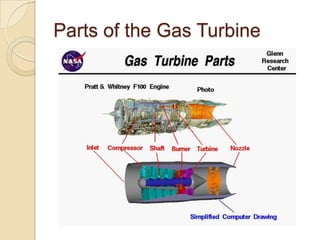
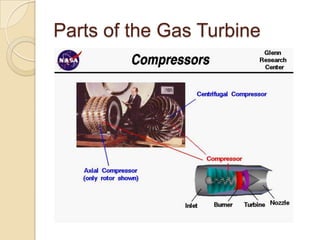
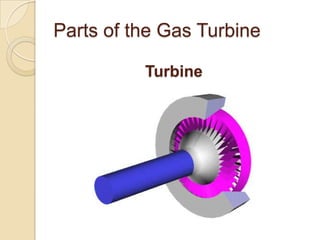
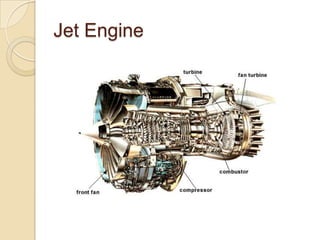
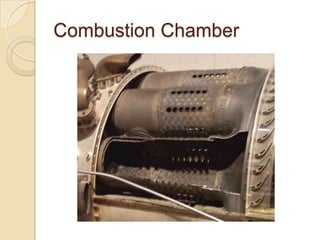
The document discusses the key parts of a gas turbine engine including the inlet, compressor, turbine, burner, and nozzle. It then focuses on jet engines, describing the materials used to manufacture different parts like titanium for the intake fan and turbine blades. The document outlines the manufacturing processes for various components, such as powder metallurgy for compressor disks, investment casting for turbine blades, and welding for the combustion chamber.