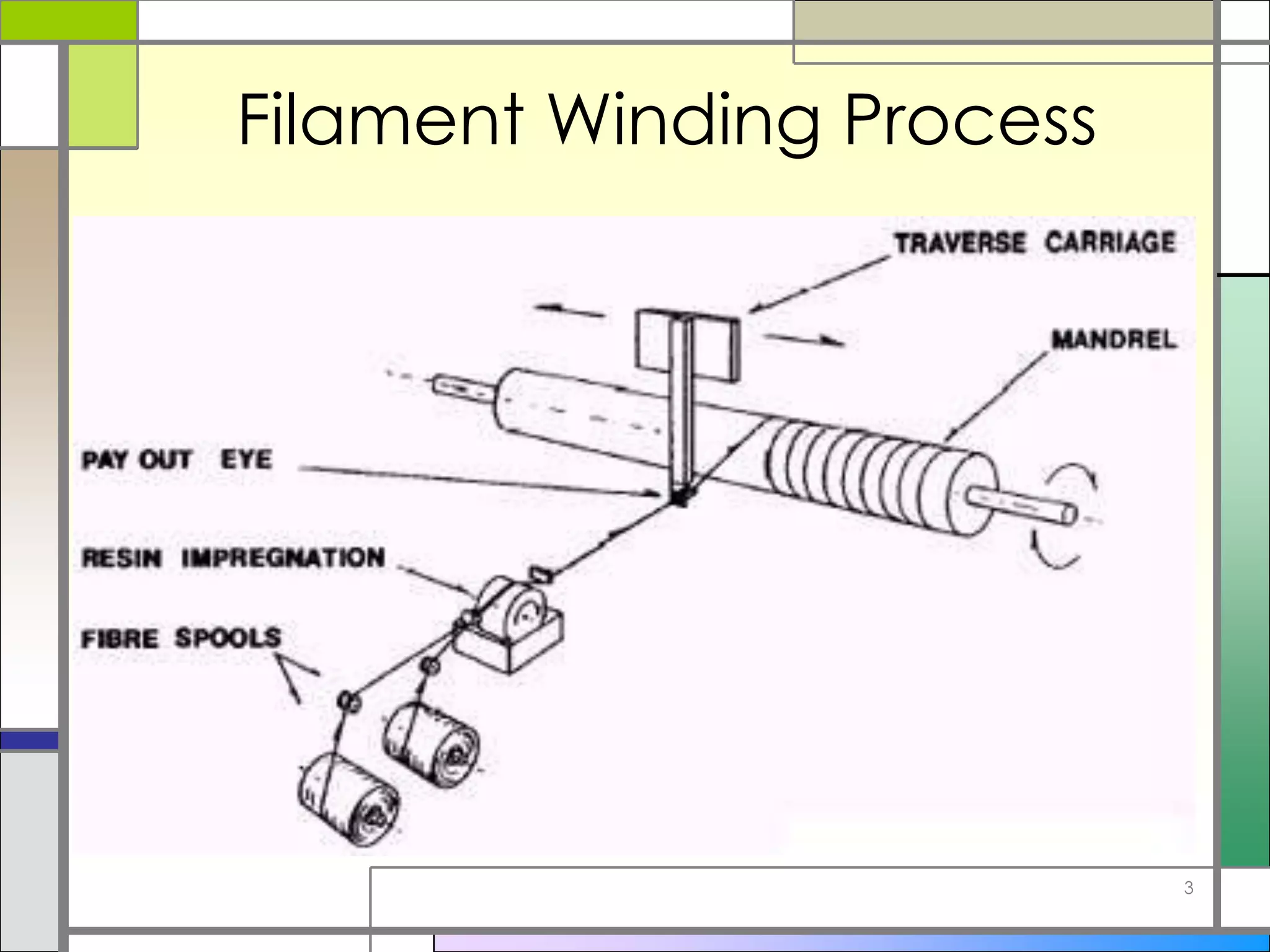
Filament winding is a process that creates circular composite products with a hollow core by winding fiber material and resin around a mandrel or core. The fiber is wound in a precise pattern while under tension. The wound part is then cured either at room temperature or in an oven, after which the mandrel is removed, leaving a hollow composite structure. Filament winding is used to create products like storage tanks, pipes, aerospace and vehicle parts, and more.