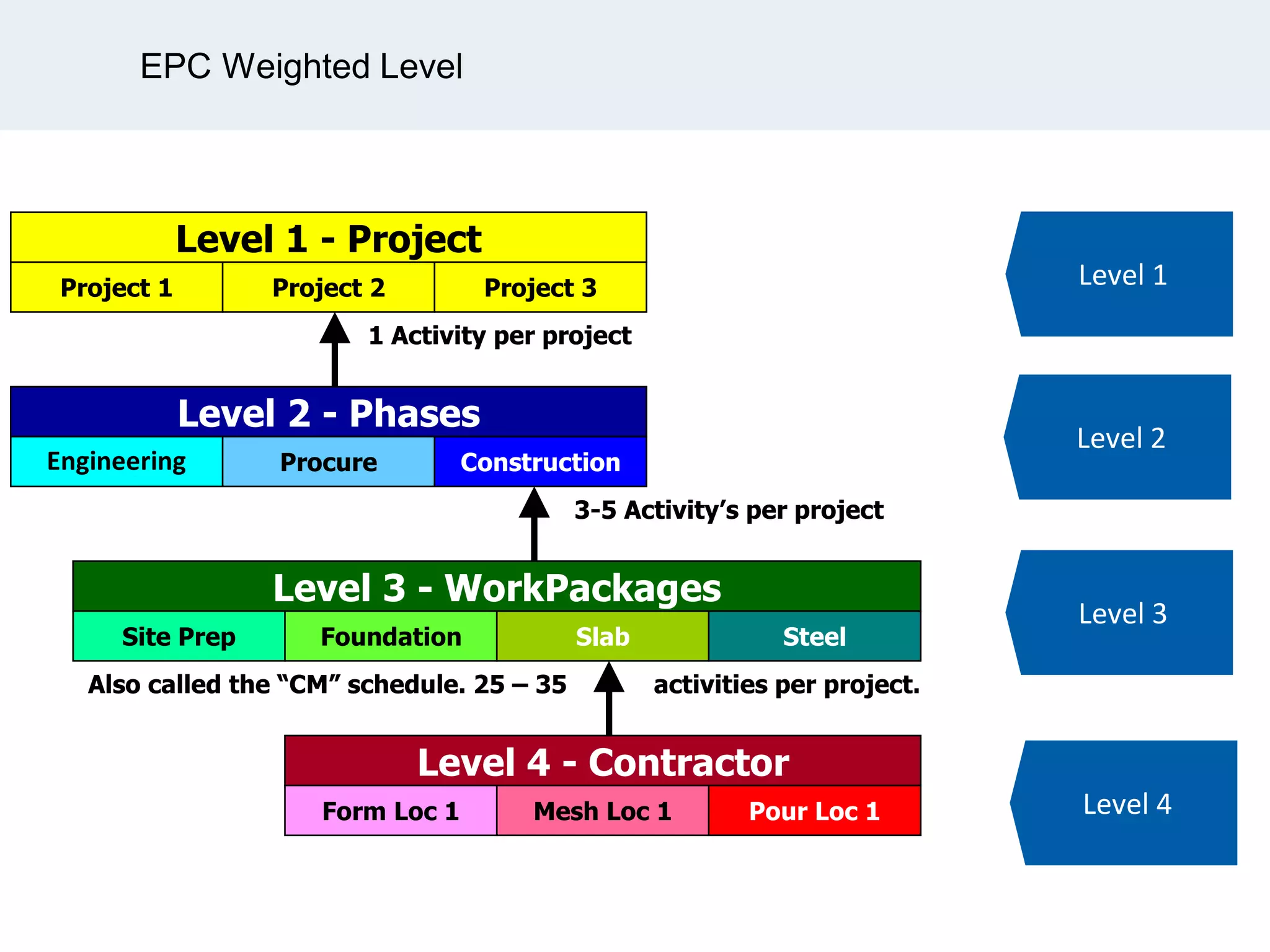
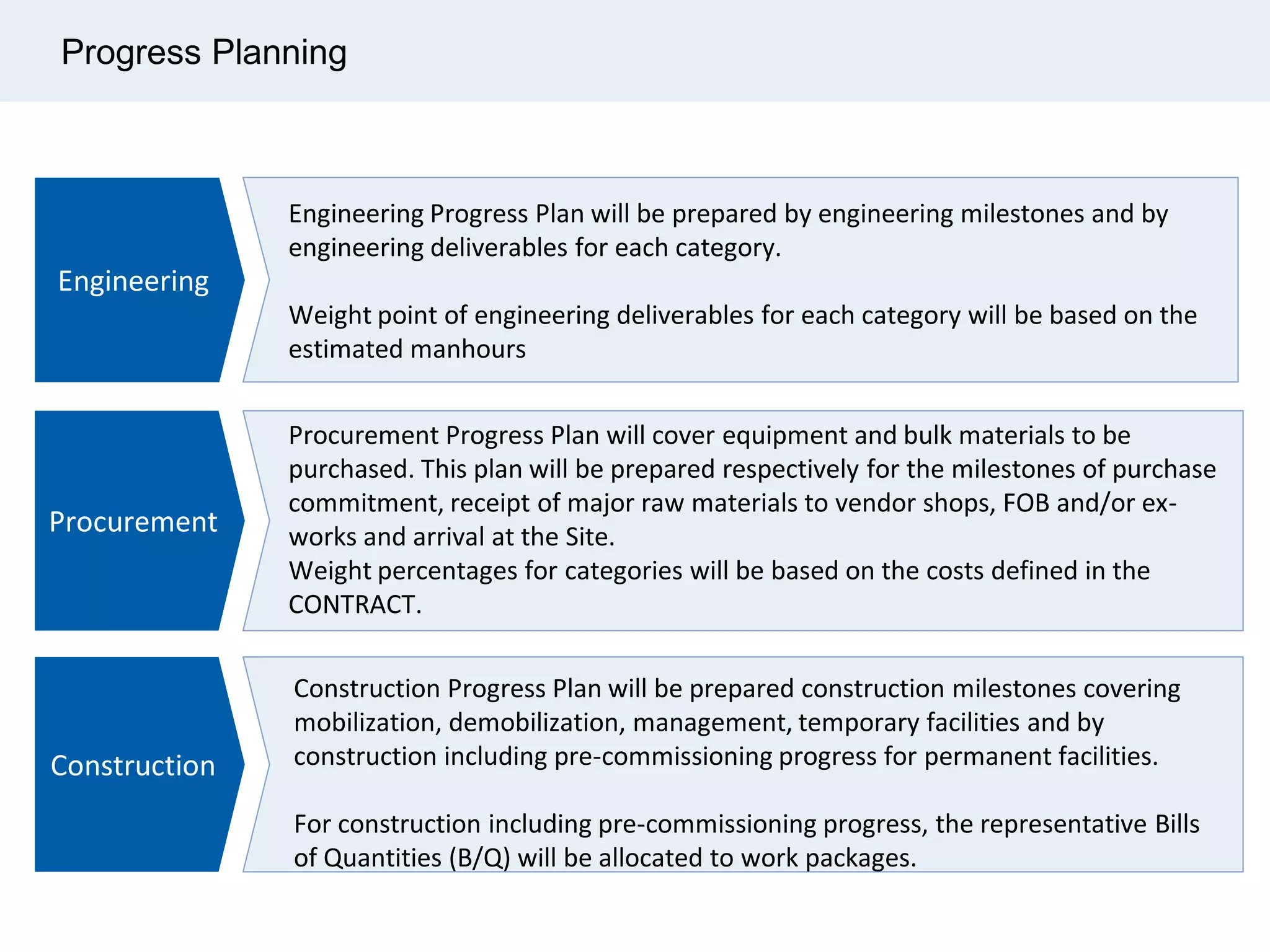
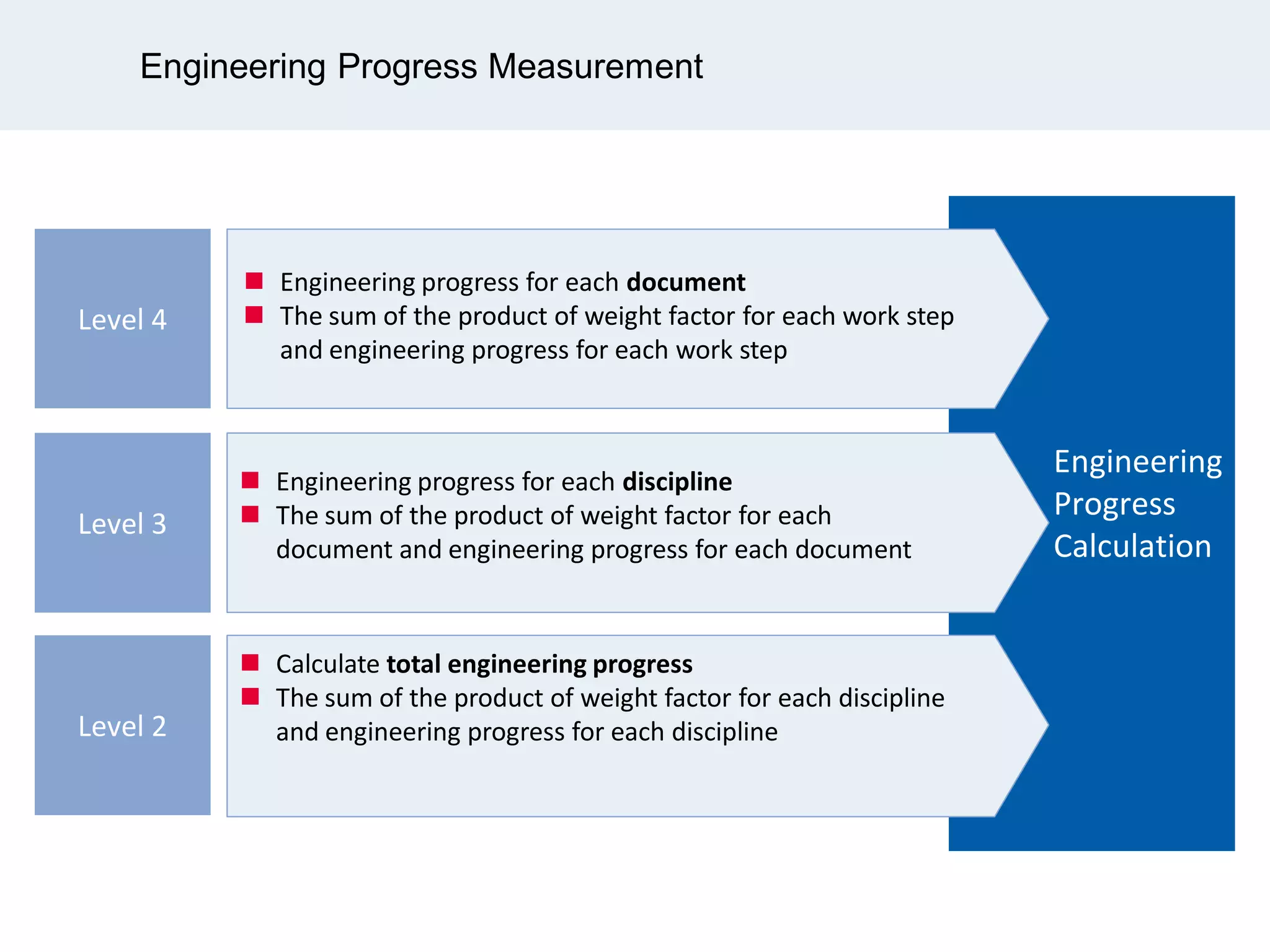
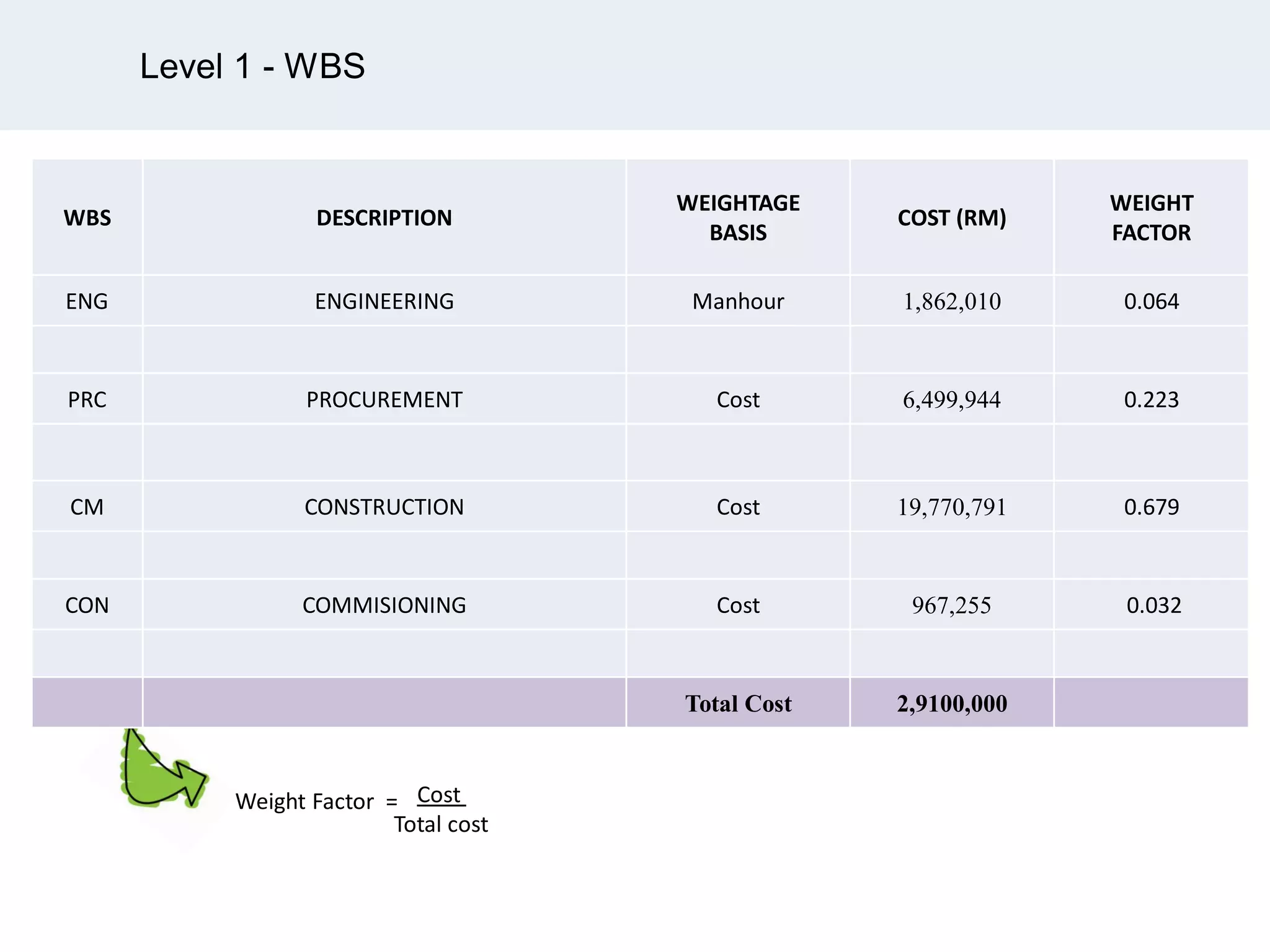
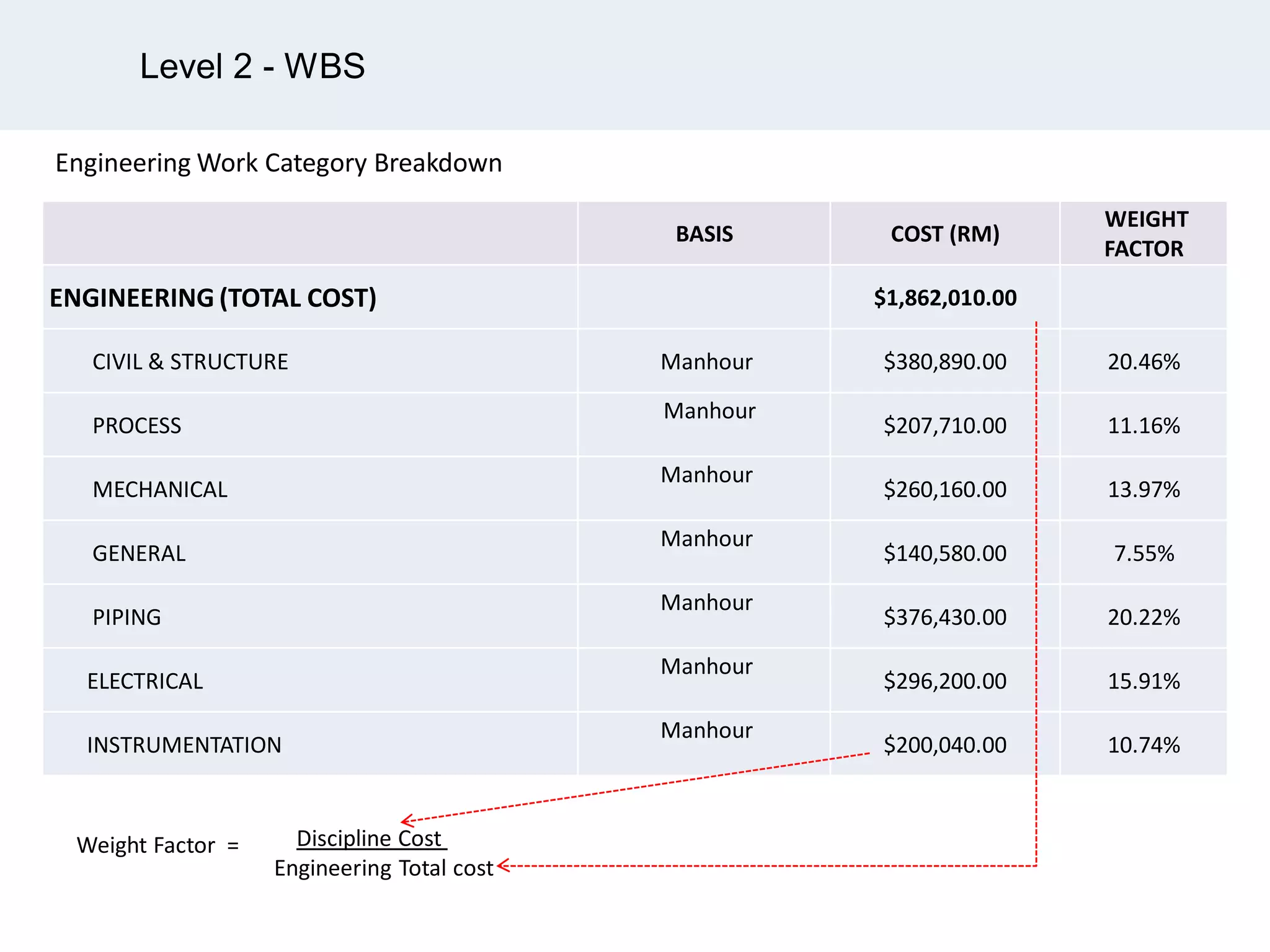
