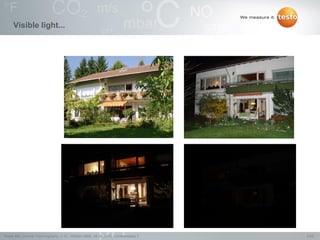
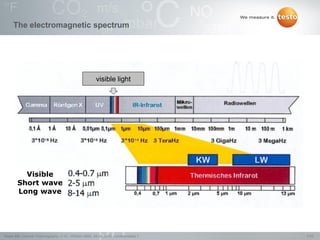
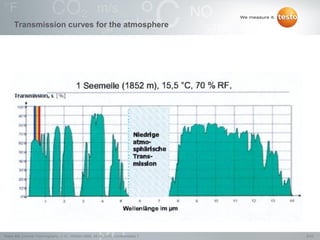
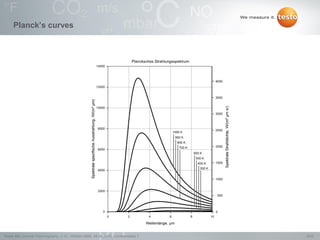
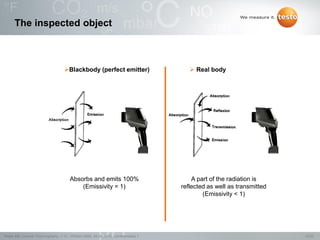
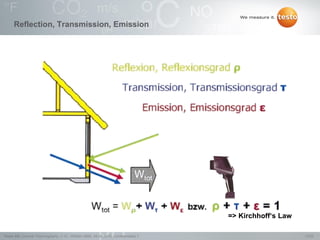
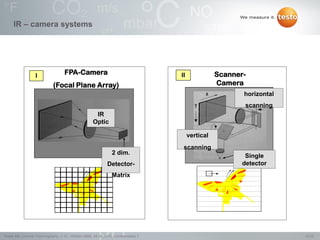
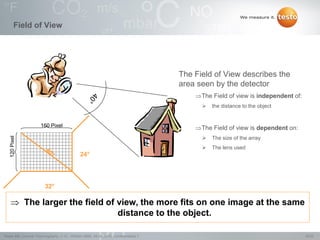
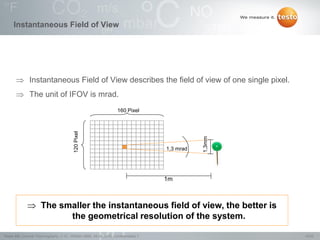
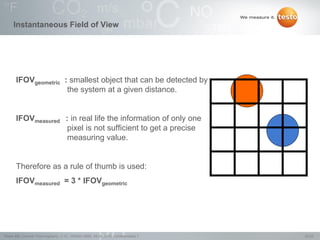
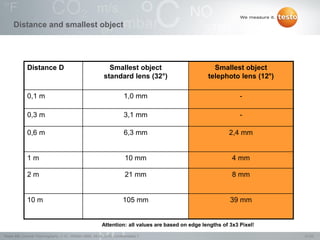
Thermography involves the graphical representation of temperature distribution on surfaces using infrared cameras. It detects electromagnetic radiation emitted from objects based on their temperature, rather than detecting temperature directly. To accurately measure temperature from radiation readings, cameras need information about the object's emissivity and reflected temperature, as real objects do not emit and absorb radiation like ideal blackbodies. Key specifications for infrared cameras include thermal sensitivity, field of view, and instantaneous field of view, which determine the camera's ability to detect small temperature differences and resolve objects at varying distances.