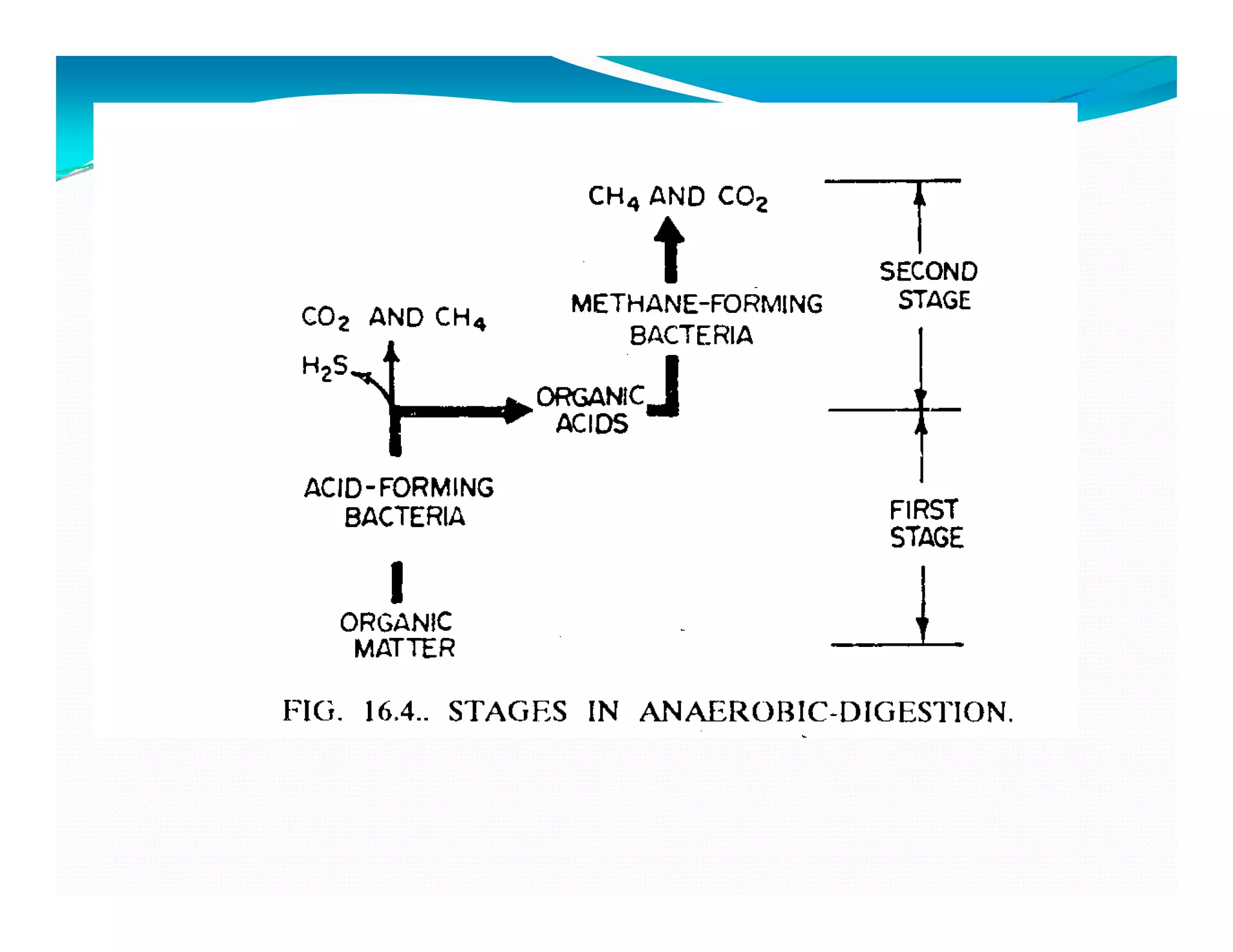
The document discusses various methods for sludge treatment, including thickening, digestion, conditioning, dewatering, drying, and disposal. It outlines processes such as anaerobic digestion, detailing the steps of hydrolysis, fermentation, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. The document also highlights disposal options for digested sludge, including spreading on farmland, composting, and incineration.