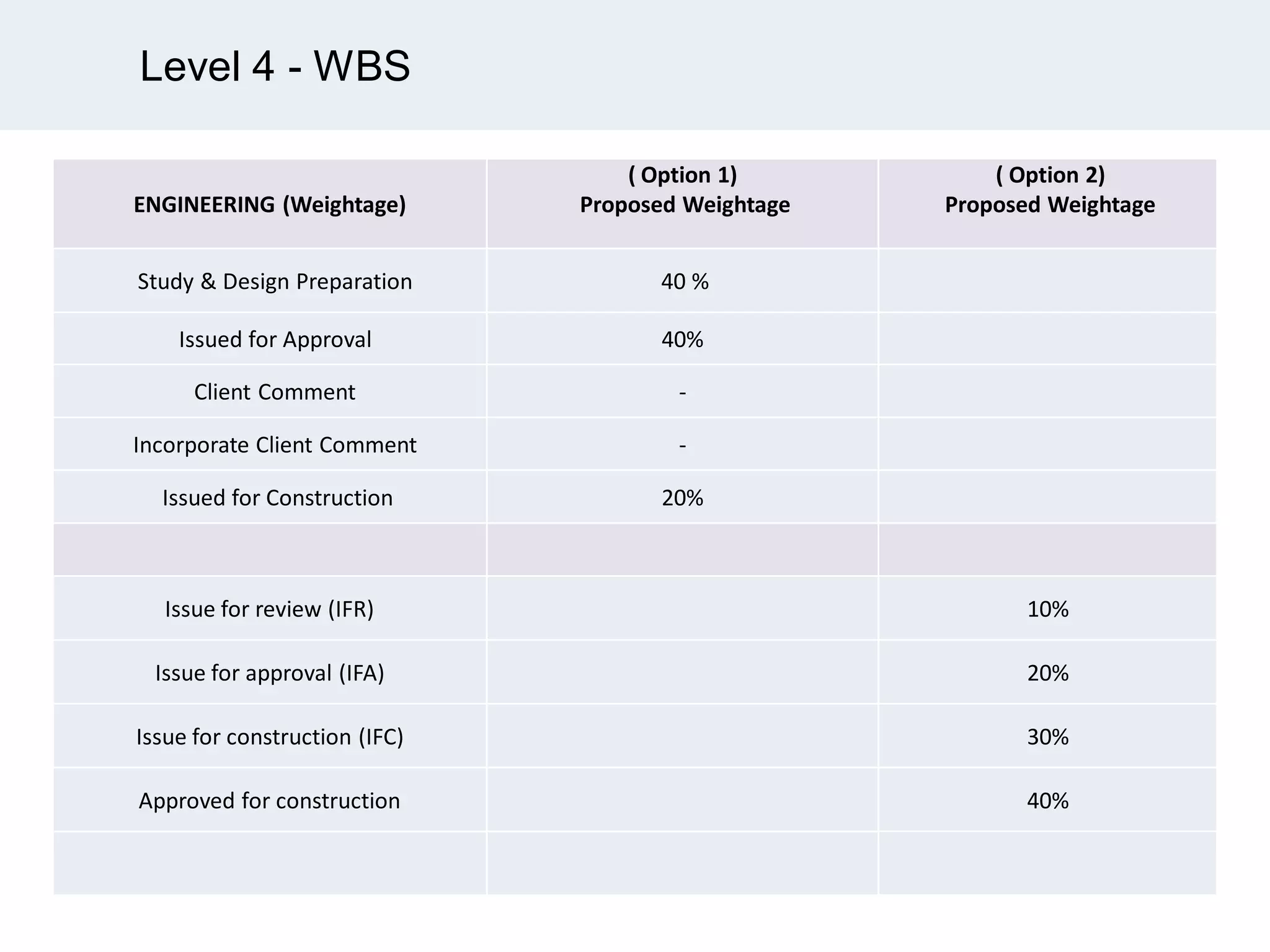
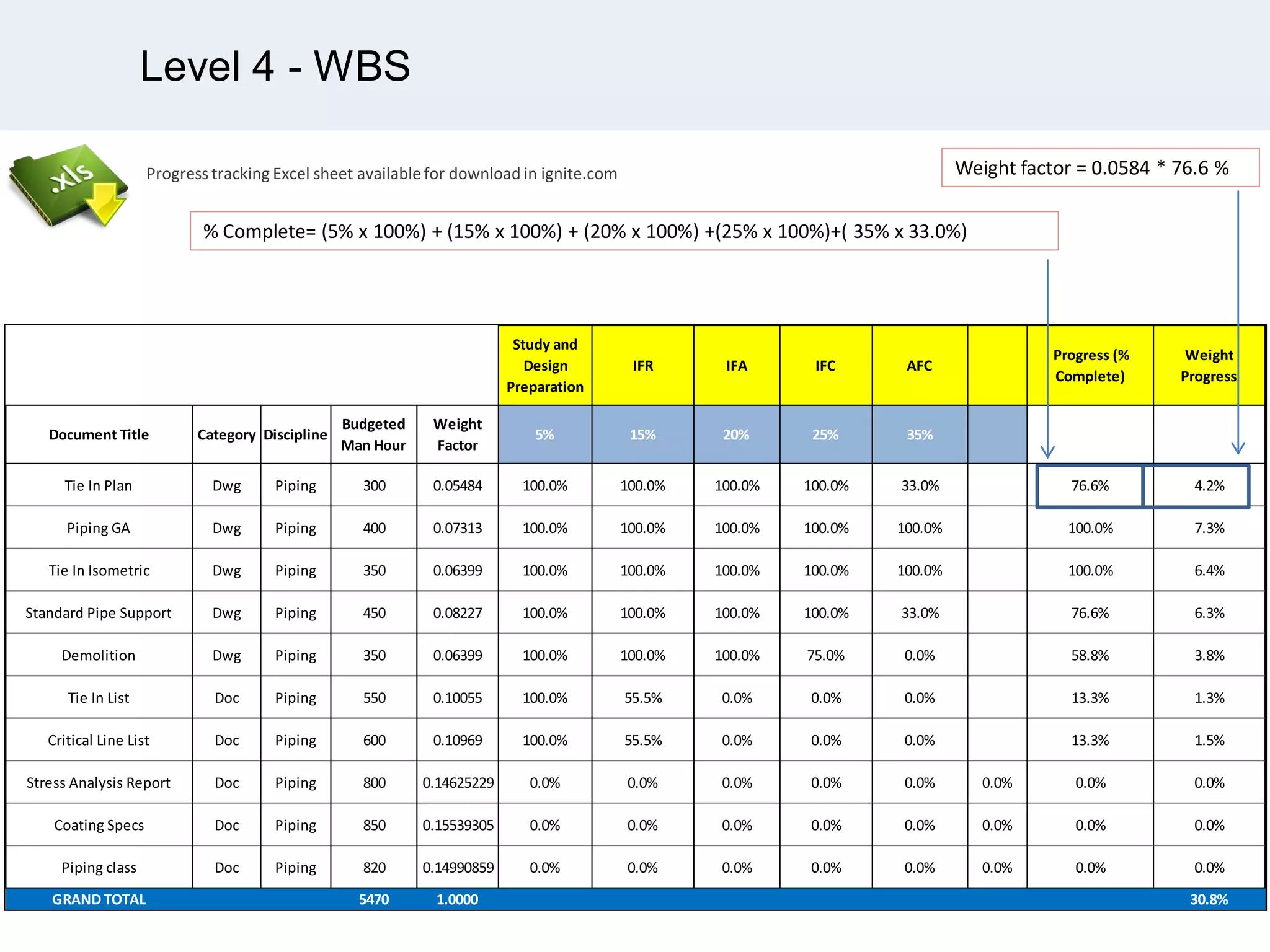
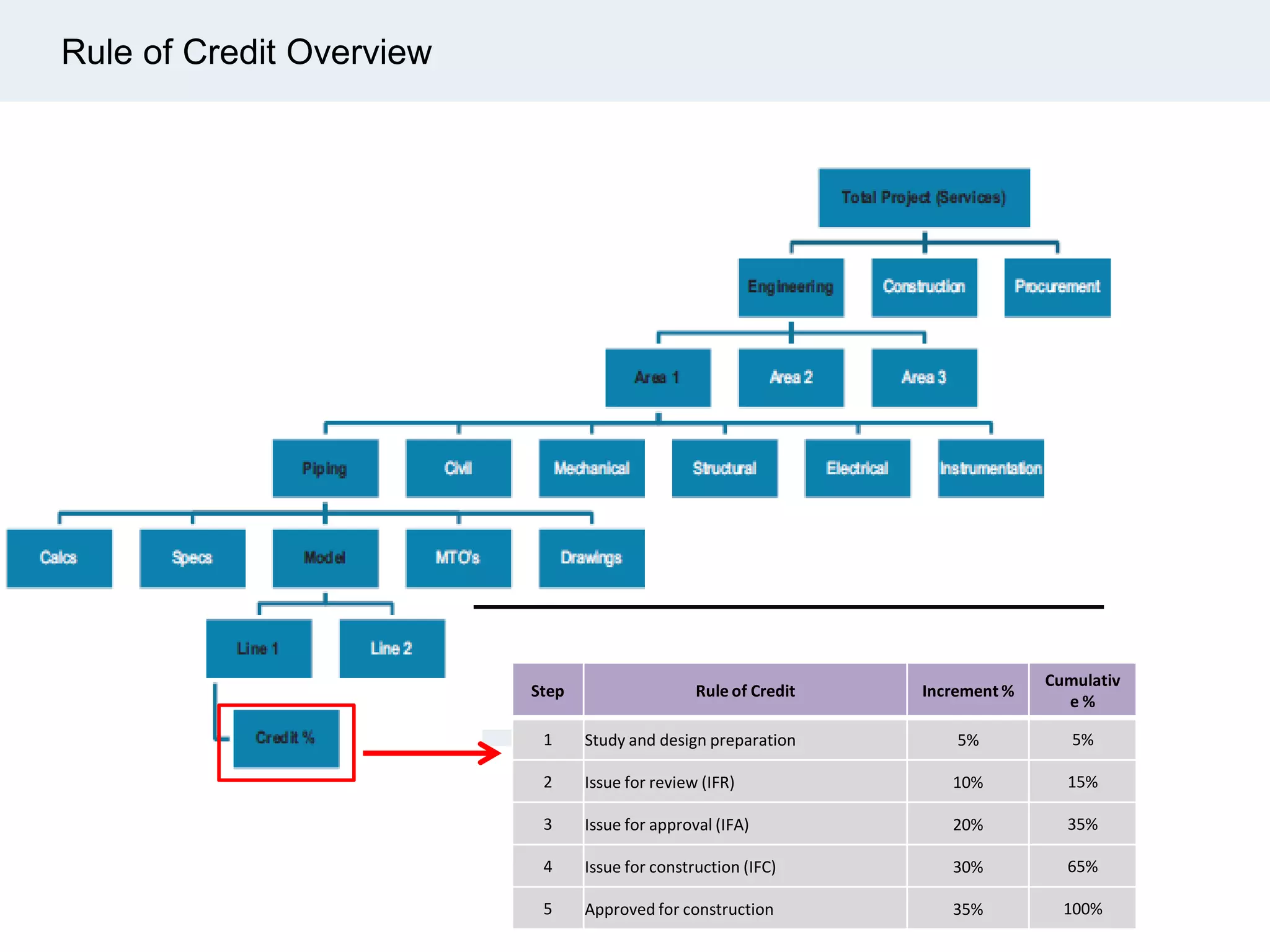
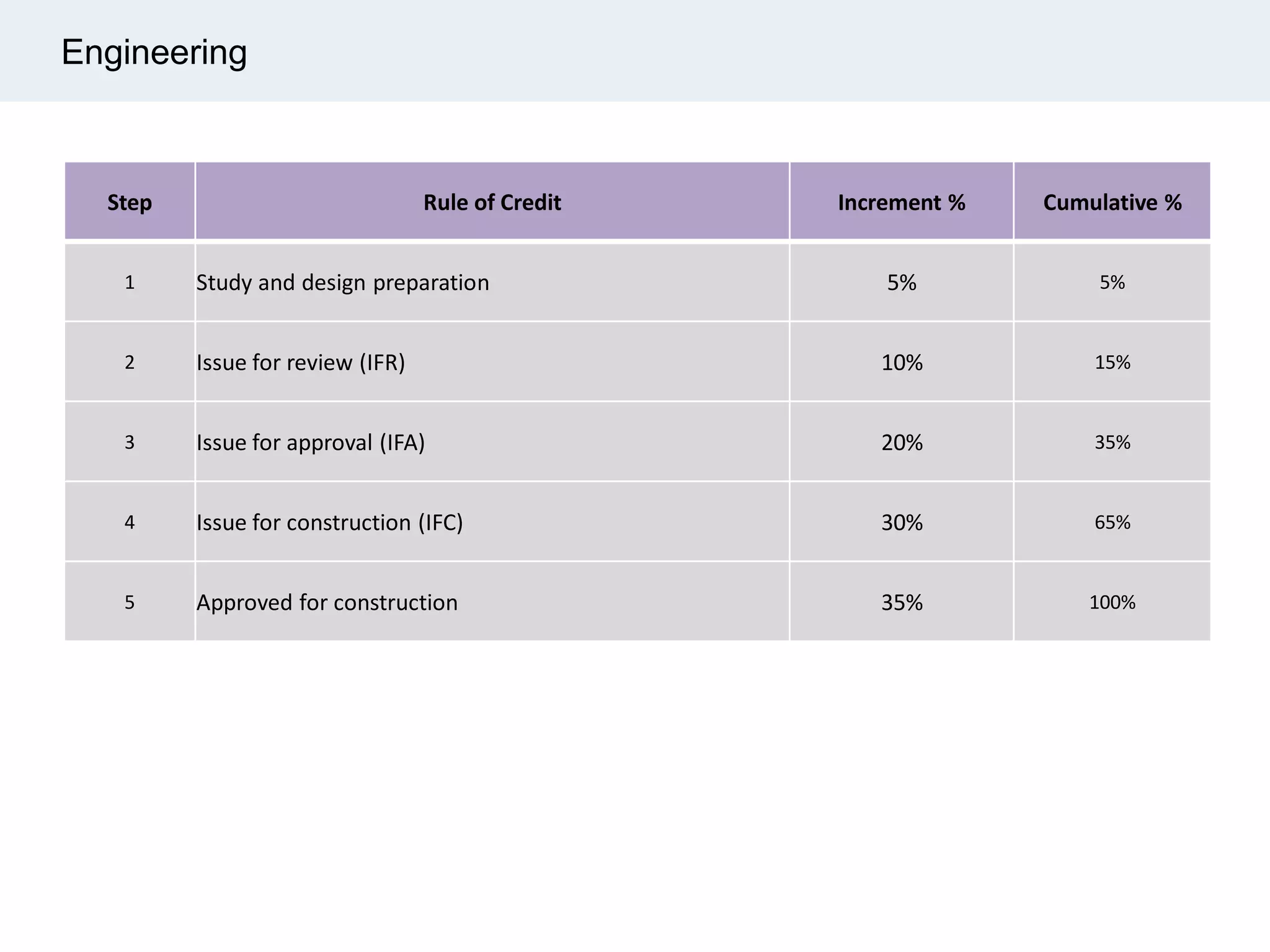
