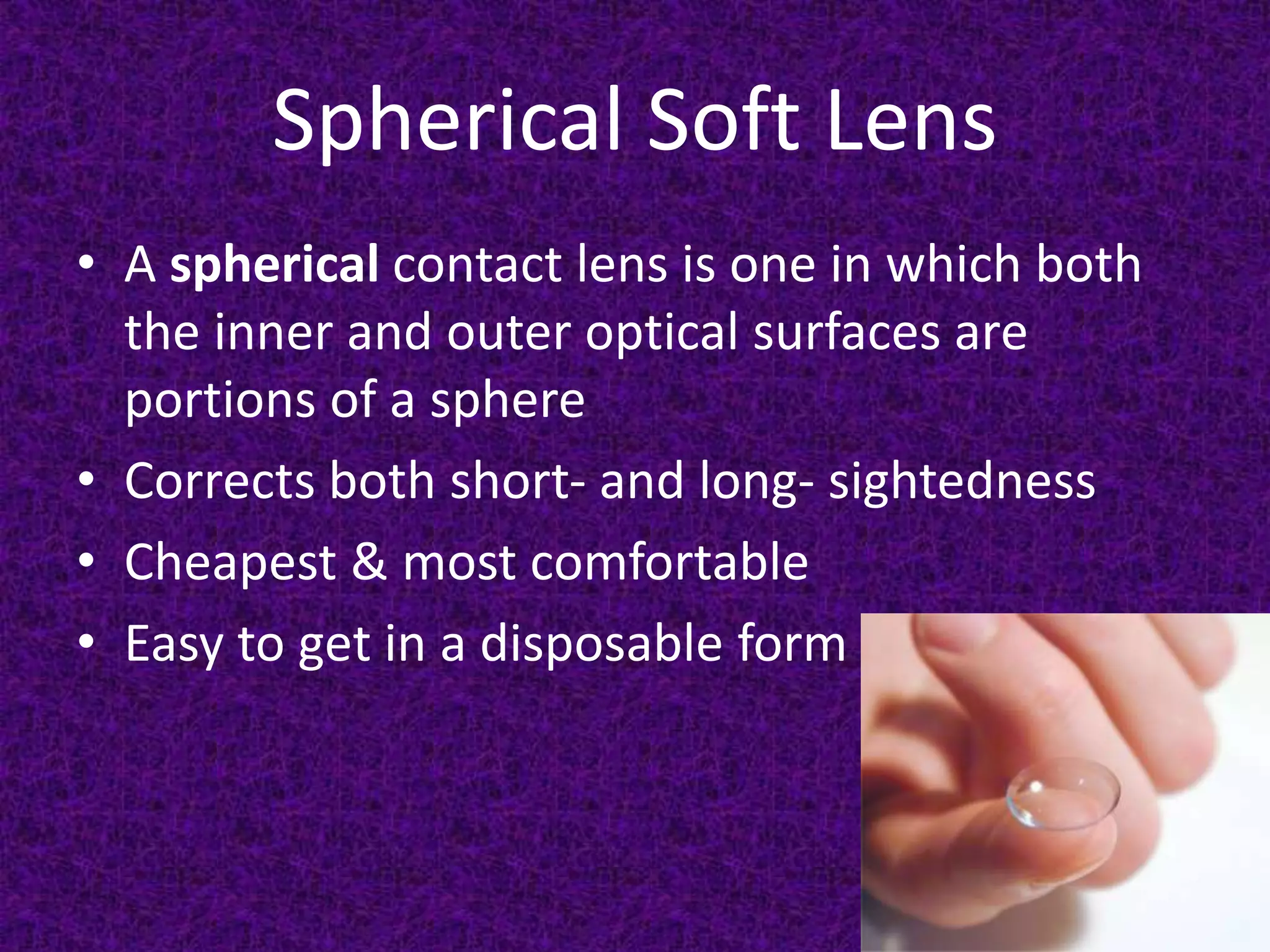
Contact lenses are artificial devices that correct refractive errors and ocular irregularities by replacing the cornea's anterior surface. They come in various types, including hard, rigid gas permeable, and soft lenses, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages related to comfort, durability, and optical quality. Indications for use extend across optical, therapeutic, cosmetic, and preventive reasons, while contraindications include certain chronic eye conditions and mental incompetence.