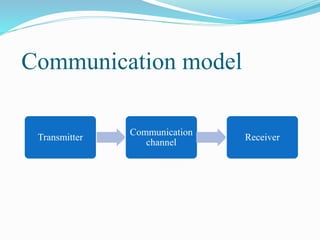
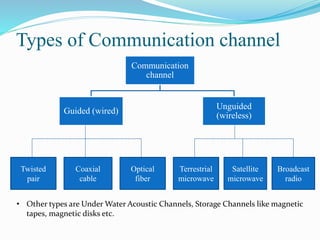
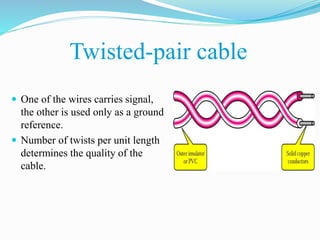
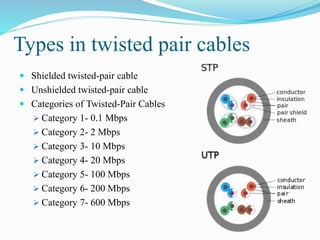
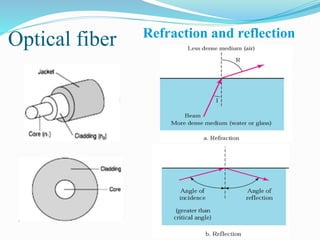
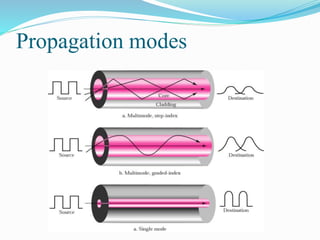
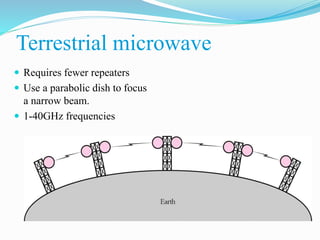
Communication channels can be either guided (wired) or unguided (wireless) and are used to transmit data between a transmitter and receiver. Guided channels include twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers which have different bandwidth and transmission properties. Unguided channels include terrestrial microwave, satellite, and broadcast radio which propagate signals through the air. The type of channel used depends on factors like bandwidth needs, data rate, distance, and number of receivers.