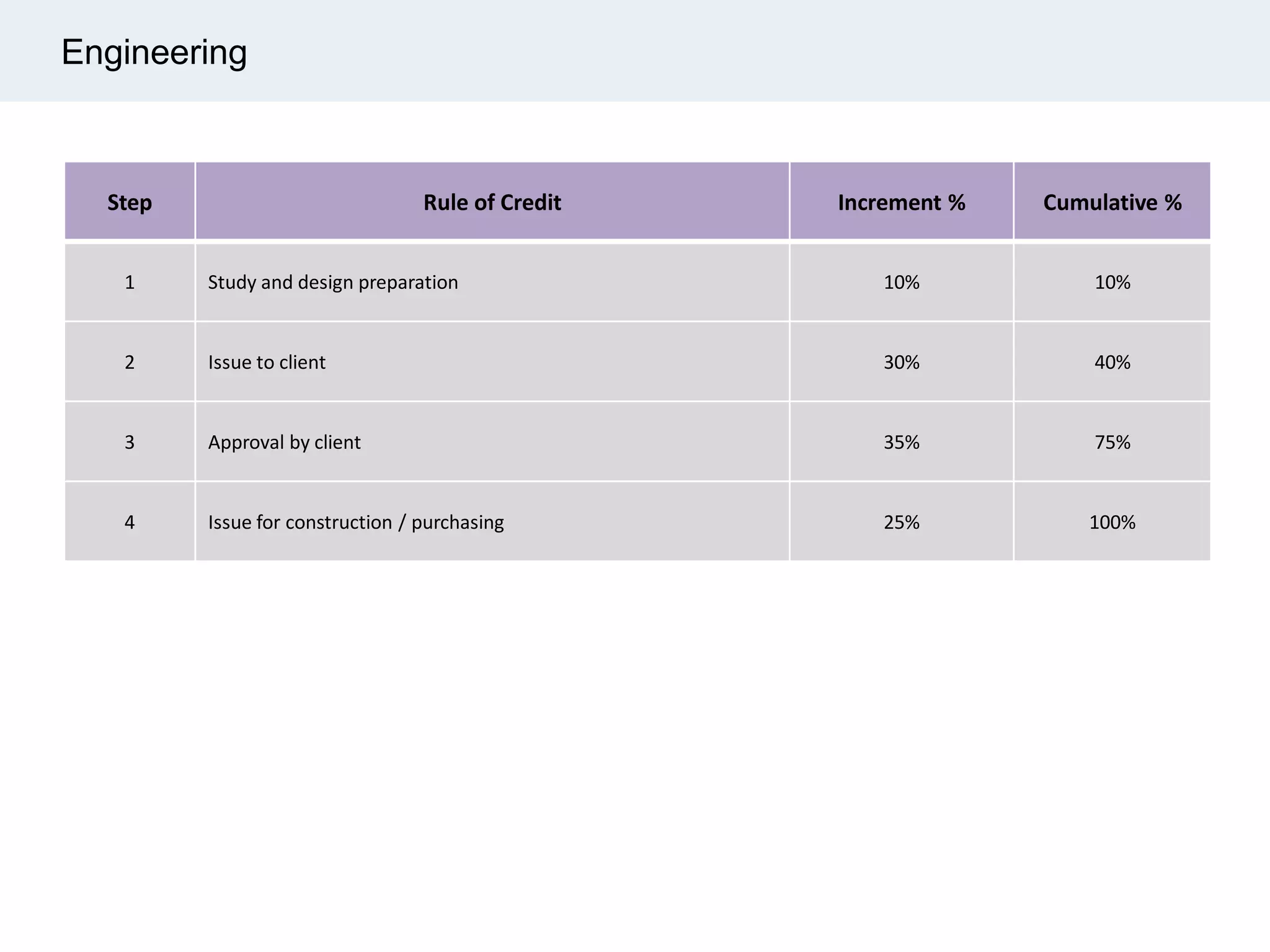
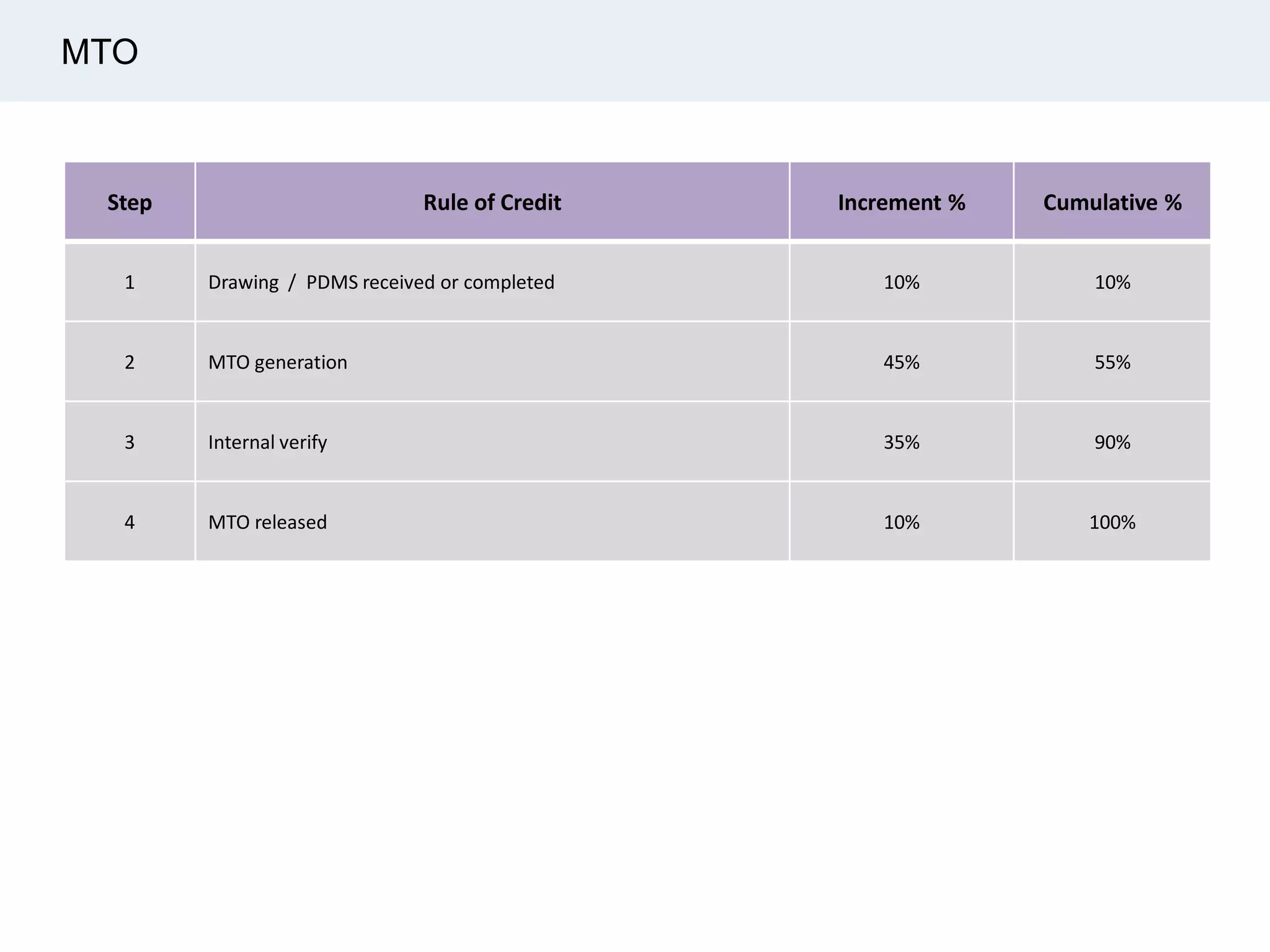
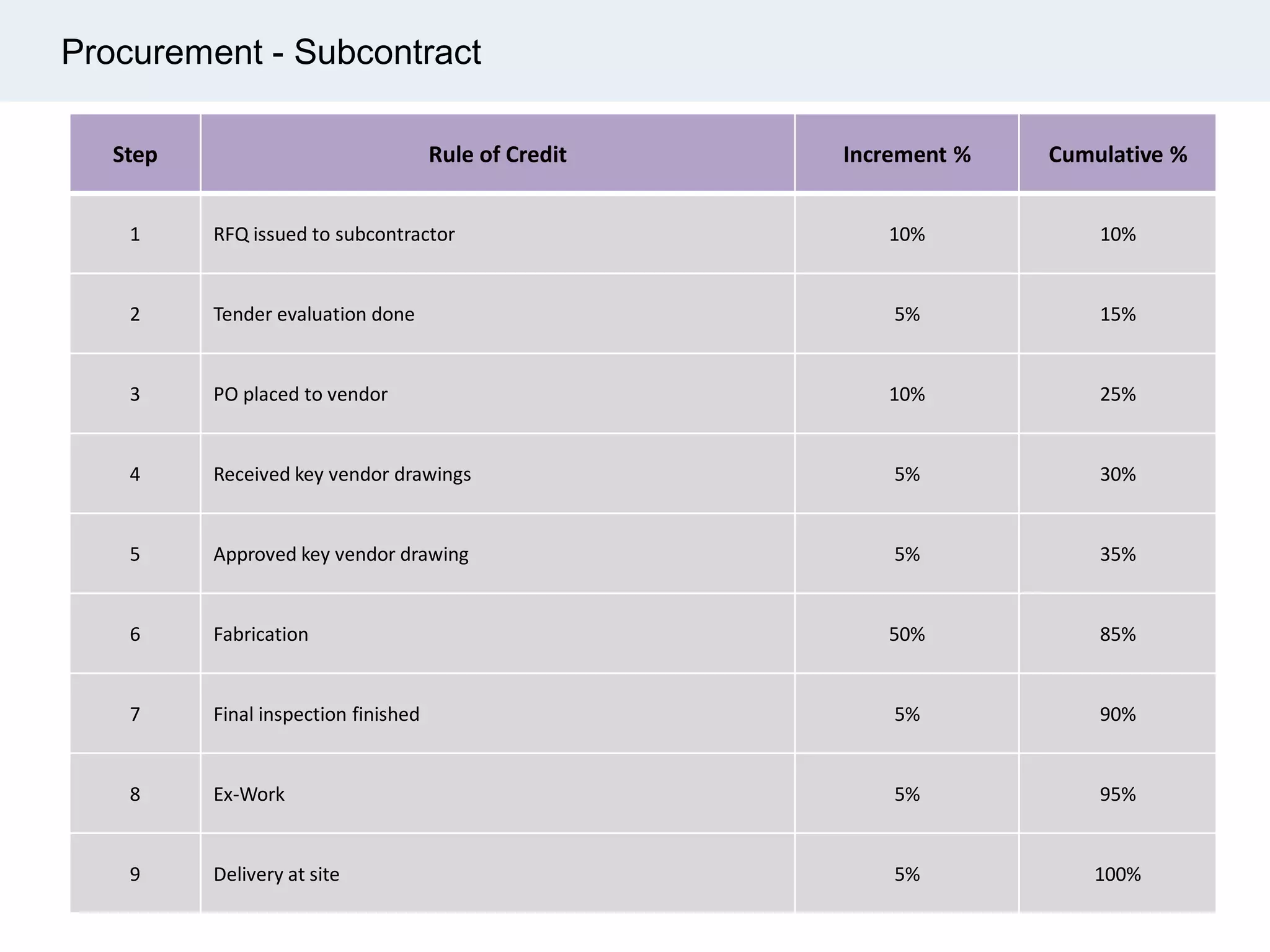
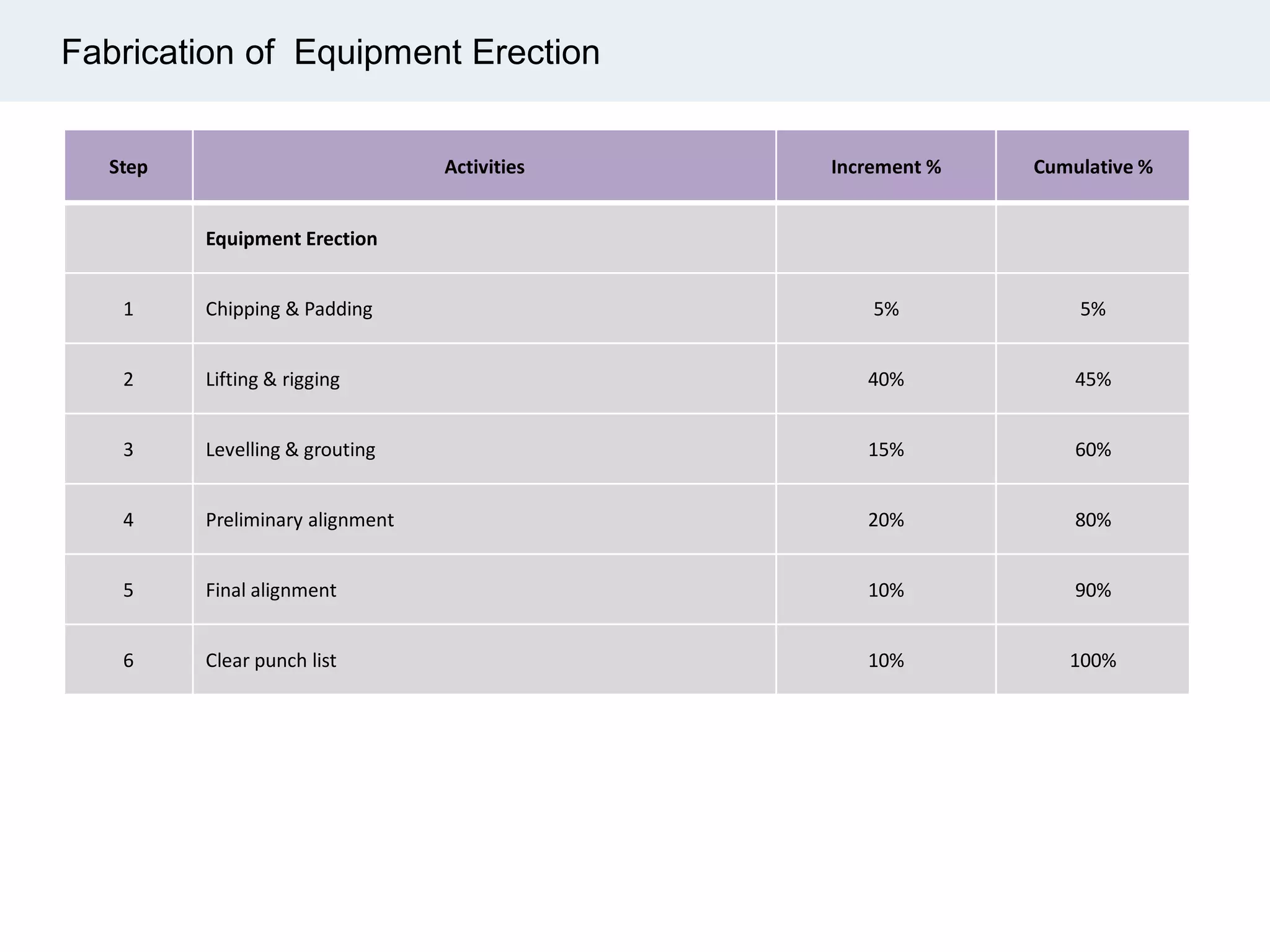
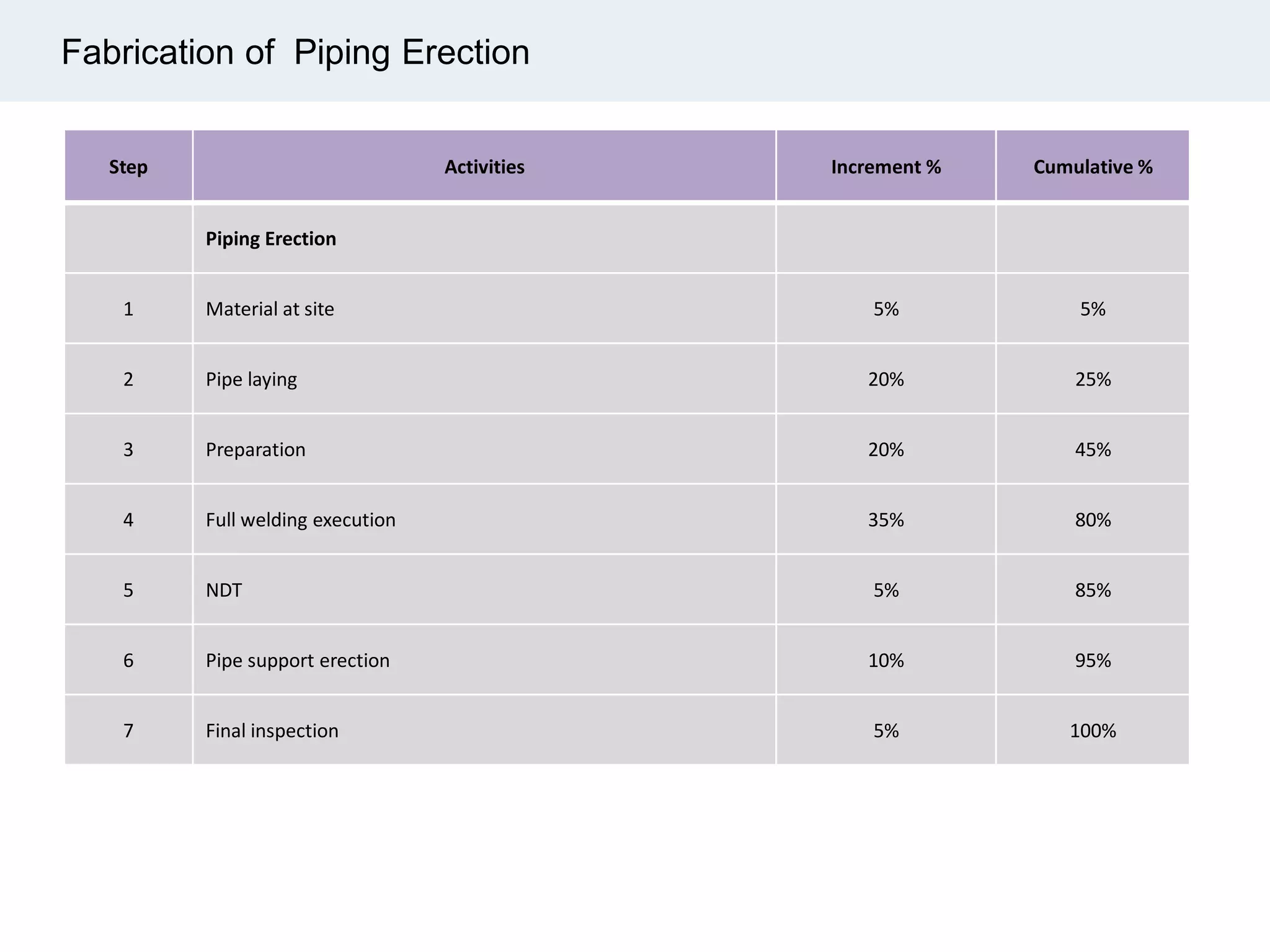