![A] SLUDGE TREATMENT
Thickening
DigestionDigestion
Conditioning
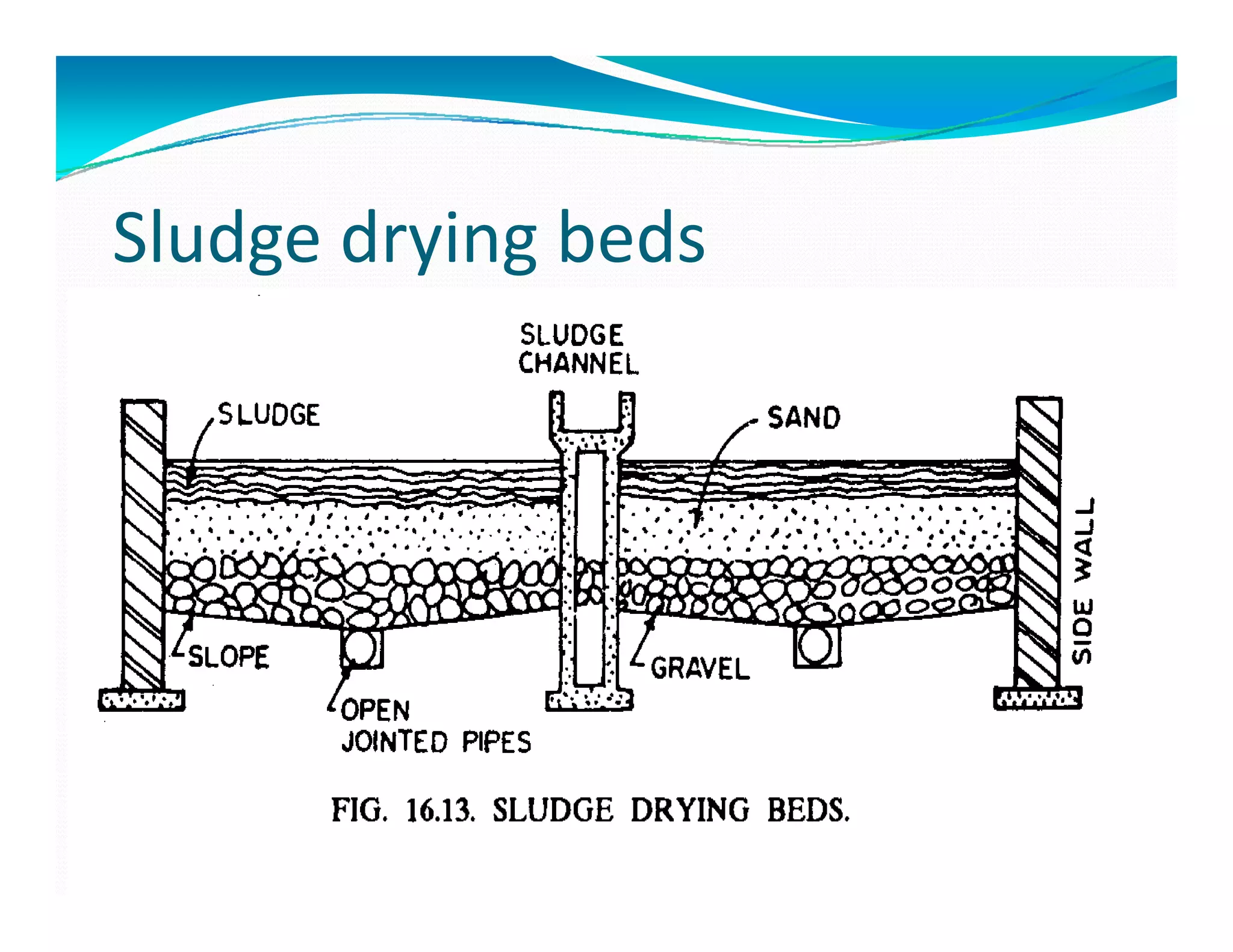
Dewatering
DryingDrying
Disposal (Incineration)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sludgemanagement-150311044832