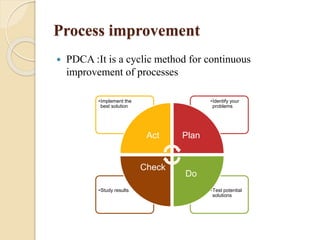
The document outlines the fundamentals of quality management, including its definition, components, principles, and benefits. Key components include quality planning, assurance, control, and continuous improvement techniques such as Total Quality Management and Six Sigma. The document emphasizes the importance of customer satisfaction, efficiency, and compliance, while providing tools and methodologies to enhance product and service quality.