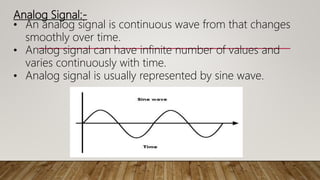
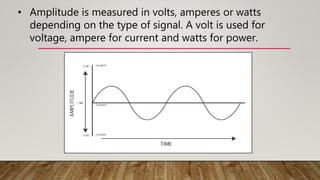
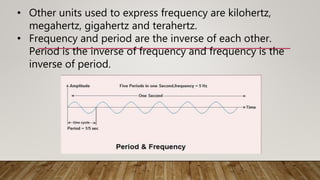
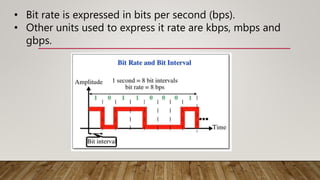
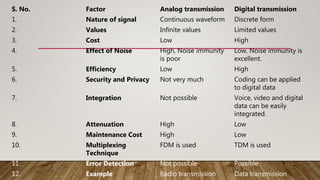
Analog signals are continuous waves that vary smoothly over time and can have an infinite number of values, while digital signals are discrete and can have only a limited set of values, such as 1 and 0. Analog signals are typically represented by sine waves, while digital signals are represented by square waves. While analog signals are best for audio and video transmission, digital signals are better suited for digital data transmission and provide benefits such as easier compression, encryption, and error detection.