-conversion-gate01/75/Sludge-management-and-Sludge-digesters-2-2048.jpg)









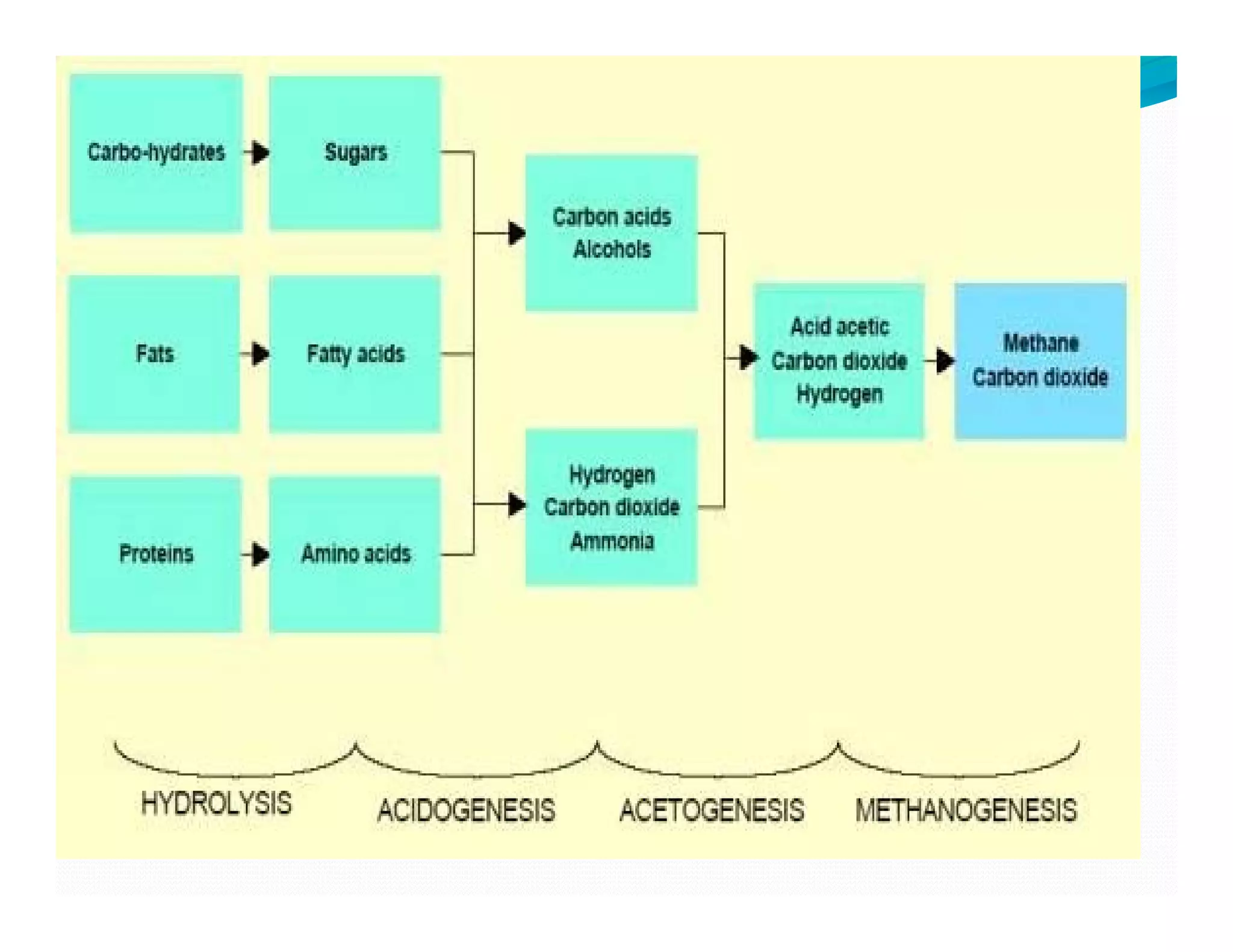
![B] Anaerobic Digestion
Consists of decomposition of
sludge from settling tankssludge from settling tanks.
