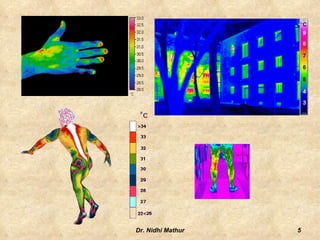
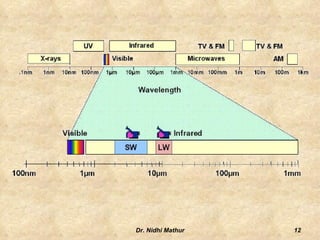
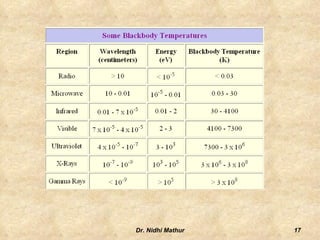
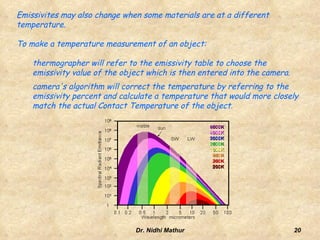
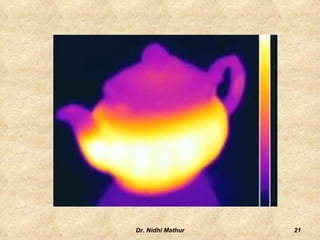
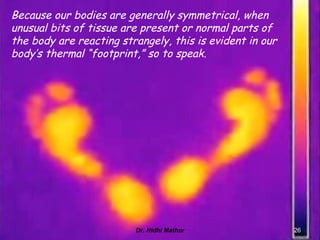
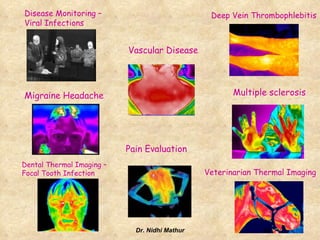
Thermography uses infrared imaging to perform medical diagnostics. It detects differences in surface temperature on the body to identify areas of abnormality. Thermography has been used in medicine for thousands of years to detect areas of excess heat or cold associated with disease. Modern medical thermography uses non-contact digital infrared thermal imaging cameras to safely obtain temperature maps of the body surface without limitations. It has applications in detecting cancers, vascular disorders, respiratory issues and more by identifying temperature variations on the skin.