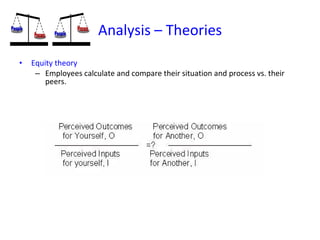
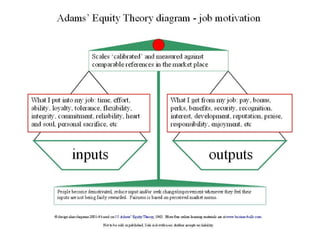
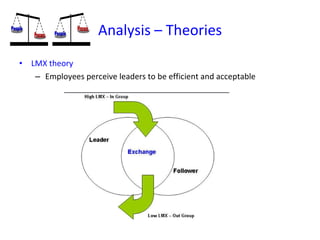
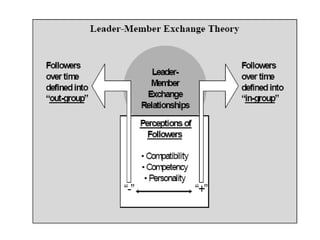
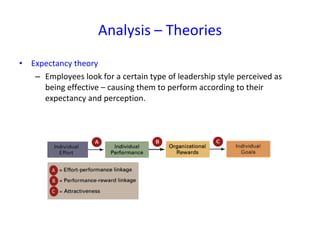
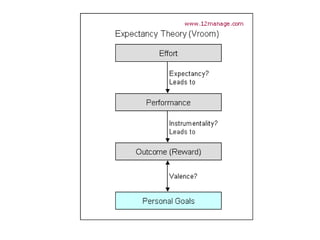
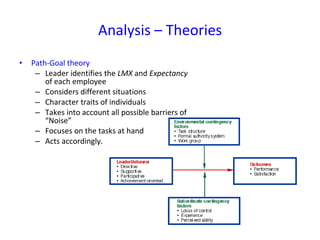
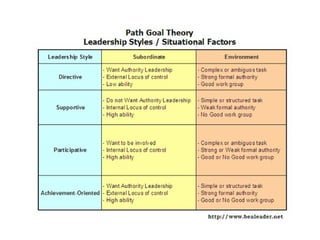
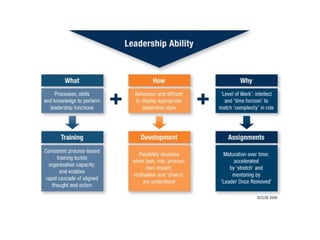
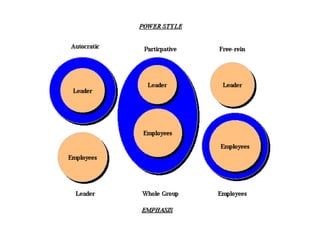
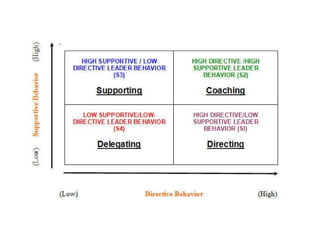
The document discusses three leadership styles - Directive Leader, Charismatic Leader, and Situational Leader - and their communication methods. A Directive Leader dictates tasks and deadlines, focusing on tasks and power. A Charismatic Leader motivates employees and avoids conflict, focusing on employee happiness. A Situational Leader identifies employee expectations and barriers, mixing the styles of the other two leaders based on each situation. The Situational Leader is presented as the most effective style.