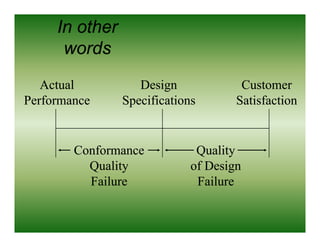
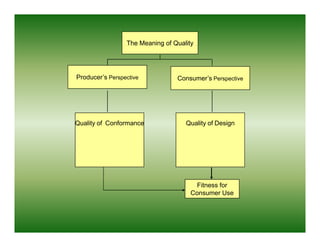
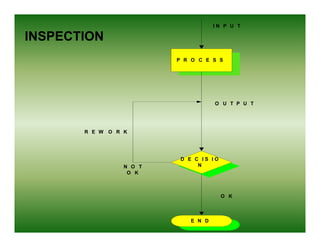
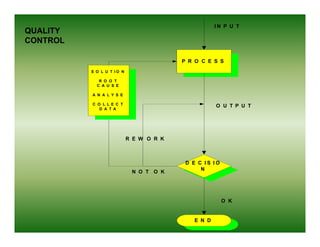
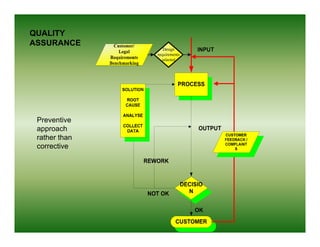
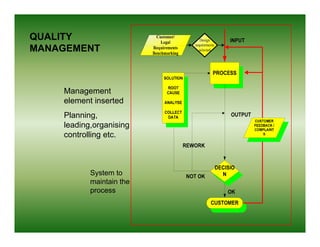
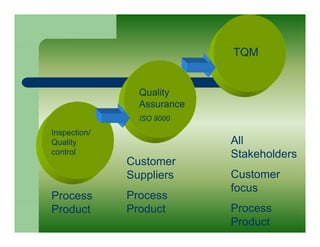
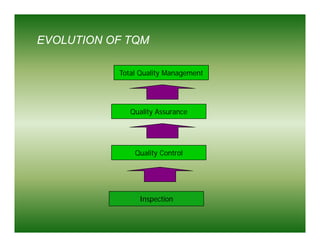
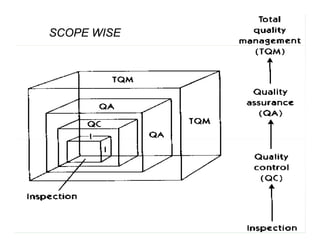
Total quality management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach to quality management that is company-wide in scope. It involves all departments and employees and focuses on continuously improving processes and meeting customer needs. TQM goes beyond traditional quality assurance methods like inspection and quality control by emphasizing prevention over detection of defects and focusing on all stakeholders rather than just internal processes or final products. The goal of TQM is to continuously increase customer satisfaction through ongoing improvements in quality, process, and product design.