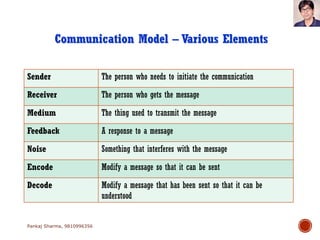
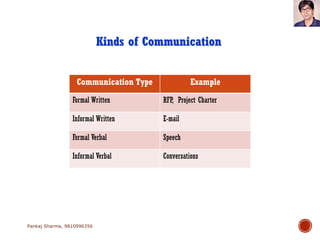
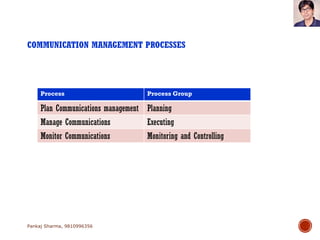
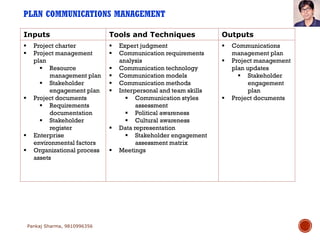
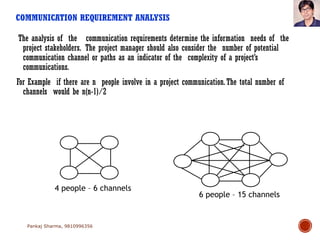
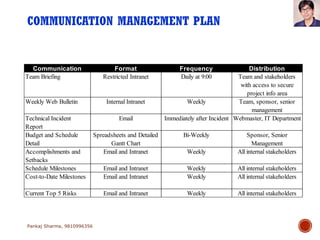
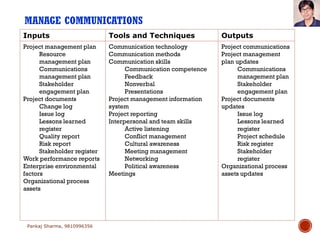
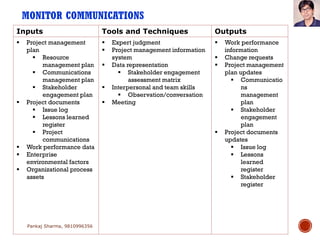
Project communications management involves determining communication needs, developing a communication plan, distributing project information, and monitoring communications. An effective project manager spends about 90% of their time communicating, with 50% of that spent communicating with the project team. The communication plan identifies what information will be shared, who it will be shared with, how often, and the communication methods. Monitoring communications ensures the right information is reaching stakeholders as defined in the plan.