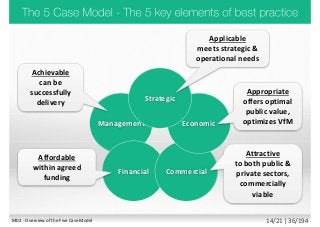
The document introduces the Better Business Cases (BBC) training course, emphasizing the importance of business cases in project management and outlining the five case model for preparing effective spending proposals. It details the structure of foundational and practitioner exams, assesses common project failures, and highlights best practices for project management. Additionally, it outlines the accreditation process associated with the BBC program developed by HM Treasury and other governmental bodies.