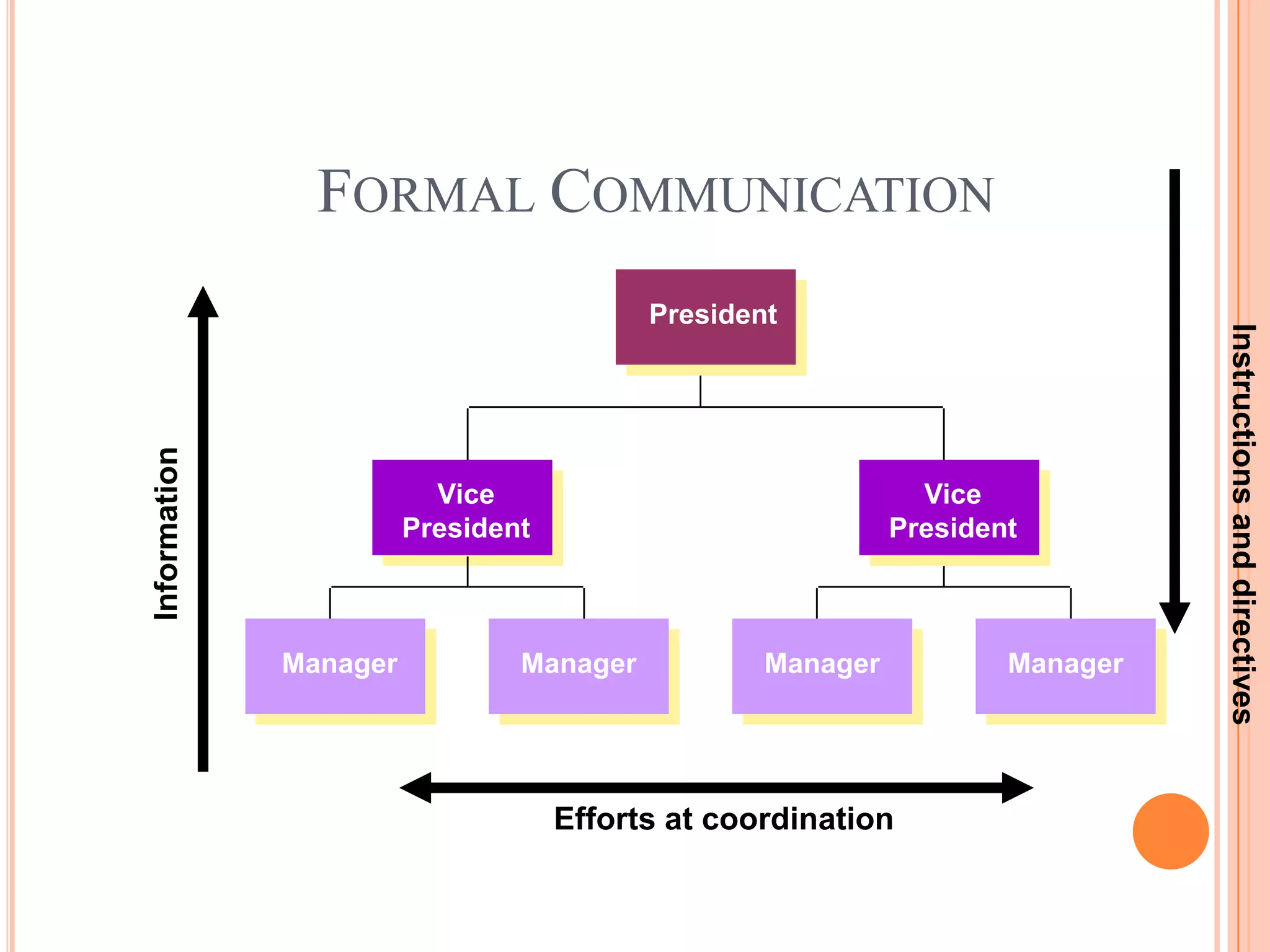
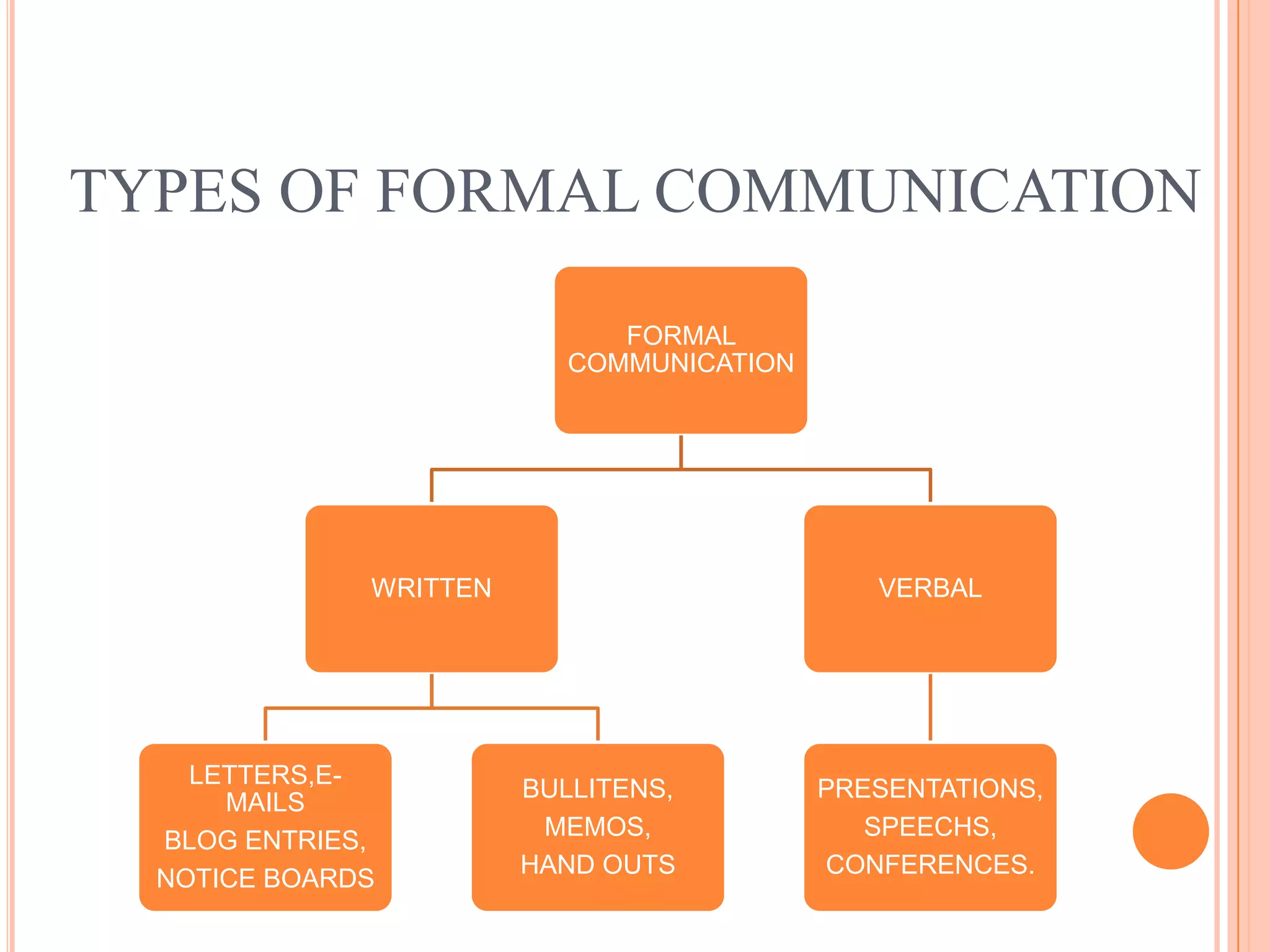
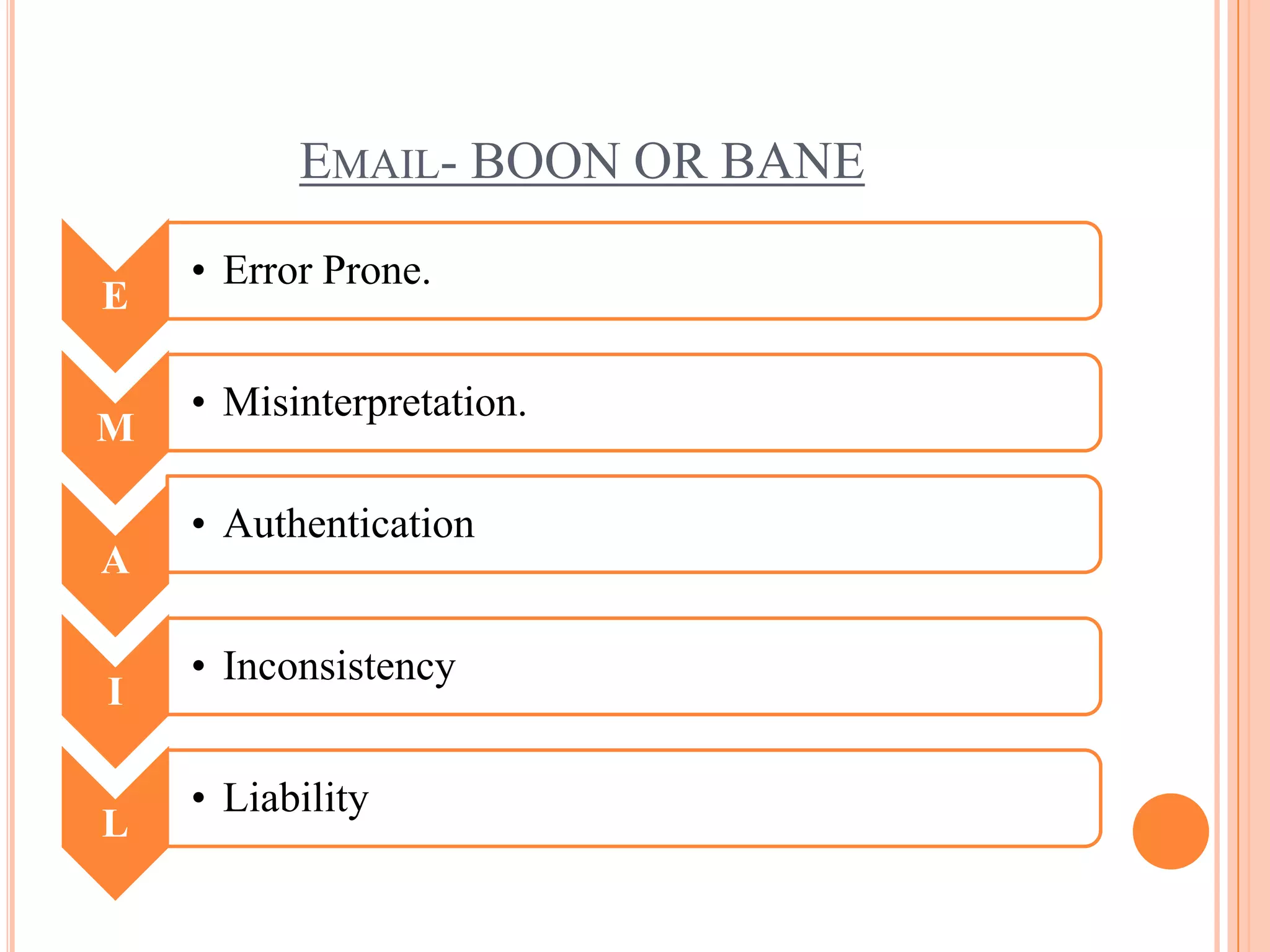
Formal communication in an organization involves the sharing of official information through approved channels. It can flow downward from managers to employees, upward from employees to managers, or horizontally between employees. Common forms of formal communication include written methods like emails, memos, letters, and notices, as well as verbal methods like presentations, meetings, and conferences. While email provides a fast and inexpensive way to communicate, it also poses risks like errors, misinterpretation, inconsistent messaging, and questions of authentication and liability that organizations must address.