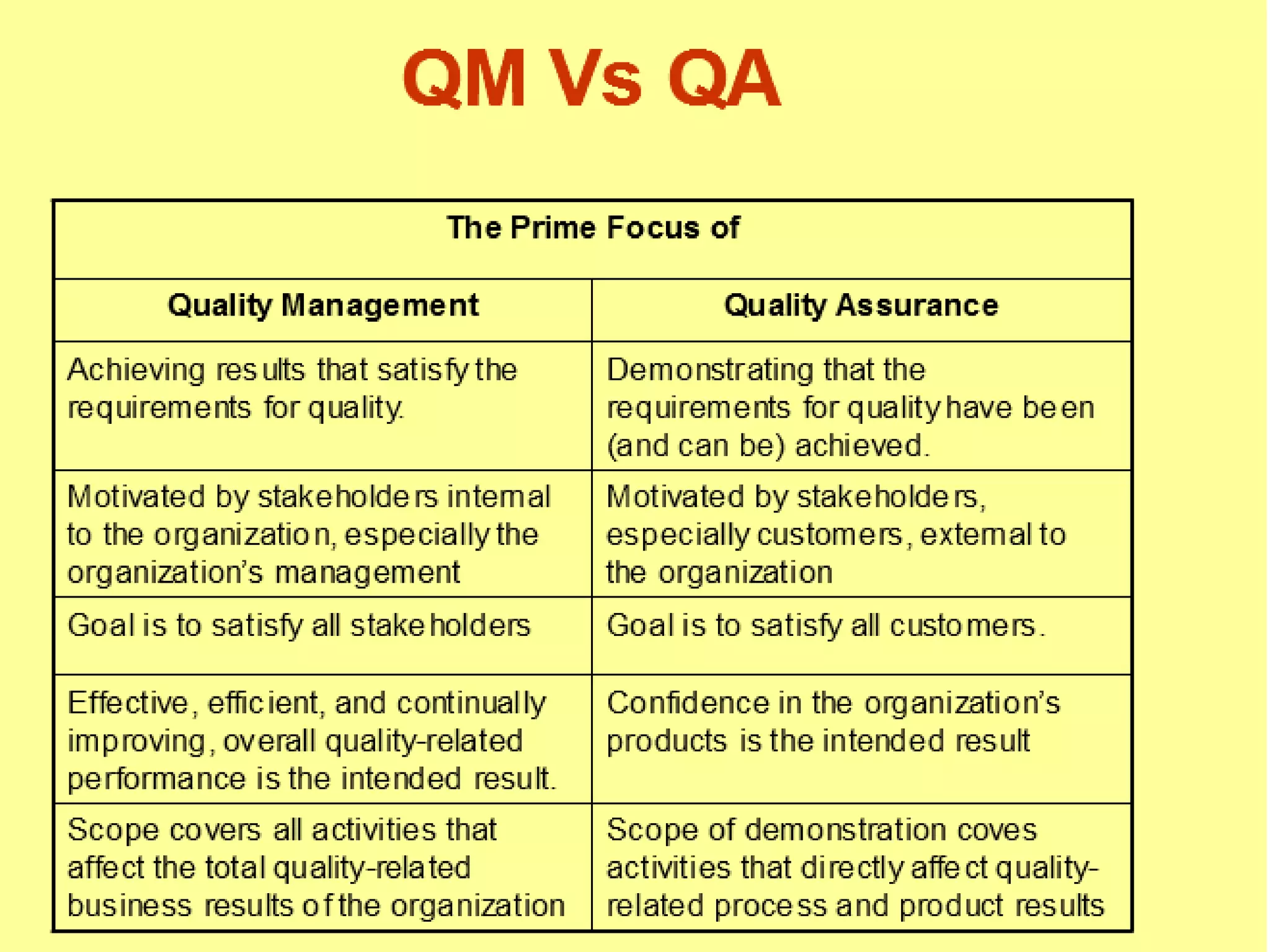
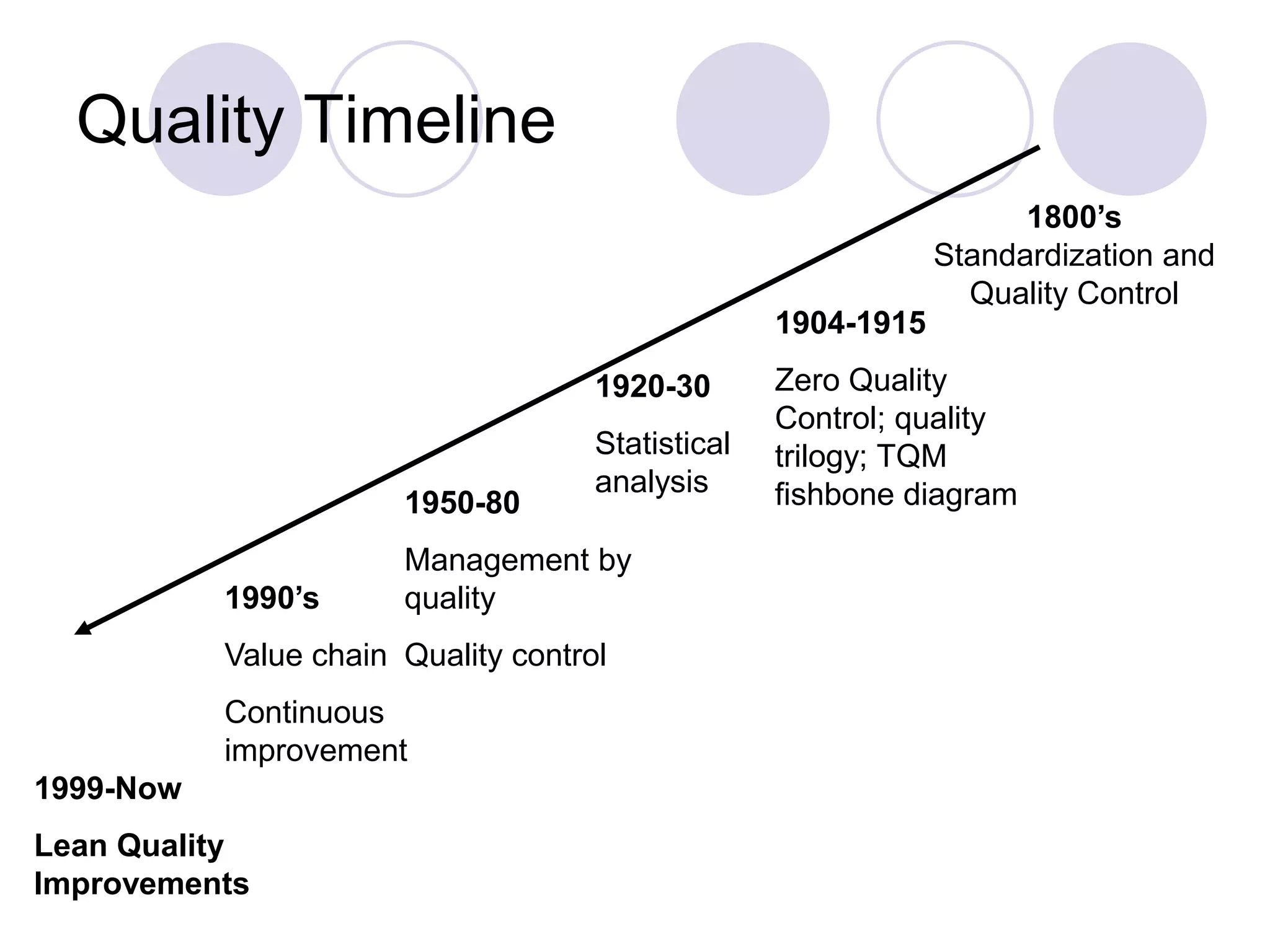
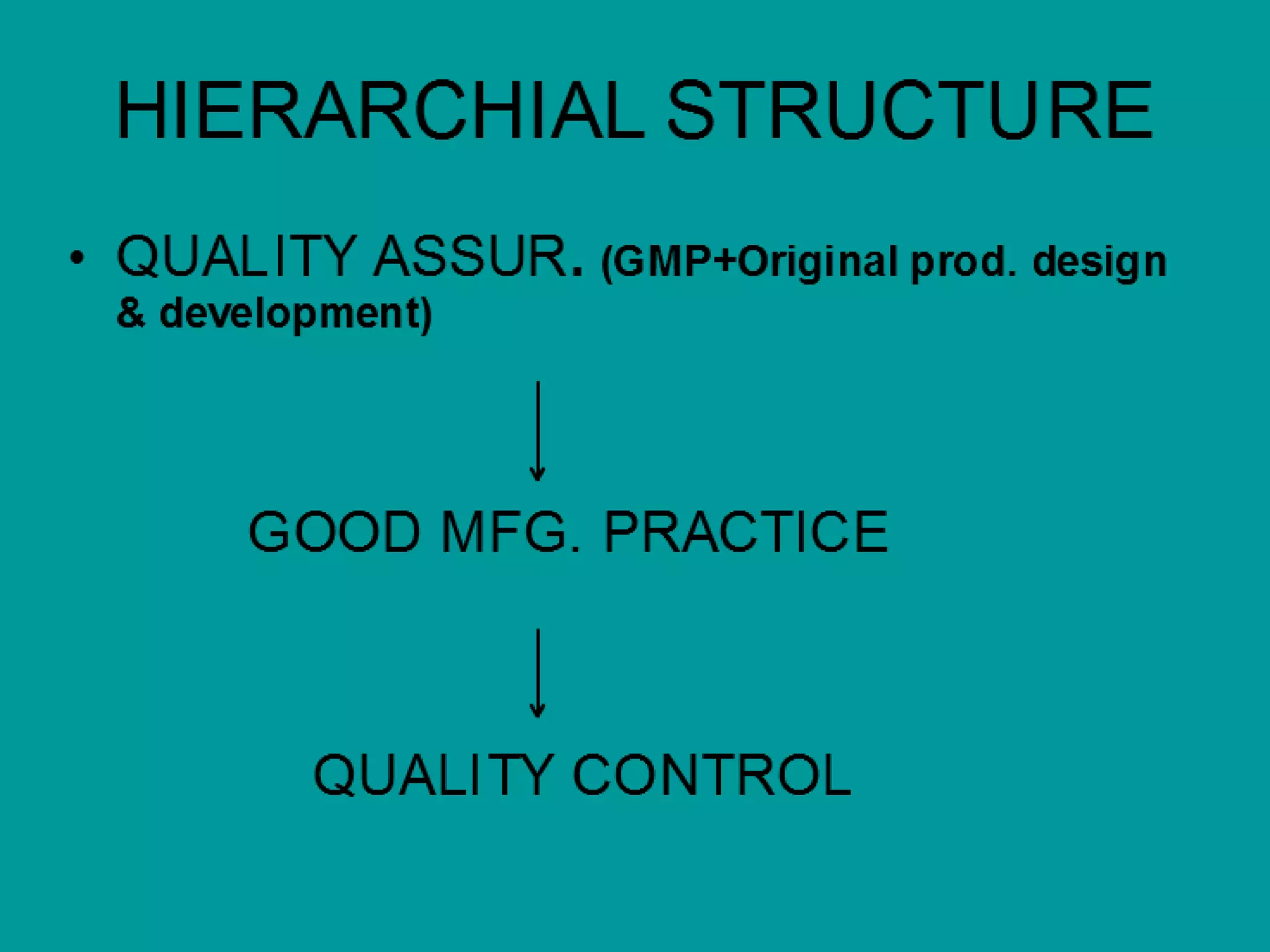
This document discusses key concepts related to quality including quality, quality control, quality assurance, quality management, total quality management, and ISO systems. It defines quality as the totality of features and characteristics that satisfy stated or implied needs. Quality control is the techniques used to fulfill quality requirements, while quality assurance refers to all planned actions to provide adequate confidence that a product or service will meet requirements for quality. Quality management is a systematic and company-wide approach to ensuring consistent business growth. Total quality management is the latest approach and focuses on individual and organizational development to increase stakeholder satisfaction. ISO systems set quality standards for documentation requirements.