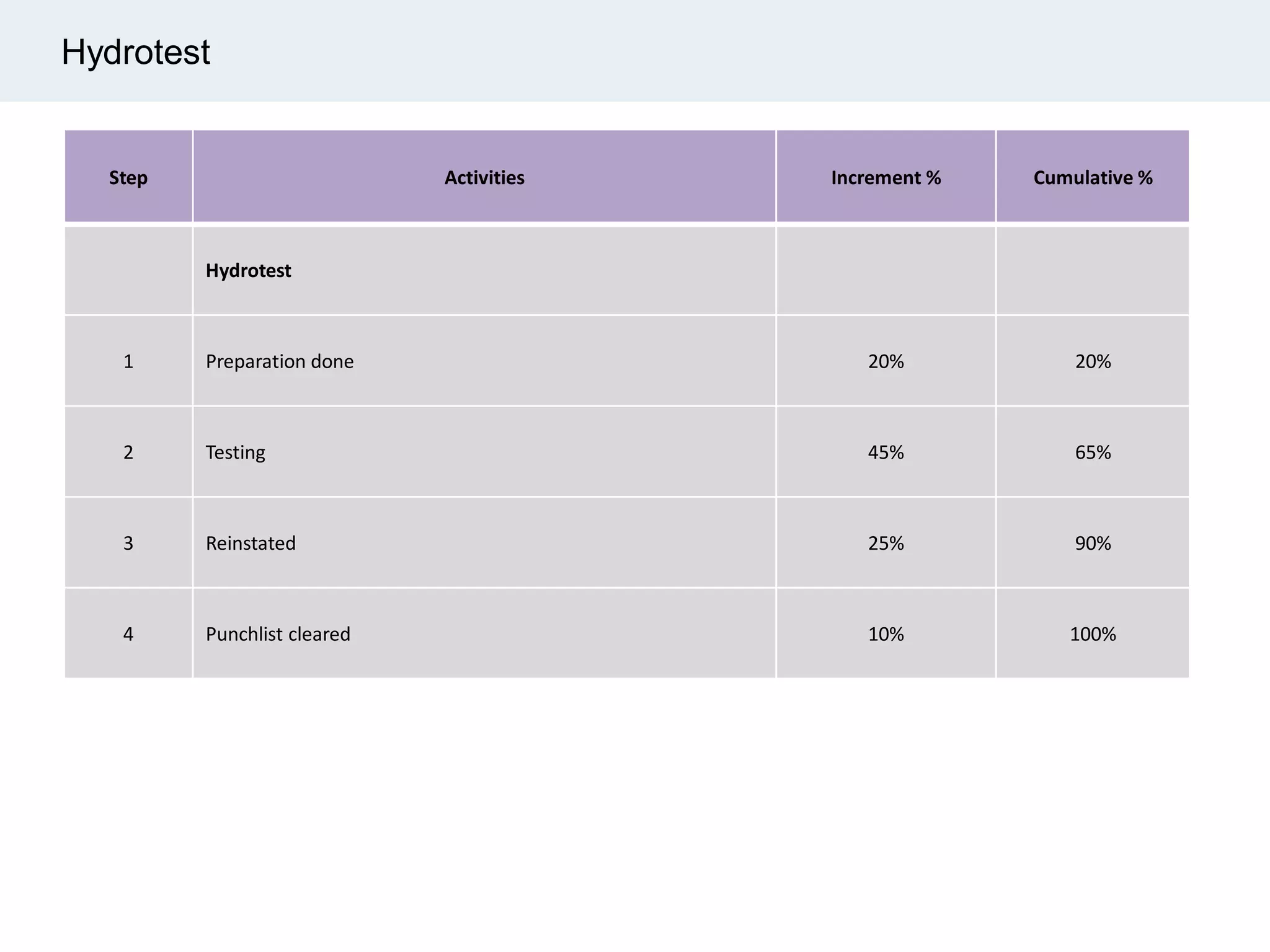
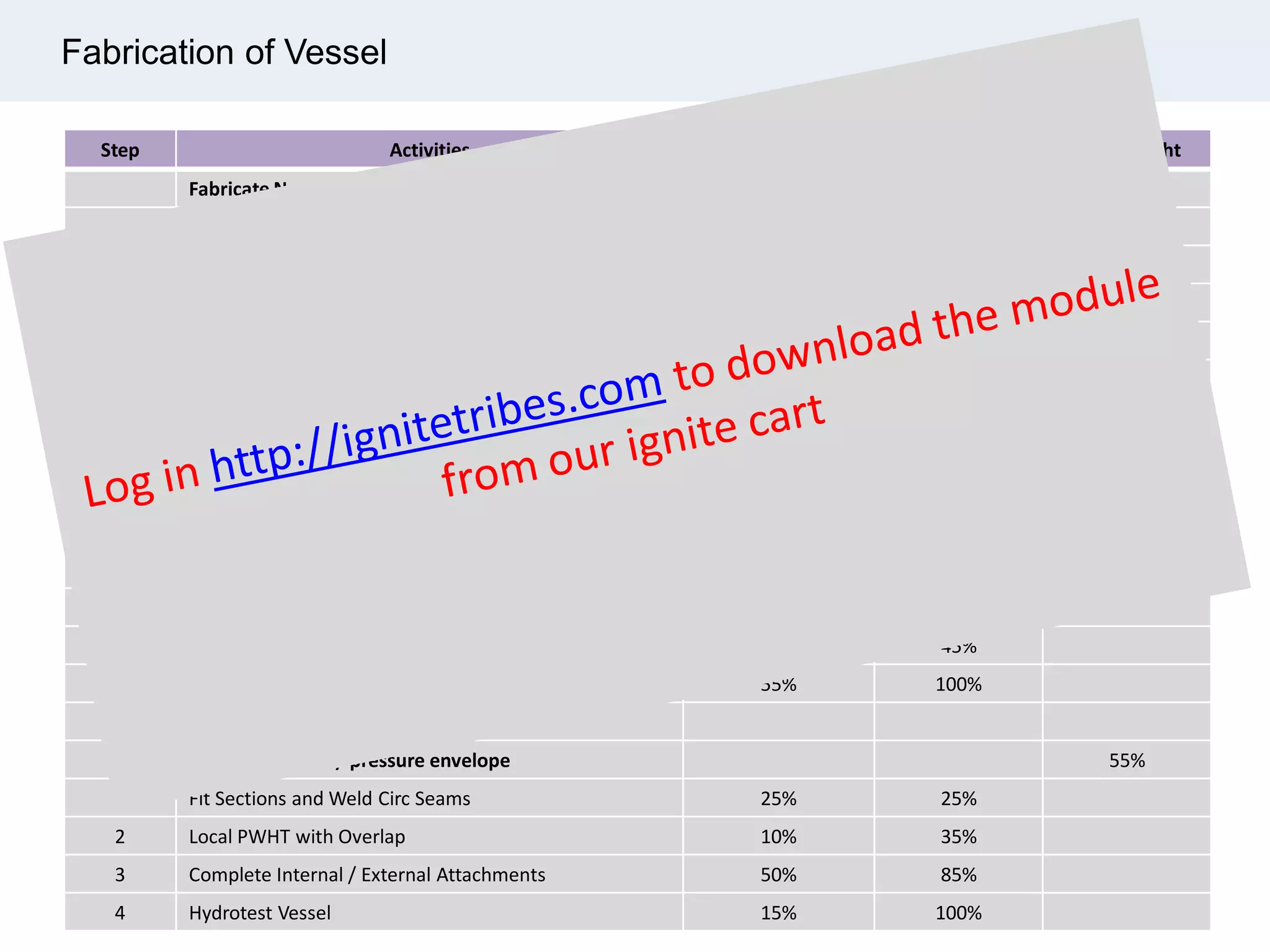
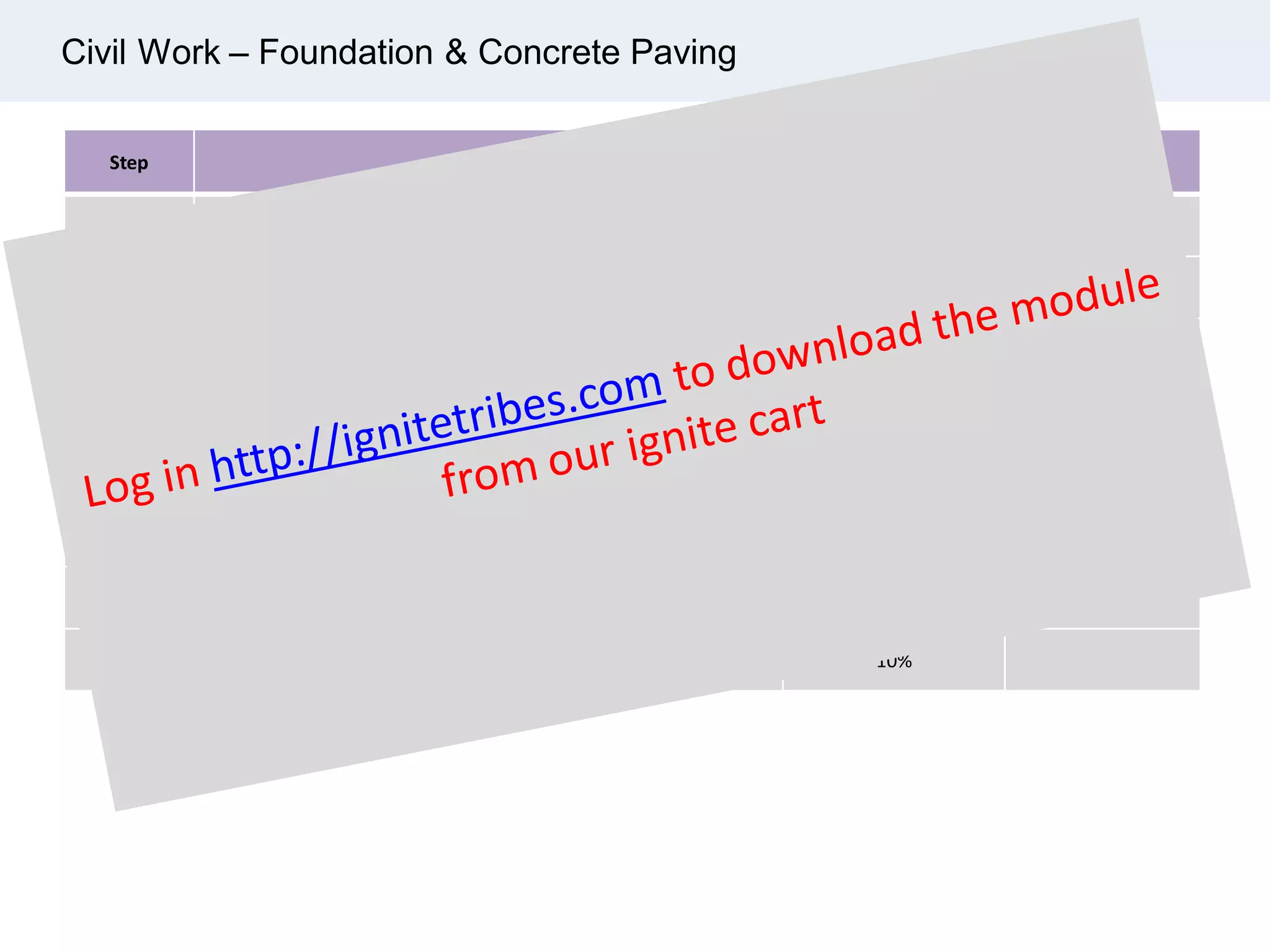
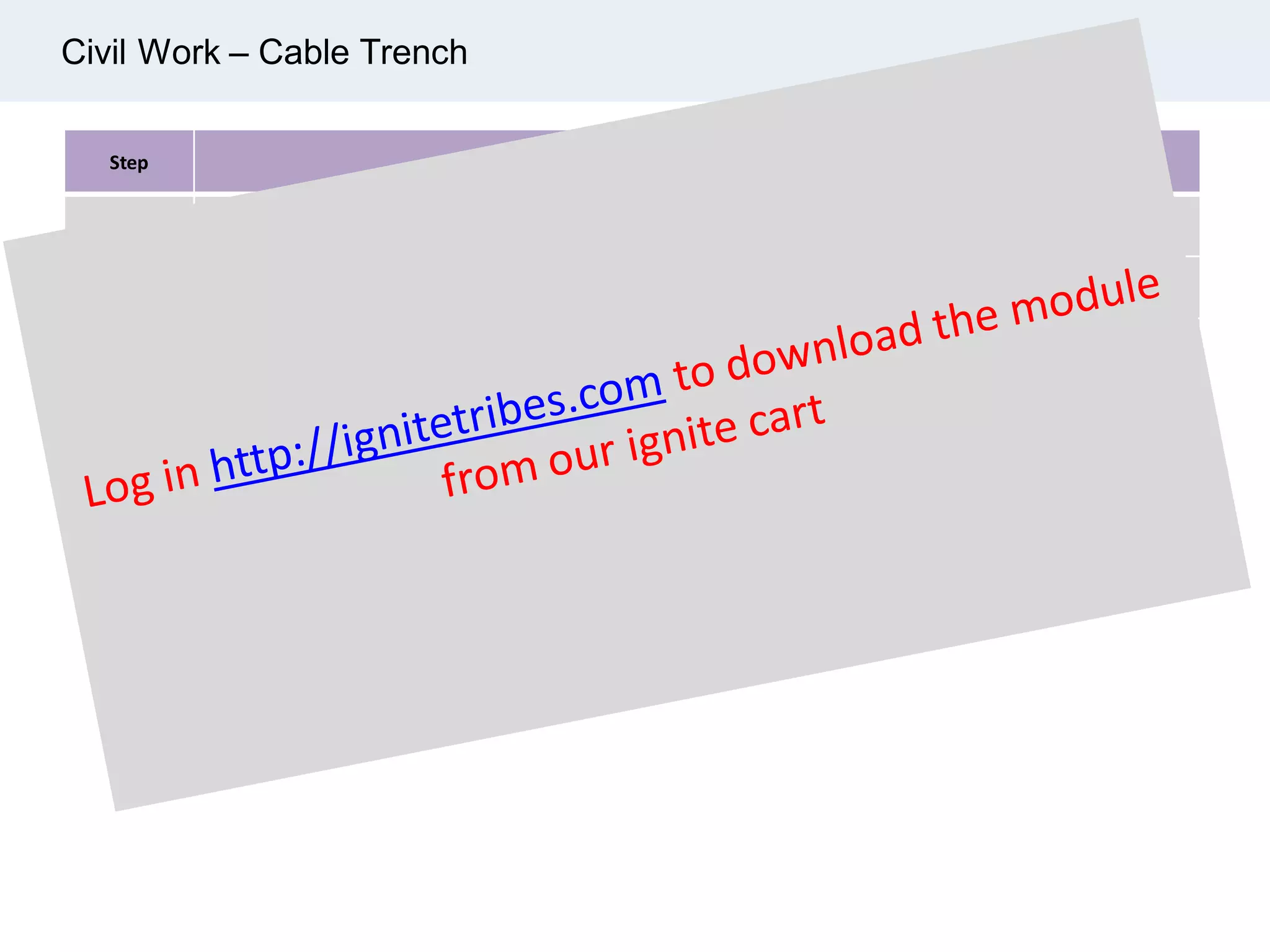
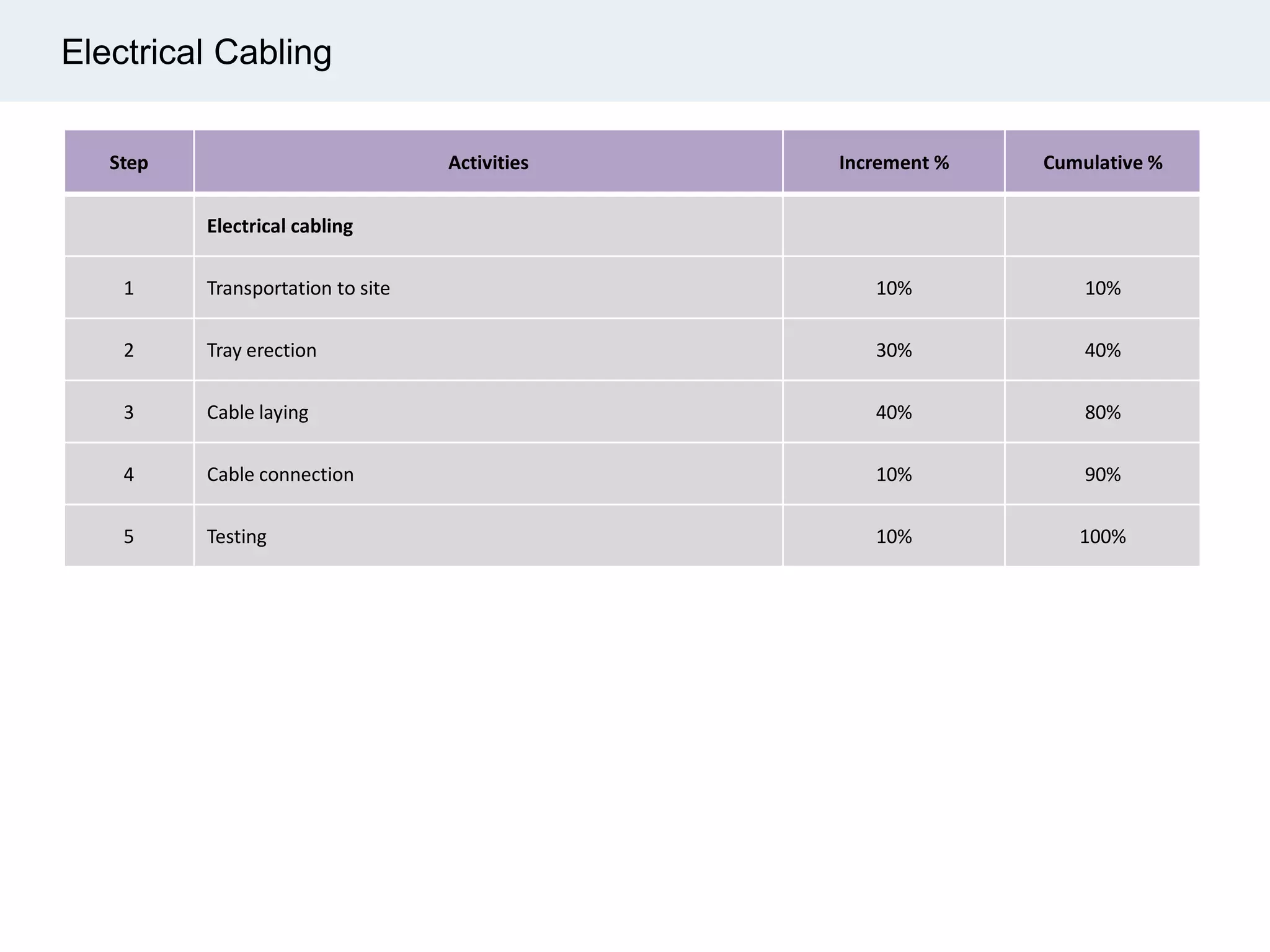