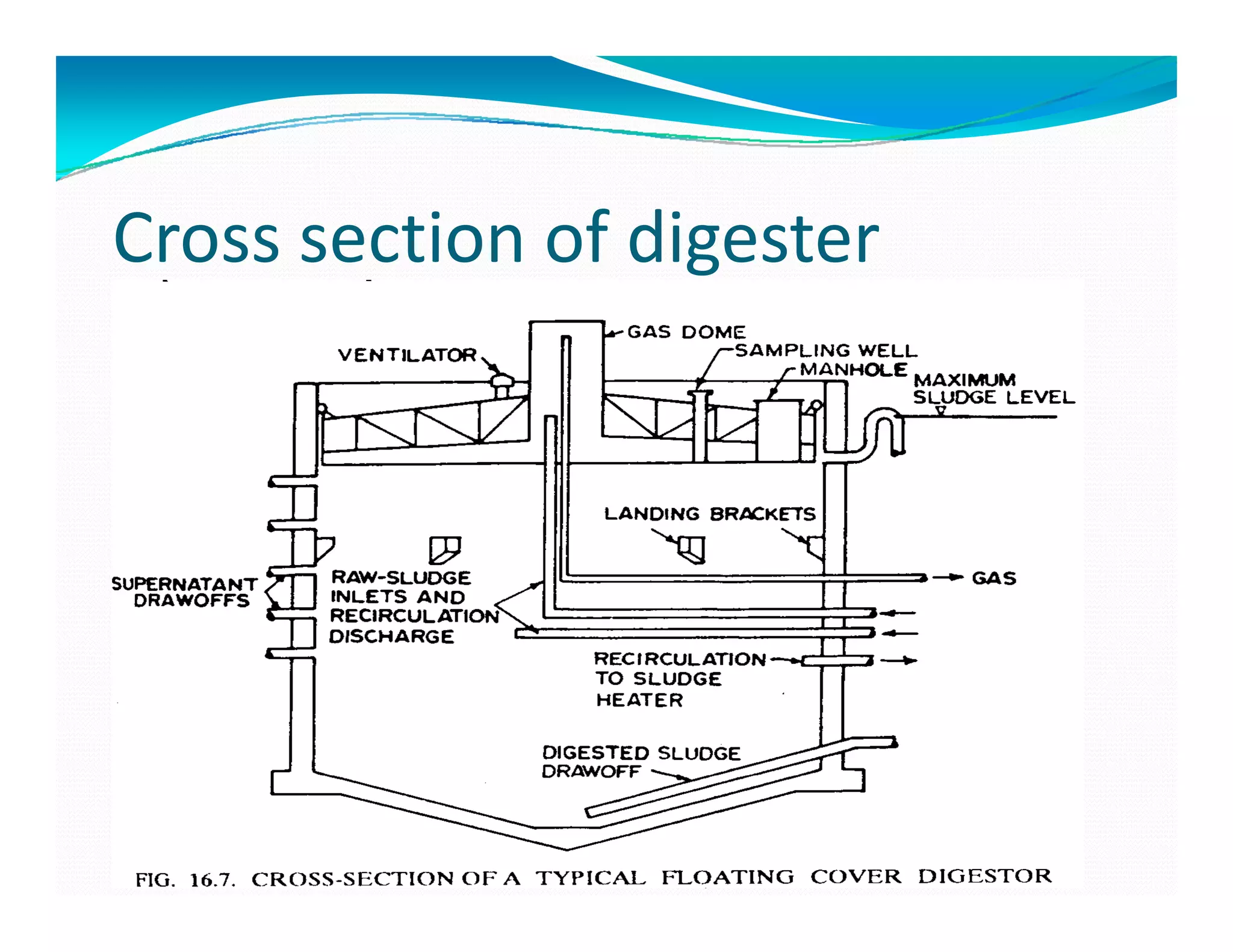
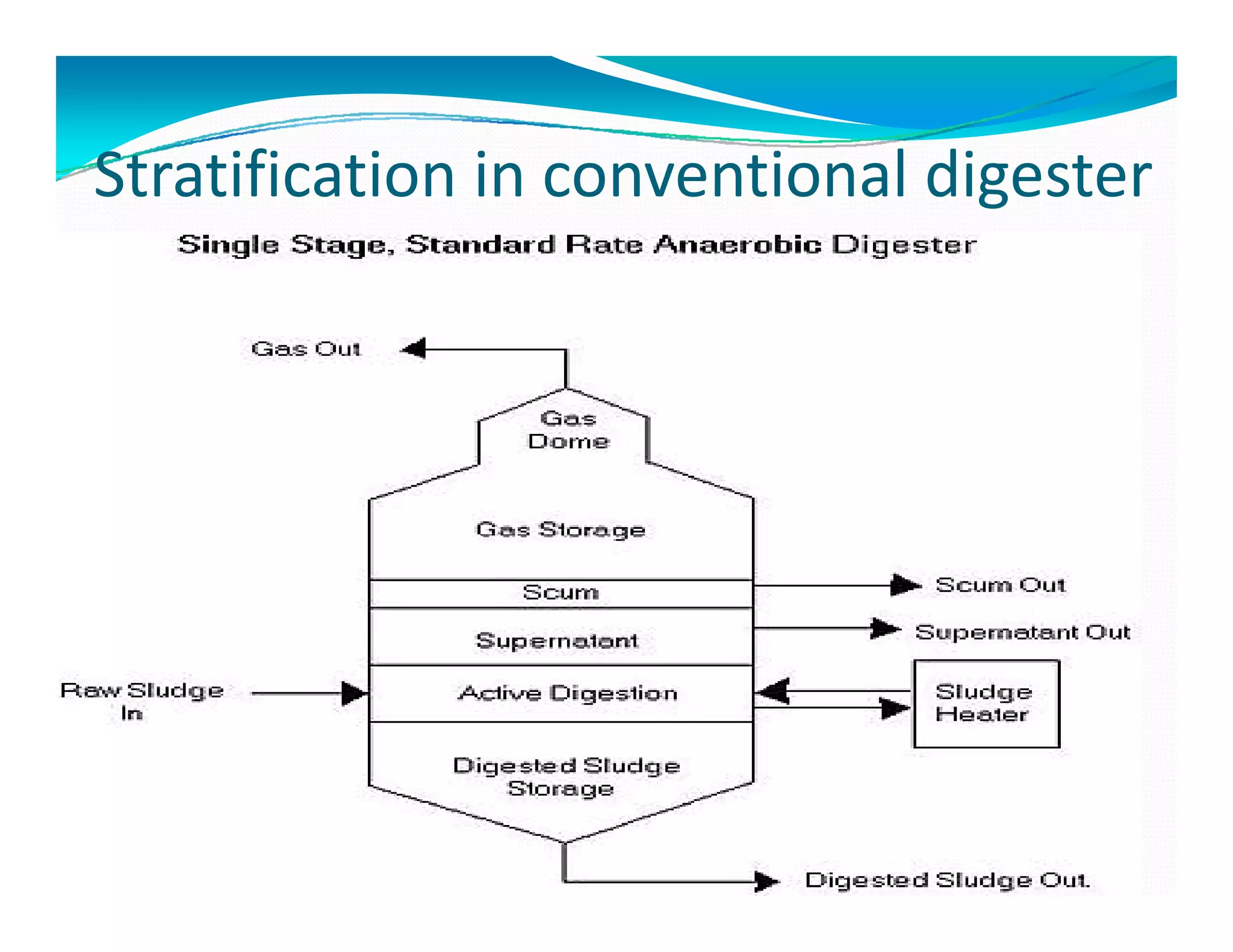
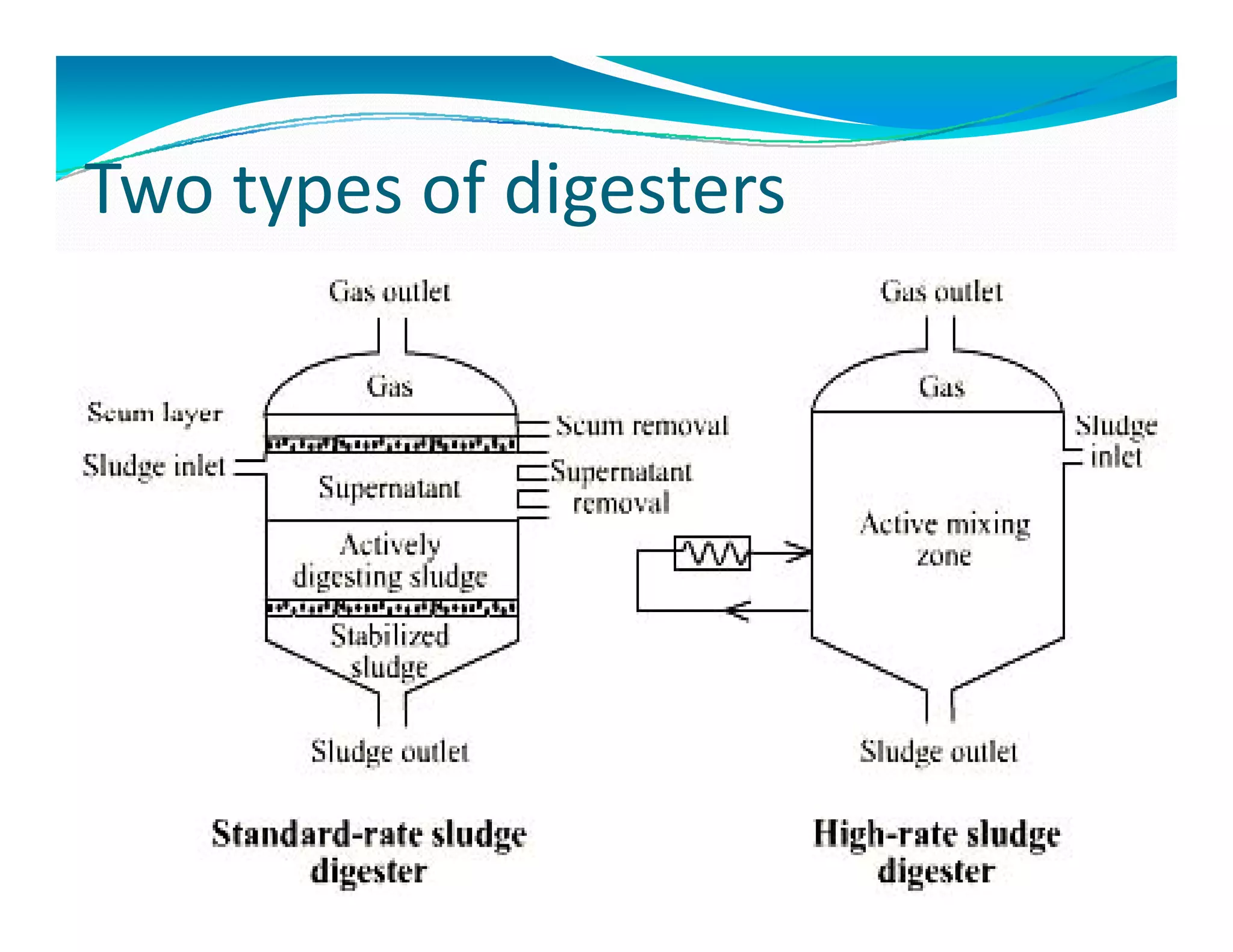
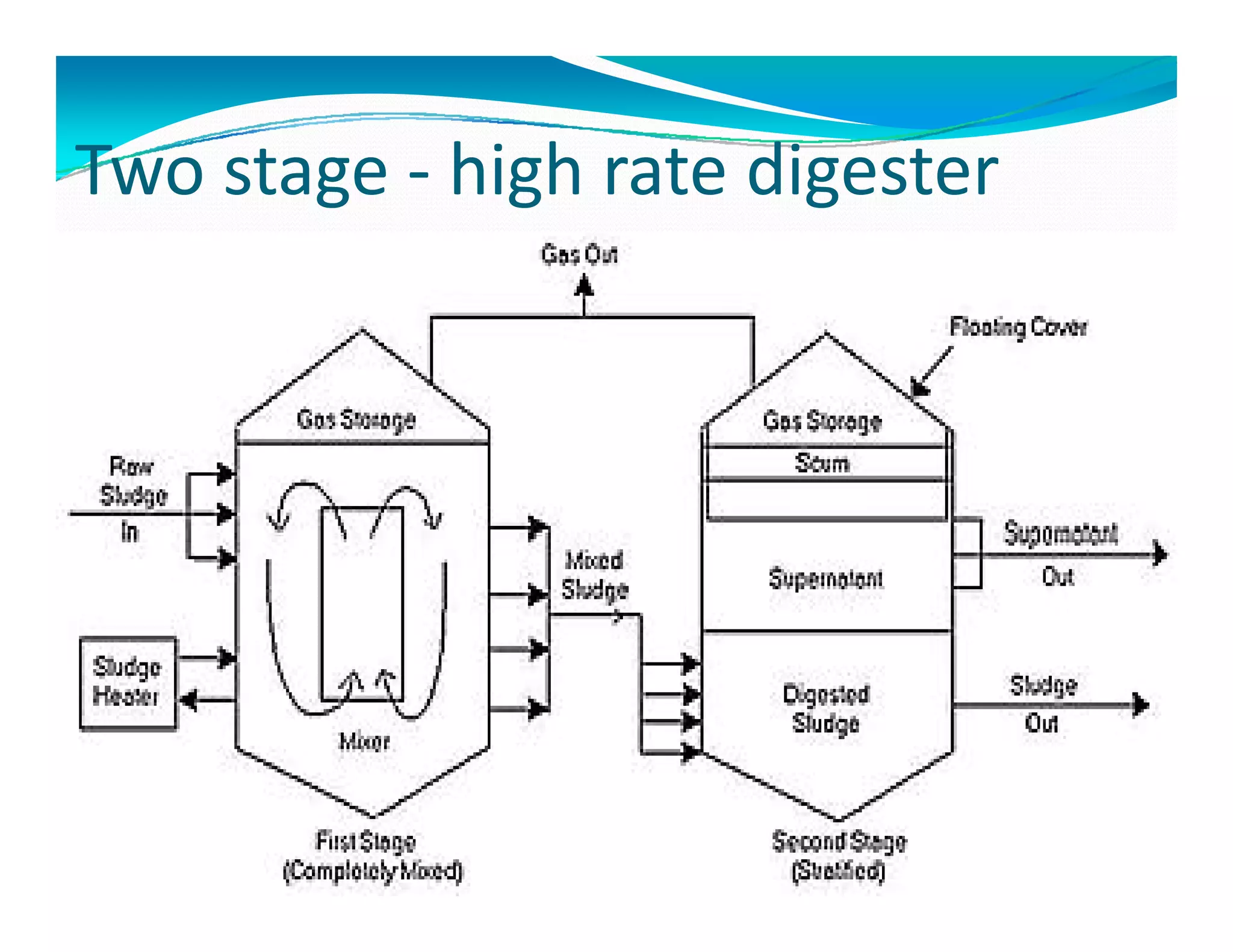
