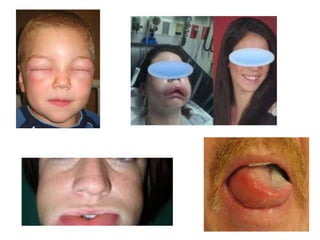
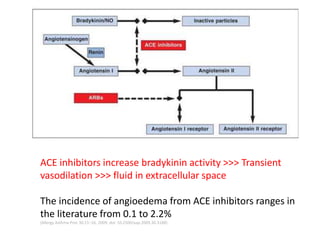
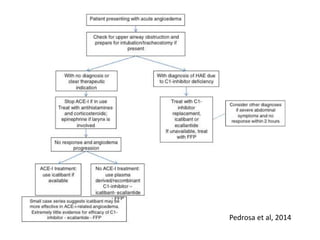
Angioedema is rapid swelling of subcutaneous tissues caused by increased vascular permeability. There are four main types: allergic angioedema caused by allergens, drug-induced non-allergic reactions, idiopathic angioedema of unknown cause, and hereditary angioedema (HAE) caused by C1 inhibitor deficiency. HAE is treated with C1 inhibitor concentrate, icatibant, or ecallantide while other types may be treated with antihistamines, steroids, and epinephrine if anaphylaxis is possible. Early airway management is important as angioedema can affect the tongue, larynx, and uvula and potentially cause