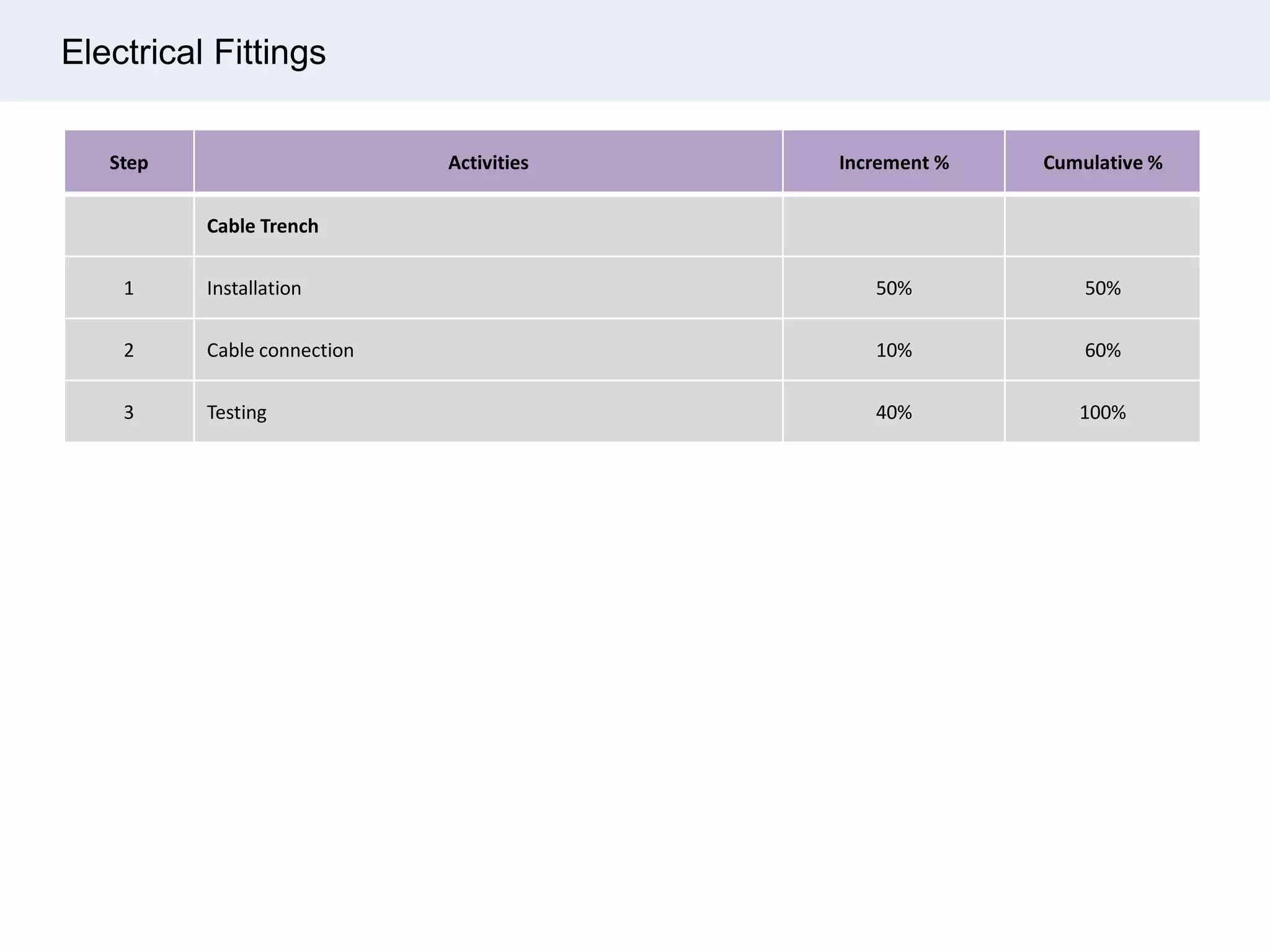
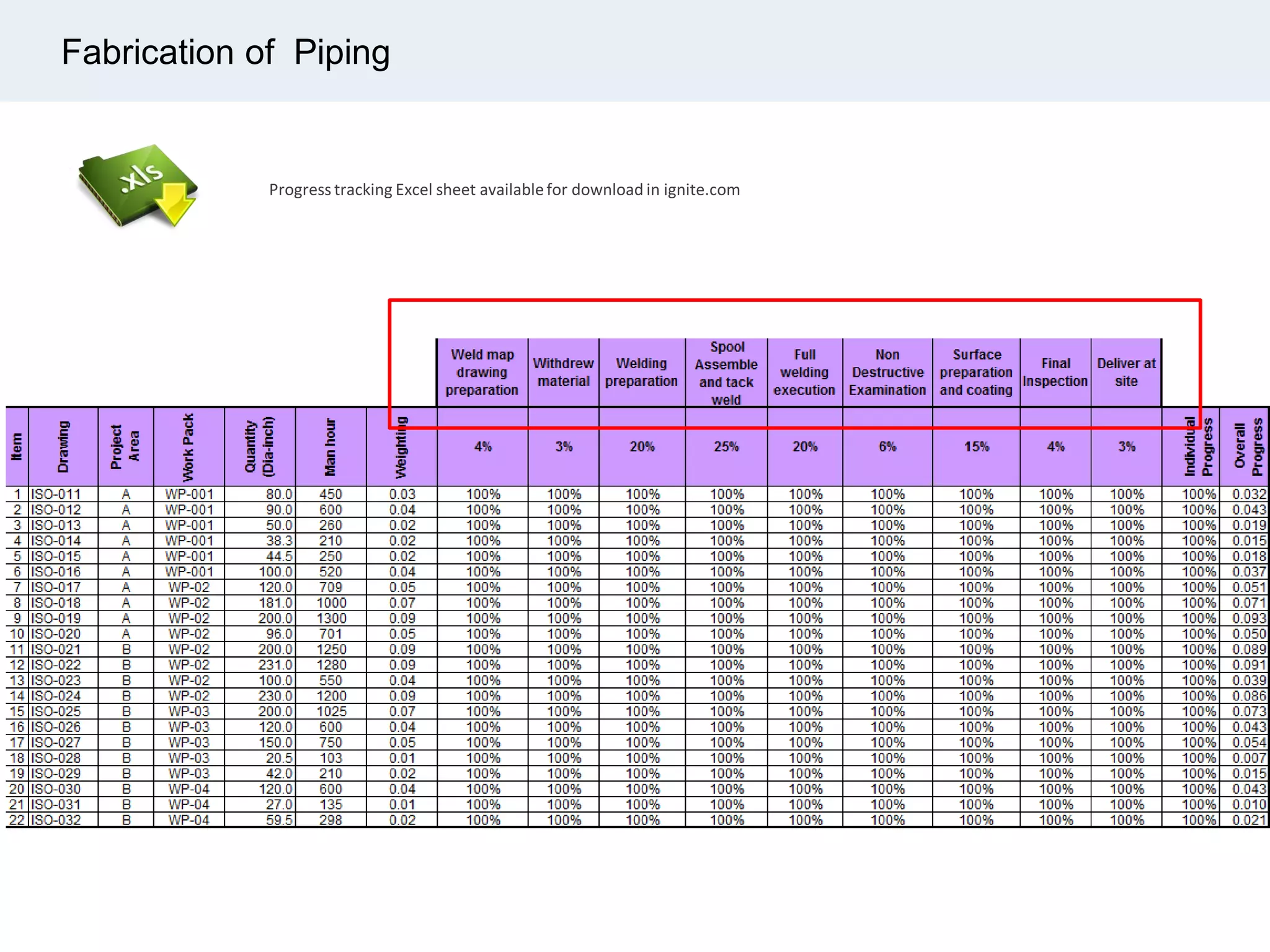
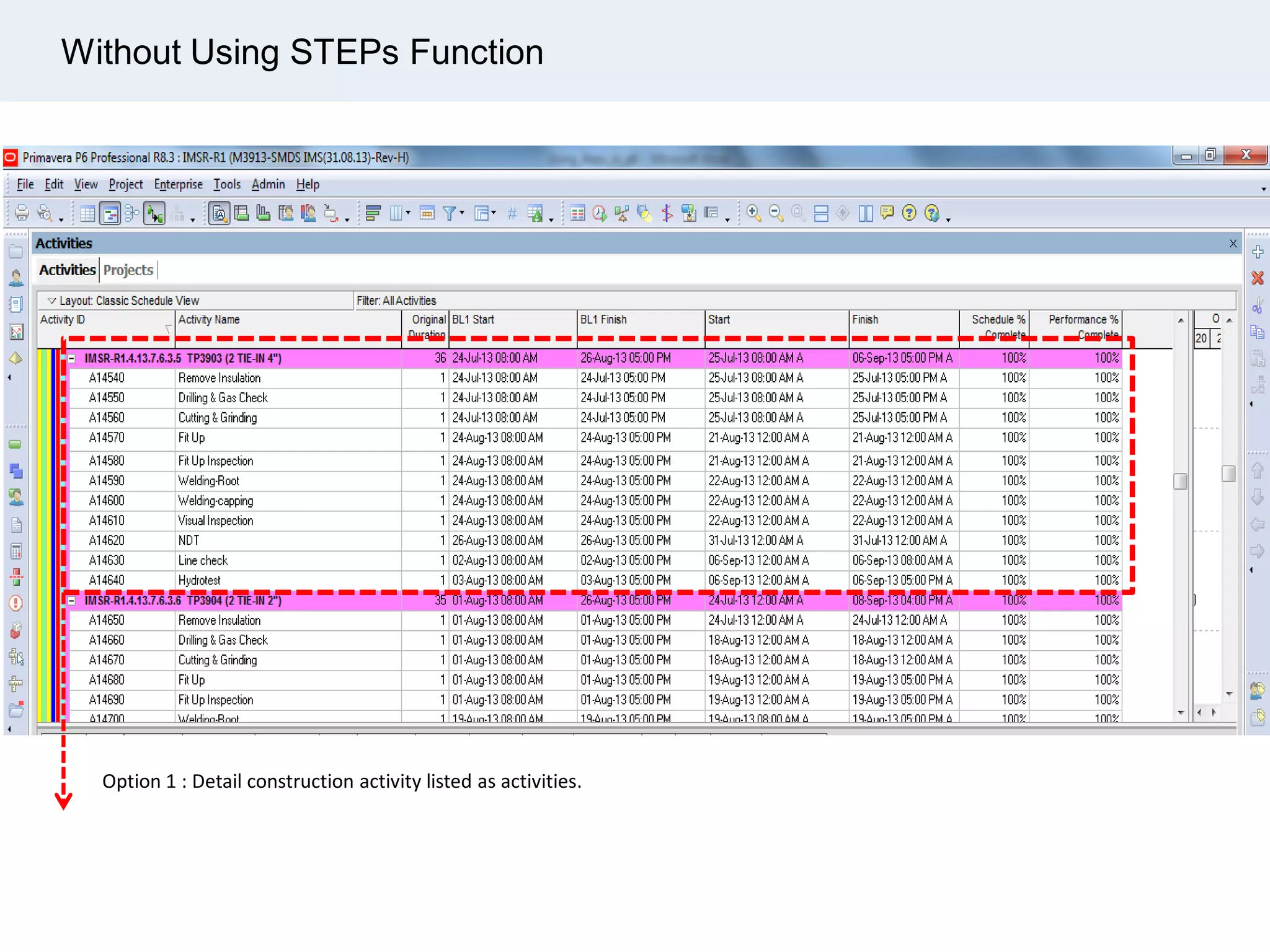
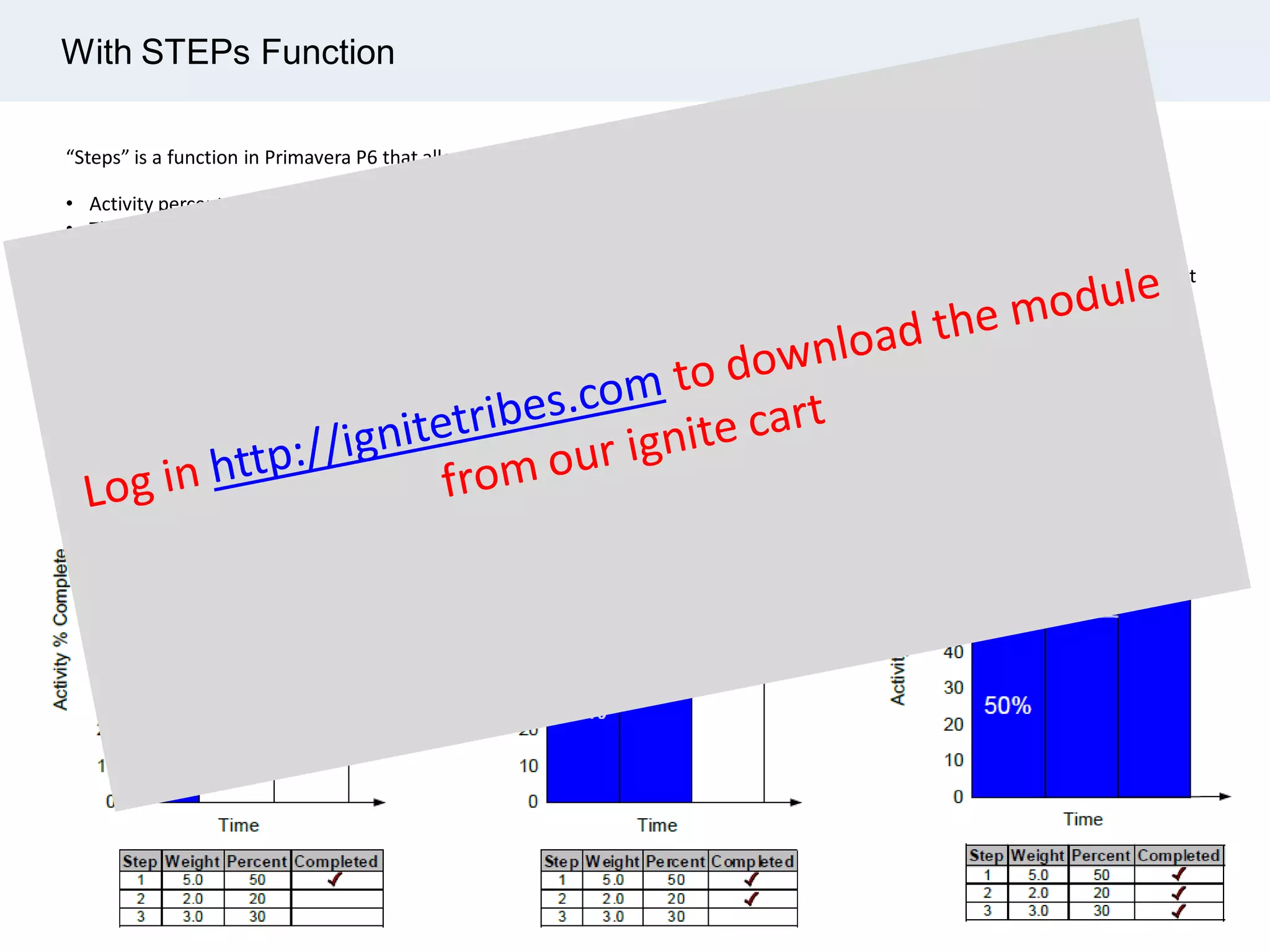
Ignite Resources is a corporate training and consulting company that specializes in developing human capital and providing customized solutions for both management and technical skills. The document outlines the importance of progress measurement in project management, detailing methodologies for assessing project progress and implementing a progress measurement system tailored to specific project needs. It emphasizes the role of the rule of credit method in defining milestones and calculating percent complete for various engineering tasks throughout the construction process.