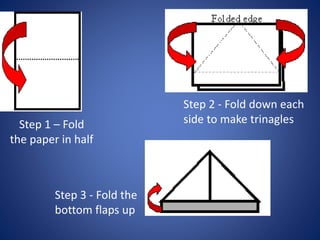
This document discusses the concepts of quality, quality systems, and their importance for businesses. It explains that quality can be measured both tangibly, through factors like reliability and durability, and intangibly, through a brand's reputation. Total Quality Management and Kaizen approaches aim to build quality into production processes and continuously improve quality through small changes. Quality standards like ISO 9001, BS5750, and CE marking indicate that a business has systems to ensure a consistent level of quality, though they do not guarantee high quality itself. Managing quality systems involves costs but can provide benefits like increased sales, reputation, and price through a good quality reputation.