Two types of digestersTwo types of digesters
i] Standard rate or conventional
Ii] High rate digester](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sludgemanagement-150311044832-conversion-gate01/75/Sludge-management-and-Sludge-digesters-13-2048.jpg)






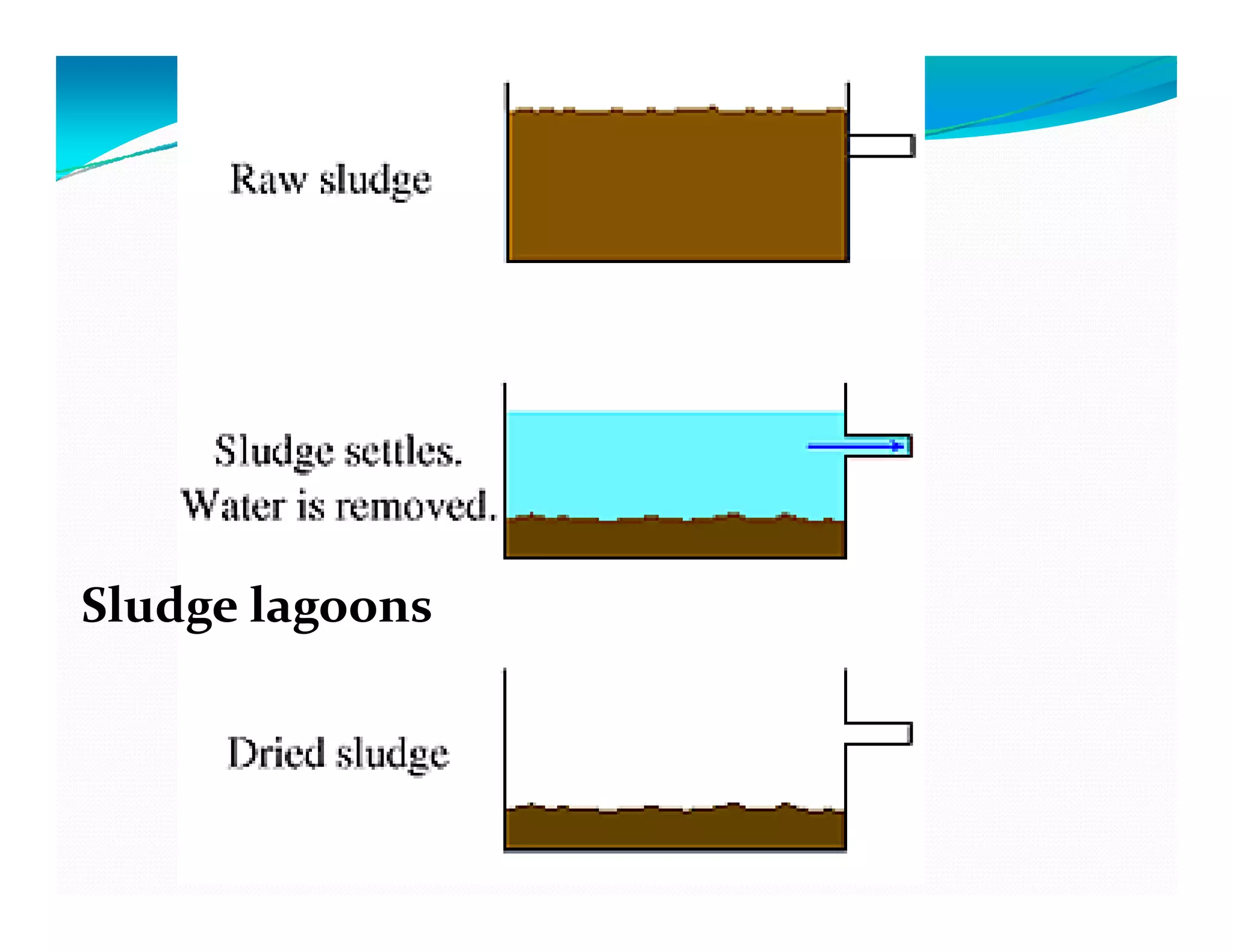
![C] DISPOSAL OF DIGESTED SLUDGE
Spreading on farm land
Dumping ( in abandoned quarries)Dumping ( in abandoned quarries)
Land filling ( Sanitary)
Sl d l iSludge lagooning
Compostingp g
Disposing in Inland water bodies or
Sea Sea.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sludgemanagement-150311044832-conversion-gate01/75/Sludge-management-and-Sludge-digesters-26-2048.jpg)