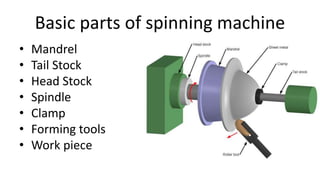
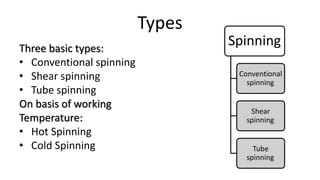
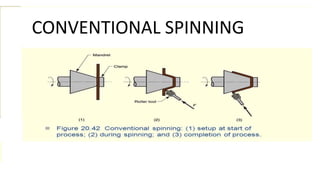
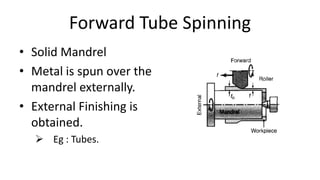
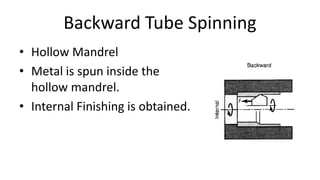
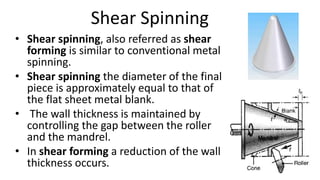
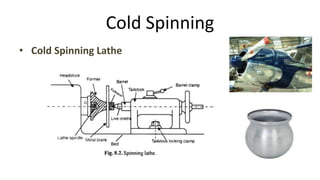
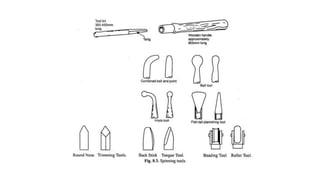
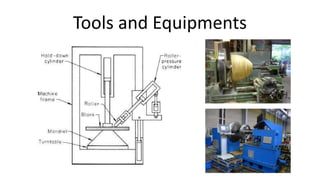
Metal spinning is a sheet metal forming process that uses rollers to form axisymmetric parts over a rotating mandrel. There are three main types: conventional spinning, shear spinning, and tube spinning. Spinning can be done hot or cold and involves placing a metal blank against a mandrel and using tools to deform the material into shape as it rotates. Applications include automotive parts, containers, and more. Key advantages are low tooling costs, design flexibility, and little material waste.